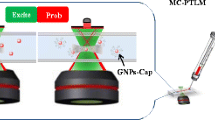
Abstract
A new approach employing a microchip in combination with photothermal lens microscopy has been described for a DNA hybridization assay using gold nanoparticles. The difference in adsorption propensities of single- and double-stranded DNAs on gold nanoparticles was used for a highly sensitive DNA hybridization assay through a photothermal lens effect in a femtoliter scale of detection volume. Under the optimized conditions, the results showed that the variation of photothermal lens signal in the focal volume of 105 fL (10−15 L) was linearly proportional to the target DNA concentration over the range of 50–500 nM with detection limits of 30.7 nM and 27.3 nM for target DNA I and II, respectively. The lowest amount of target DNA that was measured using gold nanoparticles was 2.6 zepto mole. The assay was completed within 5 min and the relative standard deviations (n = 8) for both target DNAs were about 2.34%. The hybridization process was proved by two different common methods including gel electrophoresis and in situ fluorescence monitoring of DNA hybridization. The performance of this detection method was investigated in diluted human serum sample as a complex sample. The recovery values were between 98 and 104.9%.

Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wan Y, Xu L, Zhuo N, Lu X. A novel DNA sensor based on C60NPs-PAMAM-PtPNPs to detect VKORC1 gene for guiding rational clinical therapy with warfarin. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1009:39–47.
Chen X, Roozbahani G M, Ye Z, Zhang Y, Ma R, **ang J, et al. Label-free detection of DNA mutations by nanopore analysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(14):11519–28.
Ho NRY, Lim GS, Sundah NR, Lim D, Loh TP, Shao H. Visual and modular detection of pathogen nucleic acids with enzyme–DNA molecular complexes. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):3238. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05733-0.
Borghei Y-S, Hosseini M, Dadmehr M, Hosseinkhani S, Ganjali MR, Sheikhnejad R. Visual detection of cancer cells by colorimetric aptasensor based on aggregation of gold nanoparticles induced by DNA hybridization. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;904:92–7.
Saikrishnan D, Goyal M, Rossiter S, Kukol A. A cellulose-based bioassay for the colorimetric detection of pathogen DNA. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014;406(30):7887–98.
Zhang Y, Ning X, Mao G, Ji X, He Z. Fluorescence turn-on detection of target sequence DNA based on silicon nanodot-mediated quenching. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(13):3209–16.
Zhao X, Tapec-Dytioco R, Tan W. Ultrasensitive DNA detection using highly fluorescent bioconjugated nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125(38):11474–5.
El-Yazbi AF, Wong A, Loppnow GR. A luminescent probe of mismatched DNA hybridization: location and number of mismatches. Anal Chim Acta. 2017;994:92–9.
Silvestrini M, Ugo P. Ensembles of nanoelectrodes modified with gold nanoparticles: characterization and application to DNA-hybridization detection. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013;405(2–3):995–1005.
Shamsipur M, Memari Z, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P, Faridbod F. Highly sensitive gold nanoparticles-based optical sensing of DNA hybridization using bis (8-hydroxyquinoline-5-solphonate) cerium (III) chloride as a novel fluorescence probe. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016;118:356–62.
Li Z-P, Liu C-H, Fan Y-S, Duan X-R. Chemiluminescent detection of DNA hybridization using gold nanoparticles as labels. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;387(2):613–8.
Campuzano S, Yáñez-Sedeño P, **arrón JM. Nanoparticles for nucleic-acid-based biosensing: opportunities, challenges, and prospects. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019: 411(9):1791-806.
Dreaden EC, Alkilany AM, Huang X, Murphy CJ, El-Sayed MA. The golden age: gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41(7):2740–79.
Saha K, Agasti SS, Kim C, Li X, Rotello VM. Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem Rev. 2012;112(5):2739–79.
Huang C-C, Chen C-T, Shiang Y-C, Lin Z-H, Chang H-T. Synthesis of fluorescent carbohydrate-protected Au nanodots for detection of Concanavalin A and Escherichia coli. Anal Chem. 2009;81(3):875–82.
