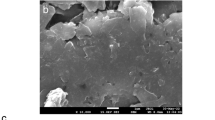
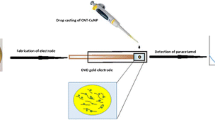
Abstract
A new electrochemical sensor based on thionine (TH), an electroactive polymer, and CuO nanoparticle (CuONP)-modified pencil graphite electrode (PGE) has been developed. Poly(thionine) (PTH) was formed on the CuO/PGE surface by electropolymerisation in ethaline deep eutectic solvent (DES) containing acetic acid dopant to form PTHEthaline/CuO/PGE. Cyclic voltammetry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and differential pulse voltammetry were utilized to evaluate the fabrication process, electrochemical properties, and performance parameters of the modified electrodes. The analytical performance of the PTHEthaline/CuO/PGE was evaluated with respect to linear range, limit of detection, repeatability, and reproducibility for the detection of acetaminophen (APAP) by electrooxidation in the presence of ascorbic acid (AA). Analytical parameters such as pH were optimized. The combined use of PTH and CuONP led to enhanced performance towards APAP due to the large electroactive surface area and synergistic catalytic effect, with a wide linear working range and low detection limit. The reliability of the proposed sensor for the detection of APAP was successfully tested in pharmaceutical samples containing APAP and AA, with very good recoveries.

Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ameer Q, Adeloju SB. Development of a potentiometric catechol biosensor by entrapment of tyrosinase within polypyrrole film. Sensor Actuat B-Chem. 2009;140:5–11.
Brett CMA. Deep eutectic solvents and applications in electrochemical sensing. Curr Opin Electrochem. 2018;10:143–8.
da Silva W, Queiroz AC, Brett CMA. Nanostructured poly(phenazine)/Fe2O3 nanoparticle film modified electrodes formed by electropolymerization in ethaline-deep eutectic solvent. Microscopic and electrochemical characterization. Electrochim Acta. 2020;347:136284.
Dalkıran B. Amperometric determination of heavy metal using an HRP inhibition biosensor based on ITO nanoparticles-ruthenium (III) hexamine trichloride composite: central composite design optimization. Bioelectrochem. 2020;135:107569.
Campbell FW, Compton RG. The use of nanoparticles in electroanalysis: an updated review. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010;396:241–59.
Lee SH, Lee JH, Tran VK, Ko E, Park CH, Chung WS, et al. Determination of acetaminophen using functional paper-based electrochemical devices. Sensor Actuat B-Chem. 2016;232:514–22.
Kim D, Kim JM, Jeon Y, Lee J, Oh J, Antink WH, et al. Novel two-step activation of biomass-derived carbon for highly sensitive electrochemical determination of acetaminophen. Sensor Actuat B-Chem. 2018;259:50–8.
Sun J, Schnackenberg LK, Holland RD, Schmitt TC, Cantor GH, Dragan YP, et al. Metabonomics evaluation of urine from rats given acute and chronic doses of acetaminophen using NMR and UPLC/MS. J Chrom B. 2008;871:328–40.
Frangu A, Pravcová K, Šilarová P, Arbneshi T, Sýs M. Flow injection tyrosinase biosensor for direct determination of acetaminophen in human urine. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411:2415–24.
Săndulescu R, Mirel S, Oprean R. The development of spectrophotometric and electroanalytical methods for ascorbic acid and acetaminophen and their applications in the analysis of effervescent dosage forms. J Pharm Biomed. 2000;23:77–87.
Bayraktepe DE, Yazan Z. Application of single-use electrode based on nano-clay and MWCNT for simultaneous determination of acetaminophen, ascorbic acid and acetylsalicylic acid in pharmaceutical dosage. Electroanal. 2020;32:1263–72.
Dalkıran B, Erden PE, Kaçar C, Kılıç E. Disposable amperometric biosensor based on poly-L-lysine and Fe3O4 NPS-chitosan composite for the detection of tyramine in cheese. Electroanal. 2019;31:1324–33.
