Abstract
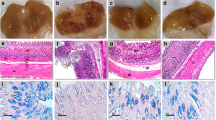
Gastric ulcer disease is associated with significant morbidity and mortality rates. The most two common causes of the ulcer are Helicobacter pylori infection and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In the past few decades, a significant decrease in the morbidity and mortality rate has been observed probably due to the discovery of proton pump inhibitors. However, the medications used to treat gastric ulcers impose several nauseous side effects. Therefore, recent studies focus on the use of natural products to treat gastric ulcers. In the current study, gastric ulcer was effectively induced using indomethacin, and the protective effect of apigenin, a potent antioxidant flavonoid, was assessed in comparison to omeprazole. The administration of a single oral indomethacin (50 mg/kg) induced gastric ulcer as manifested by hemorrhagic lesions in the gastric mucosa, increased ulcer index, and histopathological alterations. Indomethacin also increased lipid peroxidation, decreased the activities of the antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, increased the immunoreactivity of the inflammatory markers cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), increased the transcription of the apoptotic marker, Bax, and decreased that of the antiapoptotic Bcl-2. Indomethacin also decreased the immunoreactivity of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1). On the other hand, pretreatment with apigenin (10 and 20 mg/kg) resulted in a dose-dependent improvement in the macroscopic and microscopic features of the gastric mucosa in a manner comparable to that of omeprazole. The gastroprotective effects of apigenin may be attributed to its anti-inflammatory, anti-antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic activities as well as enhancing the expression of TGF-β1. Further experimental and clinical research is required to confirm activity of apigenin as anti-ulcer agent.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Adriana M, Şoimiţa S, Daniela-Rodica M, Camelia A, Doiniţa C, Doina D (2008) Oxidative stress implications in experimental gastric ulcer induced by indomethacin. Bulletin of the University of Agricultural Sciences & Veterinary Medicine Cluj-Napoca. Veterinary Medicine 65(1)
AlKreathy HM, Alghamdi MK, Esmat A (2020) Tetramethylpyrazine ameliorates indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in rats: impact on oxidative, inflammatory, and angiogenic machineries. Saudi Pharm J 28:916–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2020.06.012
Bajaj G, Sharma RK (2006) TNF-alpha-mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis involves caspase-12 and calpain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345:1558–1564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.05.059
Bampidis V, Azimonti G, Bastos MD, Christensen H, Dusemund B, Kos Durjava M, Kouba M, López‐Alonso M, López Puente S, Marcon F (2020) Safety and efficacy of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for all animal species. EFSA Journal 18(7):e06211
Bancroft JD, Gamble M (2008) Theory and practice of histological techniques. Elsevier health sciences
Bhala N, Emberson J, Merhi A et al (2013) Vascular and upper gastrointestinal effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: meta-analyses of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet (London England) 382:769–779
Clark DA, Coker R (1998) Molecules in focus transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β). Int J Biochem Cell Biol 30:293–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1357-2725(97)00128-3
Ding SZ, Lam SK, Yuen ST et al (1998) Prostaglandin, tumor necrosis factor alpha and neutrophils: causative relationship in indomethacin-induced stomach injuries. Eur J Pharmacol 348:257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-2999(98)00162-9
Ernst H, Konturek PC, Brzozowski T et al (1996) Subserosal application of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in rats with chronic gastric ulcers: effect on gastric ulcer healing and blood flow. J Physiol Pharmacol 47:443–454
Falcone Ferreyra ML, Rius SP, Casati P (2012) Flavonoids: biosynthesis, biological functions, and biotechnological applications. Front Plant Sci 3:222. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2012.00222
Freston JW (1988) The pathophysiological and pharmacological basis of peptic ulcer therapy. Toxicol Pathol 16:260–266. https://doi.org/10.1177/019262338801600219
Guo G, Ott C-E, Grünhagen J et al (2013) Indomethacin prevents the progression of thoracic aortic aneurysm in Marfan Syndrome mice. Aorta (Stamford) 1:5–12. https://doi.org/10.12945/j.aorta.2013.13.007
Hockenbery DM (1995) bcl-2, a novel reguator of cell death. BioEssays 17:631–638. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.950170709
