Abstract
Introduction
To investigate the application value of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), the difference of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADCdifference) value calculated from ADCdifference map was used, in evaluating the pathologic grade of astrocytic tumors.
Methods
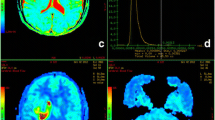
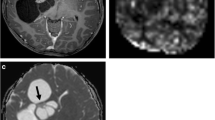
33 patients with histopathologically proven supratentorial astrocytic tumors were included in this prospective study. All of them received conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), DWI with diffusion factor of 0 and 50 s/mm2 and of 0 and 3,000 s/mm2, and perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI) examinations. Pseudo-color ADCdifference maps were obtained by means of using ADC map with low b value (0 and 50 s/mm2) minus ADC map with high b value (0 and 3,000 s/mm2).
Results
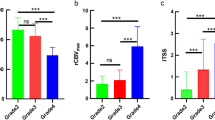
The highest ADCdifference value of grades I–II, grade III, and grade IV was (0.91 ± 0.07) × 10−3, (1.81 ± 0.38) × 10−3, and (2.36 ± 0.32) × 10−3 mm2/s, respectively, and there was statistical difference among them (p < 0.001). The highest ADCdifference value between low-grade (grades I–II) and high-grade (grades III–IV) astrocytic tumors showed statistical difference as well (p < 0.001). The highest ADCdifference value of astrocytic tumors correlated positively with the pathologic grade of tumor (r = 0.853, p < 0.001). Positive correlation was found between the highest ADCdifference value and maximum relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) value (r = 0.829, p < 0.001) in high-grade astrocytic tumors; however, the highest ADCdifference value and maximum rCBV value had no significant correlation in low-grade astrocytic tumors (r = 0.259, p = 0.536).
Conclusion
Quantitative analysis of highest ADCdifference value of supratentorial astrocytic tumors may provide valuable information of tumor microcirculation and perfusion, thus allowing a promising new method for preoperatively assessing the pathologic grade of tumor.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M (1988) Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168:497–505
Colagrande S, Carbone SF, Carusi LM, Cova M, Villari N (2006) Magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging: extraneurological applications. Radiol Med 111:392–419
Colagrande S, Pallotta S, Vanzulli A, Napolitano M, Villari N (2005) The diffusion parameter in magnetic resonance: physics, techniques, and semeiotics. Radiol Med 109:1–16
Taouli B, Vilgrain V, Dumont E, Daire JL, Fan B, Menu Y (2003) Evaluation of liver diffusion isotropy and characterization of focal hepatic lesions with two single-shot echo-planar MR imaging sequences: prospective study in 66 patients. Radiology 226:71–78. doi:10.1148/radiol.2261011904DOI:dx.doi.org
Matsuki M, Inada Y, Tatsugami F, Tanikake M, Narabayashi I, Katsuoka Y (2007) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging for urinary bladder carcinoma: initial results. Eur Radiol 17(1):201–204. doi:10.1007/s00330-006-0281-7DOI:dx.doi.org
Moteki T, Horikoshi H (2006) Evaluation of hepatic lesions and hepatic parenchyma using diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR with three values of gradient b-factor. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:637–645. doi:10.1002/jmri.20682DOI:dx.doi.org
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F, Vandecaveye V, Chen F, Sun X, Bosmans H, Hermans R, Verbeken EK, Boesch C, Marchal G, Landuyt W, Ni Y (2005) Effect of vascular targeting agent in rat tumor model: dynamic contrast-enhanced versus diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 237:492–499. doi:10.1148/radiol.2372041638DOI:dx.doi.org
Le Bihan D, Turner R, MacFall JR (1989) Effects of intravoxel incoherent motions (IVIM) in steady-state free precession (SSFP) imaging: application to molecular diffusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 10:324–337
Luciani A, Vignaud A, Cavet M, Nhieu JT, Mallat A, Ruel L, Laurent A, Deux JF, Brugieres P, Rahmouni A (2008) Liver cirrhosis: intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging—pilot study. Radiology 249:891–899. doi:10.1148/radiol.2493080080DOI:dx.doi.org
Le Bihan D, Moonen CT, van Zijl PC, Pekar J, DesPres D (1991) Measuring random microscopic motion of water in tissues with MR imaging: a cat brain study. J Comput Assist Tomogr 15:19–25
DeLano MC, Cooper TG, Siebert JE, Potchen MJ, Kuppusamy K (2000) High b value diffusion-weighted MR imaging of adult brain: image contrast and apparent diffusion coefficient map features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1830–1836
Kwee TC, Galbán CJ, Tsien C, Junck L, Sundgren PC, Ivancevic MK, Johnson TD, Meyer CR, Rehemtulla A, Ross BD, Chenevert TL (2010) Comparison of apparent diffusion coefficients and distributed diffusion coefficients in high-grade gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 31:531–537. doi:10.1002/jmri.22070
Arvinda HR, Kesavadas C, Sarma PS, Thomas B, Radhakrishnan VV, Gupta AK, Kapilamoorthy TR, Nair S (2009) Glioma grading: sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values of diffusion and perfusion imaging. J Neurooncol 94:87–96. doi:10.1007/s11060-009-9807-6
Higano S, Yun X, Kumabe T, Watanabe M, Mugikura S, Umetsu A, Sato A, Yamada T, Takahashi S (2006) Malignant astrocytic tumors: clinical importance of apparent diffusion coefficient in prediction of grade and prognosis. Radiology 241:839–846. doi:10.1148/radiol.2413051276DOI:dx.doi.org
Provenzale JM, Mukundan S, Barboriak DP (2006) Diffusion-weighted and perfusion MR imaging for brain tumor characterization and assessment of treatment response. Radiology 239:632–649. doi:10.1148/radiol.2393042031DOI:dx.doi.org
Koh DM, Collins DJ (2007) Diffusion-weighted MRI in the body: applications and challenges in oncology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188:1622–1635. doi:10.2214/AJR.06.1403DOI:dx.doi.org
Villringer A, Rosen BR, Belliveau JW, Ackerman JL, Lauffer RB, Buxton RB, Chao YS, Wedeen VJ, Brady TJ (1988) Dynamic imaging with lanthanide chelates in normal brain: contrast due to magnetic susceptibility effects. Magn Reson Med 6:164–174. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910060205DOI:dx.doi.org
Belliveau JW, Rosen BR, Kantor HL, Rzedzian RR, Kennedy DN, McKinstry RC, Vevea JM, Cohen MS, Pykett IL, Brady TJ (1990) Functional cerebral imaging by susceptibility-contrast NMR. Magn Reson Med 14:538–546. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910140311DOI:dx.doi.org
Jackson A, Kassner A, Zhu XP, Li KL (2001) Reproducibility of T2* blood volume and vascular tortuosity maps in cerebral gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:510–516
Lüdemann L, Hamm B, Zimmer C (2000) Pharmacokinetic analysis of glioma compartments with dynamic Gd-DTPA-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 18:1201–1214. doi:10.1016/S0730-725X(00)00223-XDOI:dx.doi.org
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, X., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y. et al. Grading of supratentorial astrocytic tumors by using the difference of ADC value. Neuroradiology 53, 533–539 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0846-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0846-2