Alipour E, Majidi MR, Saadatirad A, Golabi SM. Determination of uric acid in biological samples on the pretreated pencil graphite electrode. Anal Methods. 2012;4:2288–95.
Prathish KP, Carvalho R, Brett CMA. Electrochemical characterisation of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) film modified glassy carbon electrodes prepared in deep eutectic solvents for simultaneous sensing of biomarkers. Electrochim Acta. 2016;187:704–13.
Dalkıran B, Fernandes IPG, David M, Brett CMA. Electrochemical synthesis and characterization of poly(thionine)-deep eutectic solvent/carbon nanotube modified electrodes and application to electrochemical sensing. Microchim Acta. 2020;187:609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04588-x.
Xu Y, Zhang X, Wang Y, He P, Fang Y. Enhancement of electrochemical capacitance of carbon nanotubes by polythionine modification. Chinese J Chem. 2010;28:417–21.
Karyakin AA, Karyakina EE, Schmidt HL. Electropolymerized azines: a new group of electroactive polymers. Electroanal. 1999;11:149–55.
Liu T, Luo Y, Wang W, Kong L, Zhu J, Tan L. Non-enzymatic detection of hydrogen peroxide based on Fenton-type reaction on poly (azure A)-chitosan/Cu modified electrode. Electrochim Acta. 2015;182:742–50.
Pandey I, Bairagi PK, Verma N. Electrochemically grown polymethylene blue nanofilm on copper-carbon nanofiber nanocomposite: an electrochemical sensor for creatinine. Sensor Actuat B-Chem. 2018;277:562–70.
Yin Z, Wu J, Yang Z. A sensitive mercury (II) sensor based on CuO nanoshuttles/poly (thionine) modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchim Acta. 2010;170(3–4):307–12.
Reddy GRK, Kumar PS. Template electrodeposition of high-performance copper oxide nanosensors for electrochemical analysis of hydrogen peroxide. Mat Sci Eng C-Mat. 2017;75:1480–8.
Li B, Zhou Y, Wu W, Liu M, Mei S, Zhou Y, et al. Highly selective and sensitive determination of dopamine by the novel molecularly imprinted poly (nicotinamide)/CuO nanoparticles modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;67:121–8.
Ghica ME, Brett CMA. Poly(brilliant green) and poly(thionine) modified carbon nanotube coated carbon film electrodes for glucose and uric acid biosensors. Talanta. 2014;130:198–206.
Dalkiran B, Kacar C, Erden PE, Kilic E. Amperometric xanthine biosensors based on chitosan-Co3O4-multiwall carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrode. Sensor Actuat B-Chem. 2014;200:83–91.
Yang R, Ruan C, Dai W, Deng J, Kong J. Electropolymerisation of thionine in neutral aqueous media and H2O2 biosensor based on poly(thionine). Electrochim Acta. 1999;44:1585–96.
Brett CMA, Oliveira Brett AM. Electrochemistry: principles, methods, and applications. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1993.
Ghica ME, Ferreira GM, Brett CMA. Poly(thionine)-carbon nanotube modified carbon film electrodes and application to the simultaneous determination of acetaminophen and dipyrone. J Solid State Electrochem. 2015;19:2869–81.
Yang M, Guo ML, Feng YL, Lei YM, Cao YJ, Zhu DB, Yu Y, Ding L. Sensitive voltammetric detection of metronidazole based on three-dimensional graphene-like carbon architecture/polythionine modified glassy carbon electrode. J Electrochem Soc 2018;165:B:530-B535.
Zhang H, Han J, Yang B. Structural fabrication and functional modulation of nanoparticle–polymer composites. Adv Funct Mater. 2010;20:1533–50.
Feng H, Wang H, Zhang Y, Yan B, Shen G, Yu R. A direct electrochemical biosensing platform constructed by incorporating carbon nanotubes and gold nanoparticles onto redox poly(thionine) film. Anal Sci. 2007;23:235–9.