Hostetler GL, Ralston RA, Schwartz SJ (2017) Flavones: food sources, bioavailability, metabolism, and Bioactivity. Adv Nutr 8:423–435. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.116.012948
Hsu H, Shu HB, Pan MG, Goeddel DV (1996) TRADD-TRAF2 and TRADD-FADD interactions define two distinct TNF receptor 1 signal transduction pathways. Cell 84:299–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80984-8
Ibrahim R, Allam M, El-Gohary O et al (2018) Protective effect of obestatin on indomethacin-induced acute gastric ulcer in rats: role of VEGF and TNF-α. Benha Med J 35:369
Jaeschke H (2011) Reactive oxygen and mechanisms of inflammatory liver injury: present concepts. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26 Suppl 1173–179. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06592.x
Johnson AC, Greenwood-Van Meerveld B (2017) Critical evaluation of Animal models of Gastrointestinal disorders. Handb Exp Pharmacol 239:289–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/164_2016_120
Karamese M, Erol HS, Albayrak M et al (2016) Anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of apigenin in a rat model of sepsis: an immunological, biochemical, and histopathological study. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 38:228–237. https://doi.org/10.3109/08923973.2016.1173058
Kavitt RT, Lipowska AM, Anyane-Yeboa A, Gralnek IM (2019) Diagnosis and treatment of peptic Ulcer Disease. Am J Med 132:447–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.12.009
Kim YJ, Kim E-H, Hahm KB (2012) Oxidative stress in inflammation-based gastrointestinal tract diseases: challenges and opportunities. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27:1004–1010. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07108.x
Korsmeyer SJ, Yin XM, Oltvai ZN et al (1995) Reactive oxygen species and the regulation of cell death by the Bcl-2 gene family. Biochim Biophys Acta 1271:63–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-4439(95)00011-r
Lambert AA, Lam JO, Paik JJ et al (2015) Risk of community-acquired pneumonia with outpatient proton-pump inhibitor therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 10:e0128004. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128004
Lempinen M, Inkinen K, Wolff H, Ahonen J (2002) Connective tissue growth factor in indomethacin-induced rat gastric ulcer. Eur Surg Res 34:232–238. https://doi.org/10.1159/000063394
Lopez-Jornet P, Camacho-Alonso F, Gómez-Garcia F et al (2014) Effects of potassium apigenin and verbena extract on the wound healing process of SKH-1 mouse skin. Int Wound J 11:489–495. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-481X.2012.01114.x
Maity P, Bindu S, Dey S et al (2009) Melatonin reduces indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal cell apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial oxidative stress and the activation of mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. J Pineal Res 46:314–323. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00663.x
Malfertheiner P, Chan FKL, McColl KEL (2009) Peptic ulcer disease. Lancet 374:1449–1461. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60938-7
Matsui H, Shimokawa O, Kaneko T et al (2011) The pathophysiology of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)-induced mucosal injuries in stomach and small intestine. J Clin Biochem Nutr 48:107–111. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.10-79
Myoken Y, Kan M, Sato GH et al (1990) Bifunctional effects of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) on endothelial cell growth correlate with phenotypes of TGF-beta binding sites. Exp Cell Res 191:299–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4827(90)90018-6
Neamatallah T (2024) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester attenuates indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 397:1791–1801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02730-z
O’Neill LA, Kaltschmidt C (1997) NF-kappa B: a crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function. Trends Neurosci 20:252–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-2236(96)01035-1
Park JA, Ha SK, Kang TH et al (2008) Protective effect of apigenin on ovariectomy-induced bone loss in rats. Life Sci 82:1217–1223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2008.03.021
Prayoga DK, Aulifa DL, Budiman A, Levita J (2024) Plants with anti-ulcer activity and mechanism: a review of preclinical and clinical studies. Drug Des Devel Ther 18:193–213. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S446949
Rašković A, Gigov S, Čapo I et al (2017) Antioxidative and protective actions of apigenin in a Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity Rat Model. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 42:849–856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-017-0407-0
