Abstract
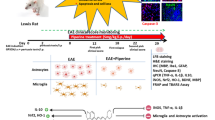
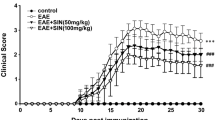
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an immune-mediated chronic inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system (CNS). The aim of the current study was to investigate the effects of magnolol in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of MS in female mice. Magnolol (0.1, 1, and 10 mg/kg) was administered once daily for 21 days after immunization of mice. Magnolol post-immunization treatment significantly reversed clinical scoring, EAE-associated pain parameters, and motor dysfunction in a dose-dependent manner. Magnolol treatment significantly inhibited oxidative stress by reducing malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO) production, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity while enhancing the level of antioxidants such as reduced glutathione (GSH), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), catalase, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the brain and spinal cord. It reduced cytokine levels in the brain and spinal cord. It suppressed CD8+ T cells frequency in the spleen tissue. Magnolol remarkably reversed the EAE-associated histopathology of the brain and spinal cord tissue. Magnolol significantly intensifies the antioxidant defense system by enhancing the expression level of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2) while decreasing the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cleaved-caspase-3 in the brain. Molecular docking results showed that magnolol possesses a better binding affinity for Nrf2, iNOS, and caspase-3 proteins. Taken together, the present study demonstrated that magnolol has significant neuroprotective properties in EAE via inhibition of oxidative stress.














Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 September 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02732-x
References
Ali H, Khan A, Ali J, Ullah H, Khan A, Ali H, Irshad N, Khan SJBP, Toxicology (2020) Attenuation of LPS-induced acute lung injury by continentalic acid in rodents through inhibition of inflammatory mediators correlates with increased Nrf2 protein expression. 21: 1-14
Ali J, Khan AU, Shah FA, Ali H, Islam SU, Kim YS, Khan S (2019) Mucoprotective effects of Saikosaponin-A in 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice model. Life Sciences 239:116888
Arruda LF, Arruda SF, Campos NA, de Valencia FF, de Almeida Siqueira EM (2013) Dietary iron concentration may influence aging process by altering oxidative stress in tissues of adult rats. PloS one 8:e61058
Atiq A, Shal B, Naveed M, Khan A, Ali J, Zeeshan S, Al-Sharari SD, Kim YS, Khan S (2019) Diadzein ameliorates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators in rodents. Eur J Pharmacol 843:292–306
Chen C, Tan R, Qu W, Wu Z, Wang Y, Urade Y, Huang Z (2011) Magnolol, a major bioactive constituent of the bark of Magnolia officinalis, exerts antiepileptic effects via the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor complex in mice. British J Pharmacol 164:1534–1546
Chen H-Y, Hung Y-C, Lee E-J, Chen T-Y, Chuang I-C, Wu T-S (2009) The protective efficacy of magnolol in hind limb ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Phytomedicine 16:976–981
Ciftci O, Ozcan C, Kamisli O, Cetin A, Basak N, Aytac B (2015) Hesperidin, a citrus flavonoid, has the ameliorative effects against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in a C57BL/J6 mouse model. Neurochem Res 40:1111–1120
Das I, Saha K, Mukhopadhyay D, Roy S, Raychaudhuri G, Chatterjee M, Mitra PKJJons, biology, medicine (2014) Impact of iron deficiency anemia on cell-mediated and humoral immunity in children: a case control study. 5: 158
DiSano KD, Linzey MR, Royce DB, Pachner AR, Gilli F (2019) Differential neuro-immune patterns in two clinically relevant murine models of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroinflam 16:1–15
Errede M, Girolamo F, Ferrara G, Strippoli M, Morando S, Boldrin V, Rizzi M, Uccelli A, Perris R, Bendotti C (2012) Blood-brain barrier alterations in the cerebral cortex in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 71:840–854
Gharagozloo M, Gris KV, Mahvelati T, Amrani A, Lukens JR, Gris D (2018) NLR-dependent regulation of inflammation in multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol 8:2012
Gilgun-Sherki Y, Melamed E, Offen D (2004) The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis: the need for effective antioxidant therapy. J Neurol 251:261–268
