Abstract
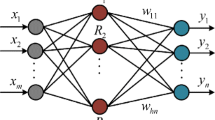
Occupant Restraint System (ORS) can effectively protect passengers from severe injury in vehicle collision, thus its design signifies a key issue in automobile engineering. To ensure a high safety rating, e.g. five or at least four stars in the European New Car Assessment Program (Euro-NCAP) rating system, which has been widely used to rate the different vehicles from different manufacturers, design optimization becomes essential. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of conventional mathematical programming methods directly integrated with numerical simulation and sensitivity analysis for optimization is of limited practical value, due to high complexity of structures, nonlinearity of materials and deformation involved. To address the issue, this paper combines a Kriging (KRG) model with Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) for vehicle ORS design. The ORS design of a 40% Offset Deformable Barrier (ODB) frontal impact test with the collision speed of 64 km/h is exemplified for the presented method. The results show that the KRG model can well predict the ORS responses for the design. Finally, the optimum result is verified by using sled physical tests. It is found that the ORS performance can be substantially improved for meeting product development requirements through the proposed approach.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar E, Guler MA, Gerceker B, Cerit ME, Bayram B (2011) Multi-objective crashworthiness optimization of tapered thin-walled tubes with axisymmetric indentations. Thin-Walled Struct 49(1):94–105
Avalle M, Chiandussi G, Belingardi G (2002) Design optimization by response surface methodology: application to crashworthiness design of vehicle structures. Struct Multidisc Optim 24(4):325–332
Bi J, Fang HB, Wang QA, Ren XC (2010) Modeling and optimization of foam-filled thin-walled columns for crashworthiness designs. Finite Elem Anal Des 46(9):698–709
Bose D, Crandall JR, Untaroiu CD, Maslen EH (2010) Influence of pre-collision occupant parameters on injury outcome in a frontal collsion. Accid Anal Prevent 42(4):1398–1407
Craig KJ, Stander N, Dooge DA, Varadappa S (2005) Automotive crashworthiness design using response surface-based variable screening and optimization. Eng Comput 22(1–2):38–61
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2000) A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm-NSGA-II. KanGAL Report Number 2000001
Del Prete A, Mazzotta D, Anglani A (2010) Design optimization application in accordance with product and process requirements. Adv Eng Softw 41(3):427–432
Elmarakbi AM (2006) Simple and effective method to predict the occupant dynamic response under sudden impulse loads. Int J Autom Technol 7(7):769–776
European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro-NCAP) (2011) Assessment Protocol – Adult Occupant Protection, Version 5.4
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard (2010) 49 CFR part 571, standard no. 208: occupant crash protection. Department of Transportation, National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, Washington, DC
Forsberg J, Nilsson L (2006) Evaluation of response surface methodologies used in crashworthiness optimization. Int J Impact Eng 32(5):759–777
Gu L, Yang RJ (2006) On reliability-based optimization methods for automotive structures. Int J Mater Prod Technol 25(1–3):3–26
Gu L, Yang RJ, Tho CH, Makowski M, Faruque O, Li Y (2001) Optimization and robustness for crashworthiness of side impact. Int J Veh Des 26(4):348–360
Hou J, Tomas J, Sparke L (1995) Optimisation of driver-side airbag and restraint system by occupant dynamics simulation. SAE Paper, 952703
Hou SJ, Li Q, Long SY, Yang XJ, Li W (2008) Multiobjective optimization of multi-cell sections for the crashworthiness design. Int J Impact Eng 35(11):1355–1367
Huang J, He W, Yang JK, Zhong ZH (2009) Numerical and experimental investigations on the behavior of the sandwiched tube-type airbag. Int J Crashworthiness 14(5):437–447
Huang ZJ, Wang CG, Chen J, Tian H (2011) Optimal design of aeroengine turbine disc based on kriging surrogate models. Comput Struct 89(1–2):27–37
Jang TS, Lee JJ, Yoon YS (1999) Occupant behavior simulation using DADS and design of seat belt for occupant safety. Int J Veh Des 21(4–5):402–423
Jiang ZY, Gu MT (2010) Optimization of a fender structure for the crashworthiness design. Mater Des 31(3):1085–1095
Kan CD, Marzougui D, Bahouth GT, Bedewi NE (2001) Crashworthiness evaluation using integrated vehicle and occupant finite element models. Int J Crashworthiness 6:387–398
Kim TW, Jeong HY (2010) Stochastic analysis of the variation in injury numbers of automobile frontal crash tests. Int J Autom Technol 11(4):481–488
