Abstract
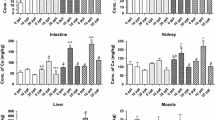
The objectives of this study were to try to determine the reasons of the external Ca2+ and Na+ enhancement of Cd2+ and Cu2+ resistance in fish. Tilapia larvae at 3 days posthatch were exposed to (A) 0 (control), 40 μg/L Cd2+, 40 μg/L Cd2+ + 2 mM Ca2+ (Cd/hyper-Ca), and 2 mM Ca2+ or (B) 0 (control), 75 μg/L Cu2+, 75 μg/L Cu2+ + 0.52 mM Na+ (Cu/hyper-Na), and 0.52 mM Na+. After 48 hours, results indicated that (1) Cd/hyper-Ca and Cu/hyper-Na treatments showed decreased growth inhibition induced by the metals; (2) metal accumulation in Cd/hyper-Ca–treated larvae was lower compared with those exposed only to Cd; and (3) metallothionein (MT) expression was significantly higher in Cu/hyper-Na–treated larvae than in the group treated with Cu only. Taking all of this into account, either supplementary Ca2+ or Na+ in ambient water may help fish to maintain Ca2+ or Na+ homeostasis, which could decrease metal accumulation and its detrimental effects. Consequently, the fish increase MT expression and retard the growth inhibition caused by metals.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldisserotto B, Chowdhury MJ, Wood CM (2005) Effects of dietary calcium and cadmium on cadmium accumulation, calcium and cadmium uptake from the water, and their interactions in juvenile rainbow trout. Aquat Toxicol 72: 99–117
Calmari D, Marchetti DR, Vailati G (1980) Influence of water hardness on cadmium toxicity to Salmo gairdneri Richardson. Water Res 14:1421–1426
Chang MH, Lin HC, Hwang PP (1997) Effects of cadmium on the kinetics of calcium uptake in develo** tilapia larvae, Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Physiol Biochem 16:459–470
Davies PH, Gorman WC, Carlson CA, Brinkman SF (1993) Effect of hardness on bioavailability and toxicity of cadmium to rainbow trout. Chem Speciat Bioavailabi 5:67–77
George SG (1989) Cadmium effects on plaice liver xenobiotic and metal detoxification systems dose-response. Aquat Toxicol 15:303–310
George SG, Hodgson PA, Tytler P, Todd K (1996) Inducibility of metallothionein mRNA expression and cadmium tolerance in larvae of a marine teleost, the turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Fundam Appl Toxicol 33:91–99
Gill TS, Epple A (1992) Impact of cadmium on the mummichog Fundulus heteroclitus and the role of calcium in suppression heavy metal toxicity. Comp Biochem Physiol 101:489–495
Grosell M, Wood CM (2002) Copper uptake across rainbow trout gills: mechanisms of apical entry. J. Exp Biol 205:1179–1188
Guven K, Duce JA, de Pomerai DI (1995) Calcium moderation of cadmium stress explored using a stress-inducible transgenic strain of Caenorhabditis elegans. Comp Biochem Physiol C 110:61–70
Heath AG (1991) Effect of water-borne copper on physiologic responses of bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus) to acute hypoxic stress and subsequent recovery. Comp Biochem Physiol C 100:559–564
Hollis L, McGeer JC, McDonald DG, Wood CM (2000) Protective effects of calcium against chronic waterborne cadmium exposure to juvenile rainbow trout. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2725–2734
Hwang PP, Yang CH (1997) Modulation of calcium uptake in cadmium-pretreated tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) larvae. Fish Physiol Biochem 16:403–410
Hwang PP, Lin SW, Lin HC (1995) Different sensitivities to cadmium in tilapia larvae (Oreochromis mossambicus; Teleostei). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 29:1–7
Iger Y, Lock RAC, Van Der M, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1994) Effects of water-borne cadmium on the skin of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 26:342–350
Kägi JHR, Schaffer A (1988) Biochemistry of metallothionein. Biochemistry 27:8509–8515
Laurén DJ, McDonald DG (1987) Acclimation to copper by rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri: Physiology. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 44:99–104
Marr JCA, Bergman HL, Lipton J, Hogstrand C (1995) Differences in relative sensitive of naïve and metals-accumulated brown and rainbow trout exposed to metals representative of the Clark Fork River, Montana. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 52:2016–2030
McGeer JC, Szebedinszky C, McDonald DG, Wood CM (2002) The role of dissolved organic carbon in moderating the bioavailability and toxicity of Cu to rainbow trout during chronic waterborne exposure. Comp Biochem Physiol C 133:147–160
Niyogi S, Kamunde CN, Wood CM (2006) Food selection, growth and physiology in relation to dietary sodium chloride content in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under chronic waterborne Cu exposure. Aquat Toxicol 77:210–221
Perschbacher PW, Wurts WA (1999) Effects of calcium and magnesium hardness on acute copper toxicity to juvenile channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Aquaculture 172:275–280
Playle RC, Dixon DG, Burnison K (1993) Copper and cadmium binding to fish gills: Estimates of metal-gill stability constants and modelling metal accumulation. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 50:2678–2687
Pratap HB, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1990) Effects of water-borne cadmium on plasma cortisol and glucose in the cichlid fish, Oreochromis mossambicus. Comp Biochem Physiol C 95:313–317
Priya K, Dinesh KPB, Ramesh M, Manavalaramanujam R (1999) Impact of copper sulphate toxicity on plasma electrolytes of a freshwater teleost fish, Cyprinus carpiovar communis. Indian J Fish 46:73–177
Pyle GG, Kamunde CN, McDonald DG, Wood CM (2003) Dietary sodium inhibits aqueous copper uptake in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Exp Biol 206:609–618
Richards JG, Playle RC (1999) Protective effects of calcium against the physiologic effects of exposure to a combination of cadmium and copper in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Can J Zool 77:1035–1047
Sloman KA, Morgan TP, McDonald DG, Wood CM (2003) Socially induced changes in sodium regulation affect the uptake of water-borne copper and silver in the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Comp Biochem Physiol C 135:393–403
Vonck APMA, Wendelaar Bonga SE, Flik G (1998) Sodium and calcium balance in Mozambique tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus, increased at different salinities. Comp Biochem Physiol A 119:441–449
Wicklund GA, Norrgren L, Müssener A (1994) Differences in uptake of inorganic mercury and cadmium in the gills of the zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio. Aquat Toxicol 30:13–26
Wong CKC, Wong MH (2000) Morphologic and biochemical changes in the gills of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) to ambient cadmium exposure. Aquat Toxicol 48:517–527
Wu SM (2002) An approach for metallothionein induction in early larval stages of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) using zinc sulfate. J Fish Soc Taiwan 29:209–217
Wu SM, Chen CC, Lee YC, Leu HT, Lin NS (2006) Cortisol and copper induce metallothionein expression in three tissues of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) with organ culture. Zool Stud 45:363–370
Wu SM, Jong KJ, Kuo SY (2003) Effects of copper sulfate on ion balance and growth in tilapia larvae (Oreochromis mossambicus). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 45:357–363
Wu SM, Weng CF, Hwang JC, Huang CJ, Hwang PP (2000) Metallothionein induction in early larval stages of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Physiol Zool 5:531–537
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by National Chiayi University. Thanks are extended to H. C. Lin and P. P. Hwang for assistance during the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S.M., Ho, YC. & Shih, M.J. Effects of Ca2+ or Na+ on Metallothionein Expression in Tilapia Larvae (Oreochromis mossambicus) Exposed to Cadmium or Copper. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 52, 229–234 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-006-0112-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-006-0112-5