Gold R, Linington C, Lassmann H (2006) Understanding pathogenesis and therapy of multiple sclerosis via animal models: 70 years of merits and culprits in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis research. Brain 129:1953–1971
Hammer LA, Zagon IS, McLaughlin PJJBRB (2013) Treatment of a relapse-remitting model of multiple sclerosis with opioid growth factor. 98: 122-131
Hao J, Liu R, Turner G, Shi F-D, Rho JM (2012) Inflammation-mediated memory dysfunction and effects of a ketogenic diet in a murine model of multiple sclerosis. PloS one 7:e35476
Harbo HF, Gold R, Tintoré M (2013) Sex and gender issues in multiple sclerosis. J Ther Adv Neurol Disorders 6:237–248
Hill KE, Zollinger LV, Watt HE, Carlson NG, Rose JW (2004) Inducible nitric oxide synthase in chronic active multiple sclerosis plaques: distribution, cellular expression and association with myelin damage. J Neuroimmunol 151:171–179
Hoi CP, Ho YP, Baum L, Chow AH (2010) Neuroprotective effect of honokiol and magnolol, compounds from Magnolia officinalis, on beta-amyloid-induced toxicity in PC12 cells. Phytother Res 24:1538–1542
Jackson S, Pryce G, Diemel L, Cuzner M, Baker D (2005) Cannabinoid-receptor 1 null mice are susceptible to neurofilament damage and caspase 3 activation. Neuroscience 134:261–268
Kan Q-C, Zhang H-J, Zhang Y, Li X, Xu Y-M, Thome R, Zhang M-L, Liu N, Chu Y-J, Zhang G-X (2017) Matrine treatment blocks NogoA-induced neural inhibitory signaling pathway in ongoing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Mol Neurobiol 54:8404–8418
Kazmi Z, Zeeshan S, Khan A, Malik S, Shehzad A, Seo EK, Khan SJN (2020) Anti-epileptic activity of daidzin in PTZ-induced mice model by targeting oxidative stress and BDNF/VEGF signaling.
Khalid S, Khan A, Shal B, Ali H, Kim YS, Khan S (2019) Suppression of TRPV1 and P2Y nociceptors by honokiol isolated from Magnolia officinalis in 3rd degree burn mice by inhibiting inflammatory mediators. Biomed Pharmacother 114:108777
Khalid S, Ullah MZ, Khan AU, Afridi R, Rasheed H, Khan A, Ali H, Kim YS, Khan S (2018) Antihyperalgesic properties of honokiol in inflammatory pain models by targeting of NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling. Front Pharmacol 9:140
Khan A, Khan A, Khalid S, Shal B, Kang E, Lee H, Laumet G, Seo EK, Khan SJM (2021a) 7β-(3-Ethyl-cis-crotonoyloxy)-1α-(2-methylbutyryloxy)-3, 14-dehydro-Z notonipetranone attenuates neuropathic pain by suppressing oxidative stress, inflammatory and pro-apoptotic protein expressions. 26: 181
Khan ASB, Khan AU, Ullah R, Baig MW, ul Haq I, Seo EK, Khan S (2021) Suppression of TRPV1/TRPM8/P2Y nociceptors by Withametelin via downregulating MAPK signaling in mouse model of vincristine-induced neuropathic pain. Intl J Mol Sci 22:6084
Khan A, Shal B, Khan AU, Bibi T, ul Islam S, Baig MW, ul Haq I, Ali H, Ahmad S, Khan S (2021b) Withametelin, a novel phytosterol, alleviates neurological symptoms in EAE mouse model of multiple sclerosis via modulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and TLR4/NF-κB signaling. Neurochem Intl 151:105211
Khan A, Shal B, Khan AU, Bibi T, ul Islam S, Baig MW, ul Haq I, Ali H, Ahmad S, Khan SJNI (2021c) Withametelin, a novel phytosterol, alleviates neurological symptoms in EAE mouse model of multiple sclerosis via modulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and TLR4/NF-κB signaling. 105211
Khan A, Shal B, Khan AU, Ullah R, Baig MW, Seo EK, Khan SJIJoMS (2021d) Suppression of TRPV1/TRPM8/P2Y nociceptors by Withametelin via downregulating MAPK signaling in mouse model of vincristine-induced neuropathic pain. 22: 6084
Khan A, Shal B, Naveed M, Nasir B, Irshad N, Ali H, Khan SJP (2020a) Matrine alleviates neurobehavioral alterations via modulation of JNK-mediated caspase-3 and BDNF/VEGF signaling in a mouse model of burn injury. 237: 2327-2343
Khan A, Shal B, Naveed M, Shah FA, Atiq A, Khan NU, Kim YS, Khan SJN (2019a) Matrine ameliorates anxiety and depression-like behaviour by targeting hyperammonemia-induced neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in CCl4 model of liver injury. 72: 38-50
Khan A, Ullah MZ, Afridi R, Rasheed H, Khalid S, Ullah H, Ali H, AlSharari SD, Kim YS, Khan SJPR (2019b) Antinociceptive properties of 25-methoxy hispidol A, a triterpinoid isolated from Poncirus trifoliata (Rutaceae) through inhibition of NF-κB signalling in mice. 33: 327-341
