Abstract
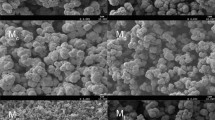
In this study, a covalent organic framework (COF)-TpBD-supported melamine sponge (MS) was fabricated through a one-step hydrothermal method. The obtained monolithic column was then applied in in-syringe solid-phase extraction (IS-SPE) for the separation of three volatile ingredients from serum samples. Given credit for the superior adsorption capacity of the COF and the homogeneous microporous property of MS, the developed column exhibited satisfactory separation of the targets. And the dominating adsorption mechanism was the hydrophobic interaction forces between TpBD and targets and the high mass transfer efficiency provided by the large pore structure of MS. The results of dynamic adsorption showed that the MS@TpBD column displayed much better adsorption performance than blank MS and TpBD. And it has featured great reusability up to 5 cycles and obtained satisfied recovery values (87.9 ~ 110.3%) in serum samples. As a result of sample clean-up, this column offers low limit of detections (LODs) down to 0.014, 0.010, and 0.020 μg/mL, respectively. In summary, we believe that this convenient separation column has prominent application promise in the fields of separating activity ingredients in biological samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang X, Sun H, Zhang A, Jiao G, Sun W, Yuan Y. Pharmacokinetics screening for multi-components absorbed in the rat plasma after oral administration traditional Chinese medicine formula Yin-Chen-Hao-Tang by ultra performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry combined with pattern recognition methods. Analyst. 2011;136(23):5068–76.
Nagana Gowda GA, Raftery D. Quantitating metabolites in protein precipitated serum using NMR spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2014;86(11):5433–40.
Guo Y, Zhang J, Xu J, Wu X, Dong F, Liu X, et al. An integrated strategy for purification by combining solid-phase extraction with dispersive-solid-phase extraction for detecting 22 pesticides and metabolite residues in fish. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69(25):7199–208.
Poole CF. New trends in solid-phase extraction. Eur J of Canc. 2003;22(6):362–73.
Rasmussen RR, Qian Y, Sloth JJ. SPE HG-AAS method for the determination of inorganic arsenic in rice–results from method validation studies and a survey on rice products. Anal and Bioanal Chem. 2013;405(24):7851–7.
Jaffrezic A, Jarde E, Soulier A, Carrera L, Marengue E, Cailleau A, et al. Veterinary pharmaceutical contamination in mixed land use watersheds: from agricultural headwater to water monitoring watershed. Sci of the Total Environ. 2017;609:992–1000.
Shirani M, Salari F, Habibollahi S, Akbari A. Needle hub in-syringe solid phase extraction based a novel functionalized biopolyamide for simultaneous green separation/preconcentration and determination of cobalt, nickel, and chromium (III) in food and environmental samples with micro sampling flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem J. 2020;152:104340.
Liu X, Hu Q, Tong Y, Li N, Ouyang S, Yang H, et al. Sample bottle coated with sorbent as a novel solid-phase extraction device for rapid on-site detection of BTEX in water. Anal Chim Acta. 2021;1152:338226.
Han J, Wang H, Li Z, Wang Z. Preparation of chitosan-modified magnetic Schiff base network composite nanospheres for effective enrichment and detection of hippuric acid and 4-methyl hippuric acid. J Chromatogr A. 2021;1652:462373.
Mirzaee MT, Seidi S, Alizadeh R. Pipette-tip SPE based on graphene/ZnCr LDH for Pb(II) analysis in hair samples followed by GFAAS. Anal Biochem. 2021;612:113949.
Florez DHA, Teixeira RA, Da Silva RCS, Pires BC, Dutra FVA, Borges KB. Pipette-tip solid-phase extraction using polypyrrole as efficient adsorbent for extraction of avermectins and milbemycins in milk. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(14):3361–74.
Chen Y, Al-Taher F, Juskelis R, Wong J, Zhang K, Hayward DG, et al. Multiresidue pesticide analysis of dried botanical dietary supplements using an automated dispersive SPE cleanup for QuEChERS and high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60(40):9991–9.
Yin L, Zheng X, Wang G, Wang W. Microwave irradiation followed by zinc oxide based dispersive solid-phase extraction coupled with HPLC for simultaneous extraction and determination of flavonoids in Veronicastrum latifolium (Hemsl.) Yamazaki. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411(5):1029–40.
Han Q, Aydan T, Yang L, Zhang X, Liang Q, Ding M. In-syringe solid-phase extraction for on-site sampling of pyrethroids in environmental water samples. Analy Chim Acta. 2018;1009:48–55.
Vargas-Munoz MA, Cerda V, Turnes Palomino G, Palacio E. Determination of long-chain fatty acids in anaerobic digester supernatant and olive mill wastewater exploiting an in-syringe dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and derivatization free GC-MS method. Anal and Bioanal Chem. 2021;413(15):3833–45.
Lohse MS, Bein T. Covalent organic frameworks: structures, synthesis, and applications. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28(33):1705553.
