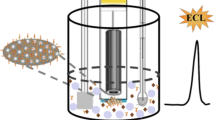
Abstract
We developed a sensing strategy that mimics the bead-based electrogenerated chemiluminescence immunoassay. However, instead of the most common metal complexes, such as Ru or Ir, the luminophore is luminol. The electrogenerated chemiluminescence of luminol was promoted by in situ electrochemical generation of hydrogen peroxide at a boron-doped diamond electrode. The electrochemical production of hydrogen peroxide was achieved in a carbonate solution by an oxidation reaction, while at the same time, microbeads labelled with luminol were deposited on the electrode surface. For the first time, we proved that was possible to obtain light emission from luminol without its direct oxidation at the electrode. This new emission mechanism is obtained at higher potentials than the usual luminol electrogenerated chemiluminescence at 0.3–0.5 V, in conjunction with hydrogen peroxide production on boron-doped diamond at around 2–2.5 V (vs Ag/AgCl).
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Experimental data are available in AMS acta at https://amsacta.unibo.it/id/eprint/7694.
References
Rusling JF, Forster RJ. Biosensors designed for clinical applications. Biomedicines. 2021;9:702.
Calidonio JM, Gomez-Marquez J, Hamad-Schifferli K. Nanomaterial and interface advances in immunoassay biosensors. J Phys Chem C. 2022;126:17804–15.
Fiorani A, Valenti G, Iurlo M, Marcaccio M, Paolucci F. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence: a molecular electrochemistry point of view. Curr Opin Electrochem. 2018;8:31–8.
Yang H, Leland JK, Yost D, Massey RJ. Electrochemiluminescence: a new diagnostic and research tool. Nat Biotechnol. 1994;12:193–4.
Richter MM. Electrochemiluminescence (ECL). Chem Rev. 2004;104:3003–36.
Miao W. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence and its biorelated applications. Chem Rev. 2008;108:2506–53.
Valenti G, Fiorani A, Li H, Sojic N, Paolucci F. Essential role of electrode materials in electrochemiluminescence applications. ChemElectroChem. 2016;3:1990–7.
Villani E, Sakanoue K, Einaga Y, Inagi S, Fiorani A. Photophysics and electrochemistry of ruthenium complexes for electrogenerated chemiluminescence. J Electroanal Chem. 2022;921: 116677.
Valenti G, Rampazzo E, Kesarkar S, Genovese D, Fiorani A, Zanut A, Palomba F, Marcaccio M, Paolucci F, Prodi L. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence from metal complexes-based nanoparticles for highly sensitive sensors applications. Coord Chem Rev. 2018;367:65–81.
Sornambigai M, Bouffier L, Sojic N, Kumar SS. Tris(2,2’-bipyridyl)ruthenium (II) complex as a universal reagent for the fabrication of heterogeneous electrochemiluminescence platforms and its recent analytical applications. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023;415:5875–98.
Haghighatbin MA, Laird SE, Hogan CF. Electrochemiluminescence of cyclometalated iridium (III) complexes. Curr Opin Electrochem. 2018;7:216–23.
Suzuki K, Kobayashi A, Kaneko S, Takehira K, Yoshihara T, Ishida H, Shiina Y, Oishi S, Tobita S. Reevaluation of absolute luminescence quantum yields of standard solutions using a spectrometer with an integrating sphere and a back-thinned CCD detector. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2009;11:9850–60.
Barbante GJ, Doeven EH, Kerr E, Connell TU, Donnelly PS, White JM, Lópes T, Laird S, Wilson DJD, Barnard PJ, Hogan CF, Francis PS. Understanding electrogenerated chemiluminescence efficiency in blue-shifted iridium(iii)-complexes: an experimental and theoretical study. Chem Eur J. 2014;20:3322–32.
Yeh H-W, Ai H-W. Development and applications of bioluminescent and chemiluminescent reporters and biosensors. Annu Rev Anal Chem. 2019;12:129–50.
Fiorani A, Difonzo M, Rizzo F, Valenti G. Versatile electrochemiluminescent organic emitters. Curr Opin Electrochem. 2022;34: 100998.