Khan AU, Khan A, Khan A, Shal B, Aziz A, Ahmed MN, Islam SU, Ali H, Shehzad A, Khan S (2021e) Inhibition of NF-κB signaling and HSP70/HSP90 proteins by newly synthesized hydrazide derivatives in arthritis model. J Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives of Pharmacology 394:1497–1519
Khan AU, Khan A, Khan A, Shal B, Aziz A, Ahmed MN, Islam SU, Ali H, Shehzad A, Khan SJN-SsAoP (2021f) Inhibition of NF-κB signaling and HSP70/HSP90 proteins by newly synthesized hydrazide derivatives in arthritis model. 1-23
Khan AU, Khan AM, Khan A, Shal B, Aziz A, Ahmed MN, Khan SJC-BI (2020b) The newly synthesized compounds (NCHDH and NTHDH) attenuates LPS-induced septicemia and multi-organ failure via Nrf2/HO1 and HSP/TRVP1 signaling in mice. 329: 109220
Khan S, Choi RJ, Lee J, Kim YS (2016) Attenuation of neuropathic pain and neuroinflammatory responses by a pyranocoumarin derivative, anomalin in animal and cellular models. Eur J Pharmacol 774:95–104
Khan S, Choi RJ, Shehzad O, Kim HP, Islam MN, Choi JS, Kim YS (2013) Molecular mechanism of capillarisin-mediated inhibition of MyD88/TIRAP inflammatory signaling in in vitro and in vivo experimental models. J Ethnopharmacol 145:626–637
Khan S, Shehzad O, Chun J, Choi RJ, Park S, Islam MN, Choi JS, Kim YS (2014) Anti-hyperalgesic and anti-allodynic activities of capillarisin via suppression of inflammatory signaling in animal model. J Ethnopharmacol 152:478–486
Lai C-S, Lai Y-S, Kuo D-H, Wu C-H, Ho C-T, Pan M-H (2011) Magnolol potently suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression via downregulating MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. J Funct Foods 3:198–206
Li LF, Lu J, Li XM, Xu CL, Deng JM, Qu R, Ma SP (2012) Antidepressant-like effect of magnolol on BDNF up-regulation and serotonergic system activity in unpredictable chronic mild stress treated rats. Phytother Res 26:1189–1194
Lin Y-R, Chen H-H, Ko C-H, Chan M-H (2007) Effects of honokiol and magnolol on acute and inflammatory pain models in mice. Life Sci 81:1071–1078
Liu X, Chen X, Zhu Y, Wang K, Wang Y (2017) Effect of magnolol on cerebral injury and blood brain barrier dysfunction induced by ischemia-reperfusion in vivo and in vitro. Metabolic Brain Disease 32:1109–1118
Lu S-H, Hsu W-L, Chen T-H, Chou T-C (2015) Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway involves the anti-inflammatory activity of magnolol in Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide-stimulated mouse RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Intl Immunopharmacol 29:770–778
Ma X, Jiang Y, Wu A, Chen X, Pi R, Liu M, Liu Y (2010) Berberine attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in C57 BL/6 mice. PLoS One 5:e13489
Mahmoodi M, Ayoobi F, Aghaei A, Rahmani M, Taghipour Z, Hosseini A, Jafarzadeh A, Sankian M (2019) Beneficial effects of Thymus vulgaris extract in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: clinical, histological and cytokine alterations. Biomed Pharmacother 109:2100–2108
Matsui N, Takahashi K, Takeichi M, Kuroshita T, Noguchi K, Yamazaki K, Tagashira H, Tsutsui K, Okada H, Kido Y (2009) Magnolol and honokiol prevent learning and memory impairment and cholinergic deficit in SAMP8 mice. Brain Res 1305:108–117
Muroyama A, Fujita A, Lv C, Kobayashi S, Fukuyama Y (2012) Mitsumoto Y (2012) Magnolol protects against MPTP/MPP+-Induced toxicity via Inhibition of oxidative stress in In vivo and In vitro models of parkinson’s disease. J Parkinson’s Disease
Naveed M, Khan SZ, Zeeshan S, Khan A, Shal B, Atiq A, Ali H, Ullah R, Khan SJN-Ssaop (2019) A new cationic palladium (II) dithiocarbamate exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activities through inhibition of inflammatory mediators in in vivo models. 392: 961-977
Nellessen A, Nyamoya S, Zendedel A, Slowik A, Wruck C, Beyer C, Fragoulis A, Clarner T (2019) Nrf2 deficiency increases oligodendrocyte loss, demyelination, neuroinflammation and axonal damage in an MS animal model. Metabolic Brain Disease: 1-10
Palumbo S, Bosetti F (2013) Alterations of brain eicosanoid synthetic pathway in multiple sclerosis and in animal models of demyelination: role of cyclooxygenase-2. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids 89:273–278
Pegoretti V, Baron W, Laman JD, Eisel UL (2018) Selective Modulation of TnF–TnFRs signaling: insights for multiple sclerosis treatment. Front Immunol 9
Rajgopal A, Missler SR, Scholten JD (2016) Magnolia officinalis (Hou Po) bark extract stimulates the Nrf2-pathway in hepatocytes and protects against oxidative stress. J Ethnopharmacol 193:657–662
