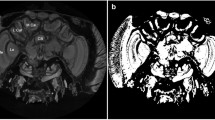
Abstract
The investigation of the internal morphology of insects is usually performed using classical microtomy yielding optical micrographs of stained thin sections. The achievement of high-quality cross sections for microtomy is time-consuming and the risk of damaging sections is unavoidable. Moreover, the approach is impractical, in particular when quick acquisition of 3D structural information is required. Recently, X-ray computed microtomography (micro-CT) with a high spatial resolution was considered as a potential tool for the morphological classification of insects. We used micro-CT to investigate Quedius beesoni Cameron at the cellular length scale. This method provides a new powerful and nondestructive approach to obtain 3D structural information on the biological organization of insects. The preliminary images presented in this contribution clearly reveal the endoskeleton and the muscles of the head and the thorax with a full 3D structure. We also reconstructed the 3D structure of the brain of Quedius beesoni Cameron, and this is the first reconstruction in Staphylinidae, which will be a great advancement for morphological and phylogenic research. We claim that both the spatial resolution and the contrast characteristic of micro-CT imaging may fulfill the requirements necessary for zoological insect morphology and phylogeny, in particular, when a classification of a rare and unique insect specimen is required.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hounsfield G (1973) Br J Radiol 46:1016
Peyrina F, Salomea M, Cloetensb P et al (1998) Technol Health Care 6:391–401
Holdsworth D, Thornton M (2002) Trends Biotechnol 20:34–39
Betz O, Thayer M, Newton A (2003) Acta Zool 84:179–238
Jorgensen S, Demirkaya O, Ritman E (1998) Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 275:H1103
Herman L (2001) Catalog of the Staphylinidae (Insecta: Coleoptera): 1758 to the end of the second millennium. American Museum of Natural History, New York
Blackwelder R (1936) Smithson Misc Collect 94:1–102
Naomi S (1987) Jpn J Entomol 55:450–458
Naomi S (1989) Jpn J Entomol 57:82–90
Betz O (1996) Zoomorphology 116:15–34
Kölsch G, Betz O (1998) Zoomorphology 118:263–272
Gorb S, Beutel R (2000) J Morphol 244:1–14
Hörnschemeyer T, Beutel R, Pasop F (2002) J Morphol 252:298–314
Beutel R, Ge S, Hörnschemeyer T (2008) Cladistics 24:270–298
Weide D, Betz O (2009) J Morphol 270:1503–1523
Zhu PP, Wang JY, Yuan QX et al (2005) Appl Phys Lett 87:264101–264103
Wang J, Zhu P, Yuan Q et al (2006) Phys Med Biol 51:3391–3396
Chapman D, Thomlinson W, Johnston R et al (1997) Phys Med Biol 42:2015–2026
Momose A (2002) J Synchrotron Radiat 9:136–142
Wilkins S, Gureyev T, Gao D et al (1996) Nature 384:335–338
Davis T, Gao D, Gureyev T et al (1995) Nature 373:595–598
Gureyev TE, Mayo S, Wilkins SW et al (2001) Phys Rev Lett 86:5827
Chao W, Harteneck B, Liddle J et al (2005) Nature 435:1210–1213
Wieland M, Wilhein T, Spielmann C et al (2003) Appl Phys B Lasers Opt 76:885–889
Cloetens P, Barrett R, Baruchel J et al (1996) J Phys D Appl Phys 29:133–146
Lewis R (1997) Phys Med Biol 42:1213–1243
Kron T (1998) Phys Med Biol 43:215–216
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the National Outstanding Youth Fund (project no. 10125523 to Z.W.), the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KJCX2-YW-N42), the Key Important Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (10734070), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 10774144 and 10979055), and the National Basic Research Program of China (2009CB930804).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Li, De., Zhu, P. et al. 3D visualization of the microstructure of Quedius beesoni Cameron using micro-CT. Anal Bioanal Chem 397, 2143–2148 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3696-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3696-6