Zhou Y, Villani E, Kurioka T, Zhang Y, Tomita I, Inagi S. Fabrication of luminescent patterns using aggregation-induced emission molecules by an electrolytic micelle disruption approach. Aggregate. 2023;4: e202.
Marquette CA, Blum LJ. Applications of the luminol chemiluminescent reaction in analytical chemistry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2006;385:546–54.
Khan P, Idrees D, Moxley MA, Corbett JA, Ahmad F, von Figura G, Sly WS, Waheed A, Hassan MI. Luminol-based chemiluminescent signals: clinical and non-clinical application and future uses. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014;173:333–55.
Roda A, Guardigli M. Analytical chemiluminescence and bioluminescence: latest achievements and new horizons. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012;402:69–76.
Villani E, Inagi S. Map** the distribution of potential gradient in bipolar electrochemical systems through luminol electrochemiluminescence imaging. Anal Chem. 2021;93:8152–60.
Villani E, Shida N, Inagi S. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of luminol on wireless conducting polymer films. Electrochim Acta. 2021;389: 138718.
Villani E, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Zhou Y, Konishi M, Tomita I, Inagi S. AC-bipolar electrosynthesis and luminol electrochemiluminescence imaging of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) and its composite films. ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2023;5:6186–98.
Hiramoto K, Komatsu K, Shikuwa R, Konno A, Sato Y, Hirano-Iwata A, Ino K, Shiku H. Evaluation of respiratory and secretory activities of multicellular spheroids via electrochemiluminescence imaging. Electrochim Acta. 2023;458: 142507.
Zhou P, Hu S, Guo W, Su B. Deciphering electrochemiluminescence generation from luminol and hydrogen peroxide by imaging light emitting layer. Fundam Res. 2022;2:682–7.
Feng M, Dauphin AL, Bouffier L, Zhang F, Wang Z, Sojic N. Enhanced cathodic electrochemiluminescence of luminol on iron electrodes. Anal Chem. 2021;93:16425–31.
Sakura S. Electrochemiluminescence of hydrogen peroxide-luminol at a carbon electrode. Anal Chim Acta. 1992;262:49–57.
Rahmawati I, Einaga Y, Ivandini TA, Fiorani A. Enzymatic biosensors with electrochemiluminescence transduction. ChemElectroChem. 2022;9: e202200175.
Miao W, Choi J-P, Bard AJ. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence 69: the Tris(2,2’-bipyridine)ruthenium(II), (Ru(bpy)32+)/Tri-n-propylamine (TPrA) system revisited - a new route involving TPrA•+ cation radicals. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:14478–85.
Sentic M, Milutinovic M, Kanoufi F, Manojlovic D, Arbault S, Sojic N. Map** electrogenerated chemiluminescence reactivity in space: mechanistic insight into model systems used in immunoassays. Chem Sci. 2014;5:2568–72.
Zanut A, Fiorani A, Canola S, Saito T, Ziebart N, Rapino S, Rebeccani S, Barbon A, Irie T, Josel H-P, Negri F, Marcaccio M, Windfuhr M, Imai K, Valenti G, Paolucci F. Insights into the mechanism of coreactant electrochemiluminescence facilitating enhanced bioanalytical performance. Nat Commun. 2020;11:2668.
Chen L, Hayne DJ, Doeven EH, Agugiaro J, Wilson DJD, Henderson LC, Connell TU, Nai YH, Alexander R, Carrara S, Hogan CF, Donnelly PS, Francis PS. A conceptual framework for the development of iridium(III) complex-based electrogenerated chemiluminescence labels. Chem Sci. 2019;10:8654–67.
Zanut A, Fiorani A, Rebeccani S, Kesarkar S, Valenti G. Electrochemiluminescence as emerging microscopy techniques. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411:4375–82.
Sojic N. Analytical electrogenerated chemiluminescence: from fundamentals to bioassays; Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC)Publishing, 2019.
Sakanoue K, Fiorani A, Santo CI, Irkham, Valenti G, Paolucci F, Einaga Y. Boron-doped diamond electrode outperforms the state-of-the-art electrochemiluminescence from microbeads immunoassay. ACS Sens. 2022;7:1145–1155.
