Abstract
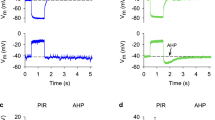
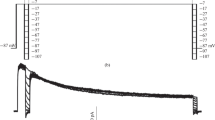
In leech P neurons the inhibition of the Na+-K+ pump by ouabain or omission of bath K+ leaves the membrane potential unaffected for a prolonged period or even induces a marked membrane hyperpolarization, although the concentration gradients for K+ and Na+ are attenuated substantially. As shown previously, this stabilization of the membrane potential is caused by an increase in the K+ conductance of the plasma membrane, which compensates for the reduction of the K+ gradient. The data presented here strongly suggest that the increased K+ conductance is due to Na+-activated K+ (KNa) channels. Specifically, an increase in the cytosolic Na+ concentration ([Na+]i) was paralleled by a membrane hyperpolarization, a decrease in the input resistance (Rin) of the cells, and by the occurrence of an outwardly directed membrane current. The relationship between Rin and [Na+]i followed a simple model in which the Rin decrease was attributed to K+ channels that are activated by the binding of three Na+ ions, with half-maximal activation at [Na+]i between 45 and 70 mM. At maximum channel activation, Rin was reduced by more than 90%, suggesting a significant contribution of the KNa channels to the physiological functioning of the cells, although evidence for such a contribution is still lacking. Injection experiments showed that the KNa channels in leech P neurons are also activated by Li+.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammann D. 1986. Ion sensitive microelectrodes. Springer, Berlin, Germany
Baylor D.A., Nicholls J.G. 1969. After-effects of nerve impulses on signalling in the central nervous system of the leech. J. Physiol. 203:571–589
Bhattacharjee A., Joiner W.J., Wu M., Yang Y., Sigworth F.J., Kaczmarek L.K. 2003. Slick (Slo2.1), a rapidly-gating sodium-activated potassium channel inhibited by ATP. J. Neurosci. 23:11681–11691
Bhattacharjee A., von Hehn C.A., Mei X., Kaczmarek L.K. 2005. Localization of the Na(+)-activated K(+) channel Slick in the rat central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 484:80–92
Bhattacharjee A., Kaczmarek L.K. 2005. For K+ channels, Na+ is the new Ca2+. Trends Neurosci. 28:422–428
Deitmer J.W., Schlue W.-R. 1981. Measurements of the intracellular potassium activity of Retzius cells in the leech central nervous system. J. exp. Biol. 91:87–101
Deitmer J.W., Schlue W.-R. 1983. Intracellular Na+ and Ca2+ in leech Retzius neurones during inhibition of the Na+-K+ pump. Pfluegers Arch. 397:195–201
Deitmer J.W., Schlue W.-R. 1987. The regulation of intracellular pH by identified glial cells and neurones in the central nervous system of the leech. J. Physiol. 388:261–283
Dierkes P.W., Hochstrate P., Schlue W.-R. 1997. Voltage-dependent Ca2+ influx into identified leech neurones. Brain Res. 746:285–293
Dierkes, P.W., Wüsten, H.J., Klees, G., Müller, A., Hochstrate, P. 2005. Ionic mechanism of ouabain-induced swelling of leech Retzius neurons. Pfluegers Arch., in press
Dierkes P.W., Schlue W.-R. 2005. Ca2+ influx into identified leech neurons induced by 5-hydroxytryptamine. J. Neurobiol. 62:106–120
Dryer S.E. 1994. Na+-activated K+ channels: a new family of large-conductance ion channels. Trends Neurosci. 17:155–160
Dryer S.E. 2003. Molecular identification of the Na+-activated K+ channel. Neuron 37:727–728
Egan T.M., Dagan D., Kupper J., Levitan I.B. 1992. Na+-activated K+ channels are widely distributed in rat CNS and in Xenopus oocytes. Brain Res. 584:319–321
Elkins T., Ganetzky B., Wu C.F. 1986. A Drosophila mutation that eliminates a calcium-dependent potassium current. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:8415–8419
Frey G., Hanke W., Schlue W.-R. 1993. ATP-inhibited and Ca2+-dependent K+ channels in the soma membrane of cultured leech Retzius neurons. J. Membrane Biol. 134:131–142
Frey G., Lucht M., Schlue W.-R. 1998. ATP-inhibited K+ channels and the membrane potential of identified leech neurons. Brain Res. 798:247–253