Chitravathi S, Munichandraiah N. Voltammetric determination of paracetamol, tramadol and caffeine using poly(Nile blue) modified glassy carbon electrode. J Electroanal Chem. 2016;764:93–103.
Serra B, Morales MD, Reviejo AJ, Hall EH, **arron JM. Rapid and highly sensitive electrochemical determination of alkaline phosphatase using a composite tyrosinase biosensor. Anal Biochem. 2015;336(2):289–94.
Habibi B, Jahanbakhshi M. Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, paracetamol and phenylephrine: carbon nanotubes ceramic electrode as a renewable electrode. Anal Bioanal Electrochem. 2015;7:45–58.
Rajabi H, Noroozifar M, Khorasani-Motlagh M. Graphite paste electrode modified with Lewatit® FO36 nano-resin for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, acetaminophen and tryptophan. Anal Methods. 2016;8:1924–34.
Kemmegne-Mbouguen JC, Ngameni E. Simultaneous quantification of dopamine, acetaminophen and tyrosine at carbon paste electrodes modified with porphyrin and clay. Anal Methods. 2017;9:4157–66.
Yang L, Huang N, Lu Q, Liu M, Li H, Zhang Y, et al. A quadruplet electrochemical platform for ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and acetaminophen based on a ferrocene derivative functional Au NPs/carbon dots nanocomposite and graphene. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;903:69–80.
Anupam Kumar M, Lakshminarayanan V, Ramamurthy SS. Platinum nanoparticles decorated graphene-modified glassy carbon electrode toward the electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and paracetamol. C R Chim. 2019;22:58–72.
Ejaz A, Jeon S. A highly stable and sensitive GO-XDA-Mn2O3 electrochemical sensor for simultaneous electrooxidation of paracetamol and ascorbic acid. Electrochim Acta. 2017;245:742–51.
Phong NH, Toan TTT, Tinh MX, Tuyen TN, Mau TX, Khieu DQ. Simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, paracetamol, and caffeine using electrochemically reduced graphene-oxide-modified electrode. J Nanomater. 2018;5348016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5348016.
Li C, Xu J, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Lei W, et al. g-C3N4 nanofibers doped poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) modified electrode for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid and acetaminophen. J Electroanal Chem. 2018;824:52–9.
Iranmanesh T, Foroughi MM, Jahani S, Zandi MS, Nadiki HH. Green and facile microwave solvent-free synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticle-decorated CNTs as a quadruplet electrochemical platform for ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and acetaminophen. Talanta. 2020;207:120318.
Ghanbari K, Bonyadi S. An electrochemical sensor based on reduced graphene oxide decorated with polypyrrole nanofibers and zinc oxide–copper oxide p–n junction heterostructures for the simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, paracetamol, and tryptophan. New J Chem. 2018;42(11):8512–23.
Taei M, Salavati H, Hasanpour F, Habibollahi S, Baghlani H. Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, acetaminophen and codeine based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified with magnetic nanoparticles paste electrode. Mat Sci Eng C-Mat. 2016;69:1–11.
Thu PTK, Trinh ND, Hoan NTV, Du DX, Mau TX, Trung VH, et al. Synthesis of cobalt ferrite and simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, acetaminophen and caffeine by voltammetric method using cobalt ferrite modified electrode. J Mater Sci Mater. 2019;30:17245–61.
Funding
B. Dalkiran thankfully acknowledges the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK 2219) for a postdoctoral fellowship. The authors thank Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), Portugal, project PTDC/QEQ-QAN/2201/2014, in the framework of Project 3599-PPCDT, co-financed by the European Community Fund FEDER, and CEMMPRE, project UIDB/EMS/00285/2020 by FEDER funds through the program COMPETE – Programa Operacional Factores de Competitividade, and by national funds through FCT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(PDF 134 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalkiran, B., Brett, C.M.A. A novel nanostructured poly(thionine)-deep eutectic solvent/CuO nanoparticle film-modified disposable pencil graphite electrode for determination of acetaminophen in the presence of ascorbic acid. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 1149–1157 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-03078-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-03078-6