Irkham, Fiorani A, Valenti V, Kamoshida N, Paolucci F, Einaga Y. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence by in situ production of coreactant hydrogen peroxide in carbonate aqueous solution at a boron-doped diamond electrode. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142:1518–1525.
Irkham, Rais RR, Ivandini TA, Fiorani A, Einaga Y. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of luminol mediated by carbonate electrochemical oxidation at a boron-doped diamond. Anal Chem. 2021;93:2336–2341.
Rebeccani S, Zanut A, Santo CI, Valenti G, Paolucci F. A guide inside electrochemiluminescent microscopy mechanisms for analytical performance improvement. Anal Chem. 2021;94:336–48.
Knezevic S, Bouffier L, Liu B, Jiang D, Sojic N. Electrochemiluminescence microscopy: from single objects to living cells. Curr Opin Electrochem. 2022;35: 101096.
Sakanoue K, Fiorani A, Irkham, Einaga Y. Effect of boron-do** level and surface termination in diamond on electrogenerated chemiluminescence. ACS Appl Electron Mater. 2021;3:4180–4188.
Pollok NE, Rabin C, Smith L, Crooks RM. Orientation-controlled bioconjugation of antibodies to silver nanoparticles. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019;30:3078–86.
Marselli B, Garcia-Gomez J, Michaud P-A, Rodrigo MA, Comninellis Ch. Electrogeneration of hydroxyl radicals on boron-doped diamond electrodes. J Electrochem Soc. 2003;150:D79–83.
Henke AH, Saunders TP, Pedersen JA, Hamers RJ. Enhancing electrochemical efficiency of hydroxyl radical formation on diamond electrodes by functionalization with hydrophobic monolayers. Langmuir. 2019;35:2153–63.
Haapakka KE, Kankare JJ. The mechanism of the electrogenerated chemiluminescence of luminol in aqueous alkaline solution. Anal Chim Acta. 1982;138:263–75.
Rahmawati I, Saepudin E, Fiorani A, Einaga Y, Ivandini TA. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of luminol at a boron-doped diamond electrode for the detection of hypochlorite. Analyst. 2022;147:2696–702.
Imai K, Valenti G, Villani E, Rapino S, Rampazzo E, Marcaccio M, Prodi L, Paolucci F. Numerical simulation of doped silica nanoparticle electrochemiluminescence. J Phys Chem C. 2015;119:26111–8.
Zhou P, Fu W, Ding L, Yan Y, Guo W, Su B. Toward mechanistic understanding of electrochemiluminescence generation by tris(2,2’-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) and peroxydisulfate. Electrochim Acta. 2023;439:141716.
Acknowledgements
AF acknowledges the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (Fellowship ID No. P19333).
Funding
AF acknowledges the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science for funding this work with Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Fellows, Grant Number 19F19333. GV and FP would like to thank the MIUR, grant numbers 20225P4EJC, P2022E5YSK, and 2020CBEYHC (AStraLI). This work was supported by Nano-ImmunoEra project that has received funding from the European Union’s MSCA Staff exchange Horizon Europe programme, grant agreement number 101086341.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Andrea Fiorani. Methodology: Andrea Fiorani, Claudio Ignazio Santo, Kohei Sakanoue. Formal analysis and investigation: Andrea Fiorani, Claudio Ignazio Santo. Writing—original draft preparation: Andrea Fiorani. Writing—review and editing: Andrea Fiorani, Claudio Ignazio Santo, Valenti Giovanni. Funding acquisition: Andrea Fiorani, Yasuaki Einaga. Resources: Andrea Fiorani, Donato Calabria, Mara Mirasoli, Francesco Paolucci, Giovanni Valenti, Yasuaki Einaga. Supervision: Andrea Fiorani.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Source of biological material
Not applicable.
Statement on animal welfare
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Published in the topical collection Optical Biosensors and Biomimetic Sensors for Chemical Analysis with guest editors Elena Benito-Peña and Guillermo Orellana.
In honor of Professor María Cruz Moreno Bondi.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fiorani, A., Santo, C.I., Sakanoue, K. et al. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence from luminol-labelled microbeads triggered by in situ generation of hydrogen peroxide. Anal Bioanal Chem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05356-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05356-z