Abstract
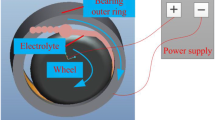
As a relatively new grinding technology, ELID (electrolytic in-process dressing) is widely used in some businesses. The oxide layer plays an important role in ELID grinding performance. The purpose of this work is to investigate the state of the oxide layer on ELID grinding wheel surfaces based on workpiece-cathode and tool-cathode. The thickness and surface topography of the oxide layer were measured from ELID grinding experiments based on workpiece-cathode and tool-cathode in different controlled dressing current. The normal grinding force was also compared in ELID grinding with workpiece-cathode and tool-cathode. According to the results, there are some caves on the surface of the oxide layer in ELID grinding with workpiece-cathode. With increasing controlled dressing current, the surface of the oxide layer becomes discontinuous in ELID grinding with workpiece-cathode. And the surface of the oxide layer becomes smoother with increasing controlled dressing current in ELID grinding with tool-cathode. Meanwhile, it was found that the oxide layer in ELID grinding with workpiece-cathode is thicker than that in ELID grinding with tool-cathode. Moreover, the normal grinding force in ELID grinding with workpiece-cathode is smaller than that in ELID grinding with tool-cathode. The results are helpful to improve the ELID grinding performance and apply ELID grinding technology with workpiece-cathode to abroad industrial applications.
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohmori H, Nakagawa T (1990) Mirror surface grinding of silicon wafer with electrolytic in-process dressing. Ann CIRP 39(1):329–332
Ohmori H, Nakagawa T (1997) Utilization of nonlinear conditions in precision grinding with ELID (electrolytic in-process dressing) for fabrication of hard material components. Ann CIRP 46(1):261–264
Biswas I, Rahman M (2010) Experimental study of wheel wear in electrolytic in-process dressing and grinding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 50:931–940
Stephenson DJ, Hedge J, Corbett J (2002) Surface finishing of Ni-Cr-B-Si composite coatings by precision grinding. Int J Mach Tool Manu 42:357–363
Liu JH, Pei ZJ, Fisher GR (2007) ELID grinding of silicon wafers: a literature review. Int Mach Tool Manu 47:529–536
Zhang C, Ohmori H, Marinescu I, Kato T (2001) Grinding of ceramic coatings with cast iron bond diamond wheels. A comparative study: ELID and rotary dresser. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 18:545–552
Shanawaz AM, Sundaram S, Pillai UTS, Aurtherson PB (2011) Grinding of aluminium silicon carbide metal matrix composite materials by electrolytic in-process dressing grinding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 57:143–150
Yu XL, Huang ST, Xu LF (2016) ELID grinding characteristics of SiCp/Al composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86:1165–1171
Park KY, Lee DG, Nakagawa T (1995) Mirror surface grinding characteristics and mechanism of carbon fiber reinforced plastics. J Mater Process Technol 52:386–398
Ohmori H, Takahashi I, Bandyopadhyay BP (1996) Ultra-precision grinding of structural ceramics by electrolytic in-process dressing (ELID) grinding. J Mater Process Technol 57:272–277
Bandyopadhyay BP, Ohmori H, Takahashi I (1997) Efficient and stable grinding of ceramics by electrolytic in-process dressing (ELID). J Mater Process Technol 66:18–24
Lim HS, Fathima K, Kumar AS, Rahman M (2002) A fundamental study on the mechanism of electrolytic in-process dressing (ELID) grinding. Int Mach Tools Manuf 42:935–943
Ohmori H, Marinescu ID, Katahira K (2011) Electrolytic in-process dressing (ELID) technologies: fundamentals and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Biswas I, Kumar AS, Rahman M (2010) A study on the equilibrium condition of the oxide layer in ELID grinding. Int J Abrasive Technol 3(1):25–36
Kato T, Itoh N, Ohmori H, Katahira K, Lin W, Hokkirigawa K (2004) Estimation of tribological characteristics of electrolyzed oxide layers on ELID-grinding wheel surfaces. Key Eng Mater 257-258:257–262
Guan JL, Guo DM, Yuan ZJ (2000) Research on the characteristics and roles of oxide film on grinding wheel of ELID mirror surface grinding. Chin J Mech Eng 36(5):89–92
Zhang CH, Ohmori H, Kato T, Morita N (2001) Evaluation of surface characteristics of ground CVD-SiC using cast iron bond diamond wheels. J Int Soc Precis Eng Nanotechnol 25:56–62
Kim HY, Ahn JH, Seo YH, Paik IH (2001) In-process measurement of ELID grinding status thickness of insulating layer. KSME Int J 15(9):1268–1273
Yang LJ, Ren CZ, ** XM (2010) Experimental study of ELID grinding based on the active control of oxide layer. J Mater Process Technol 210:1748–1753
Qian J, Ohmori H, Lin WM (2001) Internal mirror grinding with a metal/metal-resin bonded abrasive wheel. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 41:193–208
Wu ML, Ren CZ, Zhang KF (2015) ELID groove grinding of ball-bearing raceway and the accuracy durability of the grinding wheel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79:1721–1731
Wu ML, Zhang KF, Ren CZ (2015) Study on the non-uniform contact during ELID groove grinding. Precis Eng 39:116–124
Zhang KF, Ren CZ, Yang LJ, ** XM, Li QF (2013) Precision grinding of bearing steel based on active control of oxide layer state with electrolytic interval dressing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 65:411–419
Yuan LW, Ren CZ, Shu Z (2006) Research on state change of passivation layer in ELID ultraprecision mirror grinding. Aviat Precis Manuf Technol 42(1):5–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Ren, C., Chen, G. et al. A comparative study on state of oxide layer in ELID grinding with tool-cathode and workpiece-cathode. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94, 1299–1307 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0931-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0931-8