Kurtaran H, Eskandarian A, Marzougui D, Bedewi NE (2002) Crashworthiness design optimization using successive response surface approximations. Comput Mech 29(4–5):409–421
Lanzi L, Castelletti LML, Anghileri M (2004) Multi-objective optimization of composite absorber shape under crashworthiness requirements. Compos Struct 65(3–4):433–441
Liao XT, Li Q, Yang XJ, Li W, Zhang WG (2008a) A two-stage multi-objective optimization of vehicle crashworthiness under frontal impact. Int J Crashworthiness 13(3):279–288
Liao XT, Li Q, Yang XJ, Zhang WG, Li W (2008b) Multiobjective optimization for crash safety design of vehicles using stepwise regression model. Struct Multidisc Optim 35(6):561–569
Luo M, Zhou Q (2010) A vehicle seat design concept for reducing whiplash injury risk in low-speed rear impact. Int J Crashworthiness 15(3):293–311
MADYMO (2005) Theory manual, version 6.3. TNO, Road Vehicle Institute, Delft, the Netherlands
Mizuno K, Arai Y, Yamazaki K, Kubota H, Yonezawa H, Hosokawa N (2008) Effectiveness and evaluation of SEAS of SUV in frontal impact. Int J Crashworthiness 13(5):533–541
Rao A, Hassan J, Nusholtz G (2006) Effect of airbag porosity, mass flow and load limiter on the 5th and 50th hybrid dummies in a 35 Mph Crash. SAE Paper, 2006-01-0677
Redhe M, Nilsson L (2006) A multipoint version of space map** optimization applied to vehicle crashworthiness design. Struct Multidisc Optim 31(2):134–146
Sinha K (2007) Reliability-based multiobjective optimization for automotive crashworthiness and occupant safety. Struct Multidisc Optim 33(3):255–268
Su RY, Gui LJ, Fan ZJ (2011) Multi-objective optimization for bus body with strength and rollover safety constraints based on surrogate models. Struct Multidisc Optim 44(3):431–441
Sun GY, Li GY, Stone M, Li Q (2010) A two-stage multi-fidelity optimization procedure for honeycomb-type cellular materials. Comput Mater Sci 49(3):500–511
Sun GY, Li GY, Zhou SW, Li HZ, Hou SJ, Li Q (2011a) Vehicle crashworthiness design by using multiobjective robust optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 44(1):99–110
Sun GY, Li GY, Zhou SW, Xu W, Yang XJ, Li Q (2011b) Multi-fidelity optimization for sheet metal forming process. Struct Multidisc Optim 44(1):111–124
Timothy WS, Timothy MM, John JK, Farrokh M (2001) Kriging models for global approximation in simulation-based multidisciplinary design optimization. AIAA J 39(12):2233–2241
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (2007) Regulation no. 94: frontal impact. http://www.unece.org/trans/main/wp29/wp29regs81–100.html
Yang RJ, Gu L (2004) Experience with approximate reliability-based optimization methods. Struct Multidisc Optim 26(1–2):152–159
Yang RJ, Akkerman A, Anderson DF, Faruque OM, Gu L (2000) Robustness optimization for vehicular crash simulations. Comput Sci Eng 2(6):8–13
Yang RJ, Chuang C, Gu L, Li G (2005a) Experience with approximate reliability-based optimization method II: an exhaust system problem. Struct Multidisc Optim 29(6):488–497
Yang RJ, Wang N, Tho CH, Bohineau JP, Wang BP (2005b) Metamodeling development for vehicle frontal impact simulation. J Mech Des 127(5):1014–1020
Youn BD, Choi KK, Yang RJ, Gu L (2004) Reliability-based design optimization for crashworthiness of vehicle side impact. Struct Multidisc Optim 26(3–4):272–283
Yu Q, Koizumi N, Yajima H, Shiratori M (2001) Optimum design of vehicle frontal structure and occupant restraint system for crashworthiness (a multilevel approach using SDSS). JSME Int J Ser A - Solid Mech Mater Eng 44(4):594–601
Zarei HR, Kroger M (2006) Multiobjective crashworthiness optimization of circular aluminum tubes. Thin-Walled Struct 44(3):301–308
Zhan ZF, Fu Y, Yang RJ, Peng YH (2011) An automatic model calibration method for occupant restraint systems. Struct Multidisc Optim 44(6):815–822
Zhang Y, Sun GY, Li GY, Rungsiyakull C, Li Q (2011) Identification of material parameters for high strength steel under impact loading. Adv Sci Lett 44(3):708–714
Zhao D, Xue DY (2011) A multi-surrogate approximation method for metamodeling. Eng Comput 27(2):139–153
Acknowledgments
The support from National 973 Project of China (2010CB328005), The Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Vehicle NVH and Safety Technology (NVHSKL-201002), The Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control (20111113), and The Open Fund of Key Laboratory for Automotive Transportation Safety Enhancement Technology of the Ministry of Communication, PRC (CHD2011SY008) are acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, X., Sun, G., Li, G. et al. Multiobjective optimization design for vehicle occupant restraint system under frontal impact. Struct Multidisc Optim 47, 465–477 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-012-0811-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-012-0811-7