Gerard E., Hochstrate P., Schlue W.-R. 1999. Hyperpolarization-activated membrane current in leech P neurones. In: N. Elsner U. Eysel, eds., Gottingen Neurobiology Report. Vol II, Thieme, Stuttgart, p 719
Glitsch H.G. 2001. Electrophysiology of the sodium-potassium ATPase in cardiac cells. Physiol. Rev. 81:1791–1826
Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R.Y. 1985. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J. Biol. Chem. 260:3440–3450
Hartung K. 1985. Potentiation of a transient outward current by Na+ influx in crayfish neurones. Pfluegers Arch. 404:41–44
Hille B. 2001. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sinauer Associates, Inc., Sunderland, MA, USA
Hochstrate P., Schlue W.-R. 1994. Ca2+ influx into leech glial cells and neurones caused by pharmacologically distinct glutamate receptors. Glia 12:268–280
Jansen J.K.S., Nicholls J.G. 1973. Conductance changes, an electrogenic pump and the hyperpolarization of leech neurones following impulses. J. Physiol. 229:635–655
Kennedy H.J., Thomas R.C. 1996. Effects of injecting calcium-buffer solution on [Ca2+]i in voltage-clamped snail neurons. Biophys. J. 70:2120–2130
Kilb W., Schlue W.-R. 1999. Mechanism of the kainate-induced intracellular acidification in leech Retzius neurons. Brain Res. 824:168–182
Kiss T., Fujisawa Y., Laszlo Z., Muneoka Y. 2000. Mytilus inhibitory peptide (MIP) induces aNa+-activated K+-current in snail neurons. Acta Biol. Hung. 51:133–145
Liu Q.Y., Schaffner A.E., Barker J.L. 1998. Kainate induces an intracellular Na+-activated K+ current in cultured embryonic rat hippocampal neurones. J. Physiol. 510:721–734
Macagno E.R. 1980. Number and distribution of neurons in leech segmental ganglia. J. Comp. Neurol. 190:283–302
Martin A.R., Dryer S.E. 1989. Potassium channels activated by sodium. Quart. J. Exp. Physiol. 74:1033–1041
McCormick D.A., Pape H.C. 1990. Properties of a hyperpolarization-activated cation current and its role in rhythmic oscillation in thalamic relay neurones. J. Physiol. 431:291–318
Pape H.C. 1996. Queer current and pacemaker: the hyperpolarization-activated cation currents in neurons. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 58:299–327
Partridge L.D., Thomas R.C. 1974. Effect of intracellular lithium on snail neurones. Nature 249:578–580
Partridge L.D., Thomas R.C. 1976. The effects of lithium and sodium on the potassium conductance of snail neurones. J. Physiol. 254:551–563
Rose C.R. 2002. Na+ signals at central synapses. Neuroscientist 8:532–539
Schlue W.-R. 1991. Effects of ouabain on intracellular ion activities of sensory neurons of the leech central nervous system. J. Neurophysiol. 65:736–746
Schlue W.-R., Deitmer J.W. 1980. Extracellular potassium in neuropile and nerve cell body region of the leech central nervous system. J. Exp. Biol. 87:23–43
Schlue W.-R., Deitmer J.W. 1984. Potassium distribution and membrane potential of sensory neurons in the leech nervous system. J. Neurophysiol. 51:689–704
Scuri R., Mozzachiodi R., Brunelli M. 2002. Activity-dependent increase of the AHP amplitude in T sensory neurons of the leech. J. Neurophysiol. 88:2490–2500
Stewart R.R., Nicholls J.G., Adams W.B. 1989. Na+, K+ and Ca2+ currents in identified leech neurons in culture. J. Exp. Biol. 141:1–20
Weiss J.N. 1997. The Hill equation revisited: uses and misuses. FASEB J. 11:835–841
Yuan A., Santi C.M., Wei A., Wang Z.-W., Pollak K., Nonet M., Kaczmarek L., Crowder C.M., Salkoff L. 2003. The sodium-activated potassium channel is encoded by a member of the Slo gene family. Neuron 37:765–773
Acknowledgements
We thank two unknown referees for their constructive remarks and experimental suggestions, which led to a substantial improvement of our article
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klees, G., Hochstrate, P. & Dierkes, P. Sodium-dependent Potassium Channels in Leech P Neurons. J Membrane Biol 208, 27–38 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0816-x
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0816-x