Singh JPV, Selvendiran K, Banu SM et al (2004) Protective role of apigenin on the status of lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense against hepatocarcinogenesis in Wistar albino rats. Phytomedicine 11:309–314. https://doi.org/10.1078/0944711041495254
Suleyman H, Albayrak A, Bilici M et al (2010) Different mechanisms in formation and prevention of indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers. Inflammation 33:224–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-009-9176-5
Sverdén E, Agréus L, Dunn JM, Lagergren J (2019) Peptic ulcer disease. BMJ 367:l5495. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l5495
Takeda Y, Watanabe H, Yonehara S et al (1993) Rapid acceleration of neutrophil apoptosis by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Int Immunol 5:691–694. https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/5.6.691
Tandon R, Khanna HD, Dorababu M, Goel RK (2004) Oxidative stress and antioxidants status in peptic ulcer and gastric carcinoma. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 48:115–118
Uc A, Zhu X, Wagner BA et al (2012) Heme oxygenase-1 is protective against nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastric ulcers. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 54:471–476. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0b013e3182334fdf
Verrecchia F, Chu ML, Mauviel A (2001) Identification of novel TGF-beta /Smad gene targets in dermal fibroblasts using a combined cDNA microarray/promoter transactivation approach. J Biol Chem 276:17058–17062. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M100754200
Wang J, Liu Y-T, **ao L et al (2014) Anti-inflammatory effects of apigenin in lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory in acute lung injury by suppressing COX-2 and NF-kB pathway. Inflammation 37:2085–2090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9942-x
Wiseman H, Halliwell B (1996) Damage to DNA by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: role in inflammatory disease and progression to cancer. Biochem J 313(Pt 1):17–29. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3130017
Yadav RK, Mehan S, Sahu R et al (2022) Protective effects of apigenin on methylmercury-induced behavioral/neurochemical abnormalities and neurotoxicity in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 41:9603271221084276. https://doi.org/10.1177/09603271221084276
Yoshikawa T, Naito Y (2000) The role of neutrophils and inflammation in gastric mucosal injury. Free Radic Res 33:785–794. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715760000301301
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M et al (1995) Sequential reduction of mitochondrial transmembrane potential and generation of reactive oxygen species in early programmed cell death. J Exp Med 182:367–377. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.182.2.367
Zare MFR, Rakhshan K, Aboutaleb N et al (2019) Apigenin attenuates doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity via reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis in male rats. Life Sci 232:116623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116623
Zhang B-B, Li Y, Liu X-Q et al (2014a) Association between vacA genotypes and the risk of duodenal ulcer: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 41:7241–7254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3610-y
Zhang F, Li F, Chen G (2014b) Neuroprotective effect of apigenin in rats after contusive spinal cord injury. Neurol Sci 35:583–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1566-7
Zhang Y, Wang J, Cheng X et al (2015) Apigenin induces dermal collagen synthesis via smad2/3 signaling pathway. Eur J Histochem 59:2467. https://doi.org/10.4081/ejh.2015.2467
Acknowledgements
Special thanks and great appreciation to Prof. Ashraf Abdel-Naim and Dr. Gamal Abd El-Aziz, King Abdulaziz University, for their assistance in the animal handling procedures and histopathological studies.
Funding
No specific fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zaenah Zuhair Alamri is a single author. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• In this study, indomethacin was used to induce gastric ulcers in rats.
• Apigenin protected against macroscopic and gastric microscopic pathological changes.
• Apigenin showed anti-inflammatory, anti-antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic activities.
• Apigenin enhanced the expression of TGF-β1.
• Apigenin possesses a promising potential as an anti-ulcer agent.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alamri, Z.Z. Apigenin attenuates indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in rats: emphasis on antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and TGF-β1 enhancing activities. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-03200-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-03200-w