Sajad M, Zargan J, Chawla R, Umar S, Sadaqat M, Khan HA (2009) Hippocampal neurodegeneration in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE): potential role of inflammation activated myeloperoxidase. Mol Cell Biochem 328:183–188
Shal B, Khan A, Khan AU, Ullah R, Ali G, Islam SU, Ali H, Seo E-K, Khan SJIJoMS (2021) Alleviation of memory deficit by Bergenin via the regulation of reelin and Nrf-2/NF-κB pathway in transgenic mouse model. 22: 6603
Shal B, Khan A, Naveed M, Ali H, Seo EK, Choi H, Khan SJLs (2020) Neuroprotective effect of 25-methoxyhispidol A against CCl4-induced behavioral alterations by targeting VEGF/BDNF and caspase-3 in mice. 253: 117684
Shal B, Khan A, Naveed M, Khan NU, AlSharari SD, Kim YS, Khan S (2019a) Effect of 25-methoxy hispidol A isolated from Poncirus trifoliate against bacteria-induced anxiety and depression by targeting neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 111:209–223
Shal B, Khan A, Naveed M, Khan NU, AlSharari SD, Kim YS, Khan SJB, Pharmacotherapy (2019b) Effect of 25-methoxy hispidol A isolated from Poncirus trifoliate against bacteria-induced anxiety and depression by targeting neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice. 111: 209-223
Suresh C, Dixit PK (2017) Ameliorating effects of magnolol in reducing the toxicity induced by heavy metal lead in the human brain cells. J Pharmacol Toxicol 12:111–119
Tang L, Zhu Z, **e M, Cao L, Yu XL, Zhang R, Ou Z, Shan W, Zhang Z (2019) Effects of β-cyclodextrin and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusions on the degradation of magnolol by intestinal bacteria. AAPS PharmSciTech 20:244
Ur Rehman F, Mazhar K, Malik A, Naz SS, Shah KU, Khan A, Khan S, Ahmed R, Qaisar SJMSCE, (2021) Surface modified multifaceted nanocarriers for oral non-conventional cancer therapy; synthesis and evaluation. 123: 111940
Vasconcelos AR, dos Santos NB, Scavone C, Munhoz CD (2019) Nrf2/ARE pathway modulation by dietary energy regulation in neurological disorders. Frontiers in pharmacology 10
Vorobeychik G, Black D, Cooper P, Cox A (2020) Multiple sclerosis and related challenges to young women's health: Canadian expert review. J Neurodegen Disease Manag 10:1–13
Wang C-C, Lin K-C, Lin B-S, Chio C-C, Kuo J-R (2013) Resuscitation from experimental traumatic brain injury by magnolol therapy. journal of surgical research 184: 1045-1052
Watanabe Y, Müller MK, von Engelhardt J, Sprengel R, Seeburg PH, Monyer HJFimn (2016) Age-dependent degeneration of mature dentate gyrus granule cells following NMDA receptor ablation. 8: 87
Zeeshan S, Naveed M, Khan A, Atiq A, Arif M, Ahmed MN, Kim YS, Khan S (2019) N-Pyrazoloyl and N-thiopheneacetyl hydrazone of isatin exhibited potent anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive properties through suppression of NF-κB, MAPK and oxidative stress signaling in animal models of inflammation. Inflamm Res 68:613–632
Zhang H, Qi Y, Yuan Y, Cai L, Xu H, Zhang L, Su B, Nie H (2017) Paeoniflorin ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via inhibition of dendritic cell function and Th17 cell differentiation. Scientific Reports 7:41887
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. NRF-2021R1A2C1003350).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors declare that all the data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used. TB and AK designed and performed the research including behavioral and biochemical assays. AUK and BS helped in the behavioral and biochemical assays. AK and TB wrote the original manuscript. TB, AK, AUK, BS, HA, EKS, and SK analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. SK and EKS supervised the project. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
“National Institutes of Health (NIH) guidelines for animal care” were followed for the animals’ experimentation. Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad Bioethical Committee (Approval No: BEC-FBS QAU2019-179) approved the study. Maximum care was made to minimize harm to animals.
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02732-x
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bibi, T., Khan, A., Khan, A.U. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Magnolol prevented brain injury through the modulation of Nrf2-dependent oxidative stress and apoptosis in PLP-induced mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 395, 717–733 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-022-02230-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-022-02230-6