Gao Z, Qiu Z, Lu M, Shu J, Tang D. Hybridization chain reaction-based colorimetric aptasensor of adenosine 5′-triphosphate on unmodified gold nanoparticles and two label-free hairpin probes. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;89:1006–12.
Fong KE, L-YL Y. Localized surface plasmon resonance: a unique property of plasmonic nanoparticles for nucleic acid detection. Nanoscale. 2013;5(24):12043–71.
**a F, Zuo X, Yang R, **ao Y, Kang D, Vallée-Bélisle A, et al. Colorimetric detection of DNA, small molecules, proteins, and ions using unmodified gold nanoparticles and conjugated polyelectrolytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(24):10837–41.
Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL, Mucic RC, Storhoff JJ. A DNA-based method for rationally assembling nanoparticles into macroscopic materials. Nature. 1996;382(6592):607.
Sato K, Hosokawa K, Maeda M. Rapid aggregation of gold nanoparticles induced by non-cross-linking DNA hybridization. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125(27):8102–3.
Li H, Rothberg L. Colorimetric detection of DNA sequences based on electrostatic interactions with unmodified gold nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(39):14036–9.
Watson JD. The double helix: a personal account of the discovery of the structure of DNA. New York: Atheneum; 1968.
Liu P, Yang X, Sun S, Wang Q, Wang K, Huang J, et al. Enzyme-free colorimetric detection of DNA by using gold nanoparticles and hybridization chain reaction amplification. Anal Chem. 2013;85(16):7689–95.
Quinten M, Kreibig U. Optical properties of aggregates of small metal particles. Surf Sci. 1986;172(3):557–77.
Li PC. Microfluidic lab-on-a-chip for chemical and biological analysis and discovery. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2005.
Gösch M, Blom H, Holm J, Heino T, Rigler R. Hydrodynamic flow profiling in microchannel structures by single molecule fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2000;72(14):3260–5.
Shokoufi N, Madarshahian S. Thermal lens spectrometry: techniques and instrumentation. Saarbrücken: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing; 2012.
Bialkowski S. Photothermal spectroscopy methods for chemical analysis. Hoboken: Wiley; 1996.
Lv S, Zhang K, Tang D. New visual immunoassay for prostate-specific antigen using near-infrared exciting CuxS nanocrystals and imaging on smartphone. Analyst. 2019;144(12):3716–20.
Liu M. A flexible thermal lens microscope for highly sensitive detection in microfluidic chips. Laser Phys Lett. 2017;14(8):085701.
Satoa K, Kitamorib T. Integration of an immunoassay system into a microchip for high-throughput assay. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2004;4(6):575–9.
Radovanović T, Liu M, Likar P, Klemenc M, Franko M. Microfluidic flow injection analysis with thermal lens microscopic detection for determination of NGAL. Int J Thermophys. 2015;36(5–6):932–9.
Yamaoka S, Kataoka Y, Kazama Y, Fujii Y, Hibara A. Efficient thermal lens nanoparticle detection in a flow-focusing microfluidic device. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016;228:581–6.
Shokoufi N, Asbaghi BAN, Hajibaba SN. Sensitive determination of DNA based on phosphate-dye interaction using photothermal lens technique. Appl Opt. 2019;58(12):3074–82.
Cedeño E, Cabrera H, Delgadillo-López A, Delgado-Vasallo O, Mansanares A, Calderón A, et al. High sensitivity thermal lens microscopy: Cr-VI trace detection in water. Talanta. 2017;170:260–5.
Kitamori T, Tokeshi M, Hibara A, Sato K. Peer reviewed: thermal lens microscopy and microchip chemistry. Washington, DC: ACS Publications; 2004.
Liu M, Malovrh S, Franko M. Microfluidic flow-injection thermal-lens microscopy for high-throughput and sensitive analysis of sub-μL samples. Anal Methods. 2016;8(25):5053–60.