Tian Y, Lu Q, Guo X, Wang S, Gao Y, Wang L. Au nanoparticles deposited on ultrathin two-dimensional covalent organic framework nanosheets for in vitro and intracellular sensing. Nanoscale. 2020;12(14):7776–81.
Gao W, Liu Y, Zhang H, Wang Z. Electrochemiluminescence biosensor for nucleolin imaging in a single tumor cell combined with synergetic therapy of tumor. ACS Sens. 2020;5(4):1216–22.
Fan H, Gu J, Meng H, Knebel A, Caro J. High-flux membranes based on the covalent organic framework COF-LZU1 for selective dye separation by nanofiltration. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2018;57(15):4083–7.
Zhang X, Li H, Wang J, Peng D, Liu J, Zhang Y. In-situ grown covalent organic framework nanosheets on graphene for membrane-based dye/salt separation. J Membr Sci. 2019;581:321–30.
Qian H, Liu F, Liu X, Yang C, Yan X. Chiral covalent organic framework-monolith as stationary phase for high-performance liquid chromatographic enantioseparation of selected amino acids. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022;414(18):5255–62.
Wei W, Han Q, Tian S, Wang Y, Zhang H, Wang H et al. Effective separation of α-asarone and β-asarone in TCM by covalent organic framework modified magnetic solid phase extraction. Microchem J. 2022;175:107015.
Feng Y, Yao J. Design of melamine sponge-based three-dimensional porous materials toward applications. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2018;57(22):7322–30.
Gong F, Li H, Wang W, Huang J, **a D, Liao J, et al. Scalable, eco-friendly and ultrafast solar steam generators based on one-step melamine-derived carbon sponges toward water purification. Nano Energy. 2019;58:322–30.
Pham VH, Dickerson JH. Superhydrophobic silanized melamine sponges as high efficiency oil absorbent materials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(16):14181–8.
Jiang Y, Zhang B, Li J, Sun Y, Wang X, Ma P, et al. One-step fabrication of hydrophilic MIL-68(Al)/chitosan-coated melamine sponge for vortex-assisted solid-phase extraction of parabens in water samples. Talanta. 2021;224:121799.
Li J, Yang Y, Ma W, Li G, Lu Q, Lin Z. One-pot room-temperature synthesis of covalent organic framework-coated superhydrophobic sponges for highly efficient oil-water separation. J Hazard Mater. 2021;411:125190.
Toro RG, Calandra P, Federici F, De Caro T, Mezzi A, Cortese B, et al. Development of superhydrophobic, self-cleaning, and flame-resistant DLC/TiO2 melamine sponge for application in oil–water separation. J Mater Sci. 2019;55(7):2846–59.
Feng Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, Yao J. Furfuryl alcohol modified melamine sponge for highly efficient oil spill clean-up and recovery. J Mater Chem A. 2017;5(41):21893–7.
Sun Q, Aguila B, Perman JA, Butts T, **ao F-S, Ma S. Integrating superwettability within covalent organic frameworks for functional coating. Chem. 2018;4(7):1726–39.
Jiang Y, Li X, Piao H, Qin Z, Li J, Sun Y, et al. A semi-automatic solid phase extraction system based on MIL-101(Cr) foam-filled syringe for detection of triazines in vegetable oils. J Sep Sci. 2021;44(6):1089–97.
Wang Y, Wang K, Lin J, **ao L, Wang X. The preparation of nano-MIL-101(Fe)@chitosan hybrid sponge and its rapid and efficient adsorption to anionic dyes. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;165:2684–92.
Lin D, Duan P, Yang W, Huang X, Zhao Y, Wang C et al. Facile fabrication of melamine sponge@covalent organic framework composite for enhanced degradation of tetracycline under visible light. Chem Eng J. 2022;430:132817.
Wang L, Yang C, Yan X. In situ growth of covalent organic framework shells on silica microspheres for application in liquid chromatography. ChemPlusChem. 2017;82(6):933–8.
Han P, Han T, Peng W, Wang X. Antidepressant-like effects of essential oil and asarone, a major essential oil component from the rhizome of Acorus tatarinowii. Pharm Bio. 2013;51(5):589–94.
Chellian R, Pandy V, Mohamed Z. Pharmacology and toxicology of alpha- and beta-asarone: a review of preclinical evidence. Phytomedicine. 2017;32:41–58.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Natural Sciences Foundation of Liaoning Province (No.20180550681), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81872835), and the Young Elite Scientist Sponsorship Program of Bei**g Association for Science and Technology (2021–2023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The animals experiments are approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Tsinghua University and performed in compliance with the Animal Management Rules of the Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China (Document no. 55, 2001).
Statement on animal welfare
We have taken great efforts to reduce the number of animals used in this work and also taken efforts to reduce animal suffering from pain and discomfort.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, W., Lu, Z., Wu, T. et al. One-step fabrication of COF-coated melamine sponge for in-syringe solid-phase extraction of active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicine in serum samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 8071–8079 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04340-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04340-9