Abbasi-Ahd A, Shokoufi N, Kargosha K. Headspace single-drop microextraction coupled to microchip-photothermal lens microscopy for highly sensitive determination of captopril in human serum and pharmaceuticals. Microchim Acta. 2017;184(7):2403–9.
Burgos E, Thompson C, Giordano M, Thomas MA. Pre-breeding studies in Panicum coloratum var. coloratum: characterization using agro-morphological traits and molecular markers. Trop Grassl-Forrajes Trop. 2018;6(2):82–92.
Zhang F, Zeng L, Zhang Y, Wang H, Wu A. A colorimetric assay method for Co 2+ based on thioglycolic acid functionalized hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide modified Au nanoparticles (NPs). Nanoscale. 2011;3(5):2150–4.
Shokoufi N, Abbasi-Ahd A, Kargosha K. Laser induced thermal lens microscopy for highly sensitive determination of captopril. Appl Opt. 2017;56(11):E58–63.
Henry CS. Microchip capillary electrophoresis: methods and protocols. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media; 2006.
Abbasi-Ahd A, Shokoufi N, Adeleh S, Kargosha K. Femtoliter scale detection of an antithyroid drug using gold nanoparticles in a microfluidic chip. J Braz Chem Soc. 2017;28(10):1843–9.
Abbasi-Ahd A, Shokoufi N, Kargosha K. Molecular counting of captopril by a microfluidic chip-thermal lens microscopy system. Curr Anal Chem. 2017;13(6):508–14.
Tokeshi M, Yamaguchi J, Hattori A, Kitamori T. Thermal lens micro optical systems. Anal Chem. 2005;77(2):626–30.
Tamaki E, Hibara A, Tokeshi M, Kitamori T. Microchannel-assisted thermal-lens spectrometry for microchip analysis. J Chromatogr A. 2003;987(1–2):197–204.
Smirnova A, Proskurnin MA, Mawatari K, Kitamori T. Desktop near-field thermal-lens microscope for thermo-optical detection in microfluidics. Electrophoresis. 2012;33(17):2748–51.
Liu M, Novak U, Plazl I, Franko M. Optimization of a thermal lens microscope for detection in a microfluidic chip. Int J Thermophys. 2014;35(11):2011–22.
Kikutani Y, Mawatari K, Katayama K, Tokeshi M, Fukuzawa T, Kitaoka M, et al. Flowing thermal lens micro-flow velocimeter. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2008;133(1):91–6.
Tokeshi M, Uchida M, Uchiyama K, Sawada T, Kitamori T. Single-and countable-molecule detection of non-fluorescent molecules in liquid phase. J Lumin. 1999;83:261–4.
Shokoufi N, Abbasi-Ahd A, Madarshahian S. Online monitoring of gold nanoparticles and induced aggregation by photothermal lens microscopy. Instrum Sci Technol. 2018;46(1):93–101.
Zeng Y, Zhang D, Qi P, Zheng L. Colorimetric detection of DNA by using target catalyzed DNA nanostructure assembly and unmodified gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta. 2017;184(12):4809–15.
Zhou W, Ren J, Zhu J, Zhou Z, Dong S. Accurate and visual discrimination of single-base mismatch by utilization of binary DNA probes in gold nanoparticles-based biosensing strategy. Talanta. 2016;161:528–34.
Nourisaeid E, Mousavi A, Arpanaei A. Colorimetric DNA detection of transgenic plants using gold nanoparticles functionalized with L-shaped DNA probes. Physica E Low Dimens Syst Nanostruct. 2016;75:188–95.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the support from the Research Council of Chemistry & Chemical Engineering Research Center of Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 155 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shokoufi, N., Abbasgholi Nejad Asbaghi, B. & Abbasi-Ahd, A. Microfluidic chip-photothermal lens microscopy for DNA hybridization assay using gold nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 6119–6128 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01999-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01999-5