Abstract
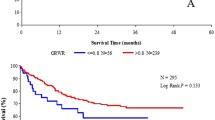
Graft size is known to be a major risk factor in living donor adult liver transplantation (LDALT). The aim of this study is to reassess whether graft size is a critical factor in LDALT or not. A series of 75 LDALTs excluding auxiliary transplantation and ABO blood-type incompatible transplantation were analyzed. The patients were divided into two groups, according to graft volume (GV) and standard liver volume (SLV): group 1 (small-size group) (GV/SLV: <40%), and group 2 (non-small-size group) (≥40%). Perioperative clinical data were compared between the two groups, including graft survival and postoperative complications. These parameters were also compared under the conditions of cirrhotic recipients. No difference in graft survival was found between the two groups. No difference was found in incidence of postoperative complications, such as intractable ascites and persistent hyperbilirubinemia. Even in cirrhotic patients with Child–Pugh’s class C, there was no difference in graft survival between the two groups. Risk factors related to graft loss were a preoperative urgent status due to chronic liver disease, pre-operative hyperbilirubinemia of over 10 mg/dl, and ABO blood type of not identical but compatible combination between donor and recipient. Graft size is not always considered to be a major risk factor in LDALT, although the number of patients was small in this study. Therefore, a left-lobe graft, even a “small-for-size” graft for adult recipients, remains a feasible option in LDALT.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sugawara Y, Makuuchi M, Takayama T, Imamura H, Dowaki S, Mizuta K, Kawarasaki H, Hashizume K. Small-for-size grafts in living-related liver transplantation. J Am Coll Surg 2001; 192:510.
Ben-Haim M, Emre S, Fishbein TM, Sheiner PA, Bodian CA, Kim-Schluger L, Schwarte ME, Miller CM. Critical graft size in adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation: impact of the recipient’s disease. Liver Transpl 2001; 7:948.
Kiuchi T, Kasahara M, Uryuhara K, Inomata Y, Uemoto S, Asonuma K, Egawa H, Fujita S, Hayashi M, Tanaka K. Impact of graft size mismatching on graft prognosis in liver transplantation from living donors. Transplantation 1999; 67:321.
Sugawara Y, Makuuchi M, Takayama T, Imamura H. Living-related liver transplantation for primary biliary cirrhosis. Transplantation 2001; 72(6):1087.
Kawasaki S, Makuuchi M, Matsunami H, Hashikura Y, Ikegami T, Nakazawa Y, Chisuwa H, Terada M, Miyagawa S. Living related liver transplantation in adults. Ann Surg 1998; 227:269.
Lo CM, Fan ST, Chan JK, Wei W, Lo RJ, Lai CL. Minimum graft volume for successful adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation for fulminant hepatic failure. Transplantation 1996; 62:696.
Lo CM, Fan ST, Liu CL, Wei WI, Lo RJ, Lai CL, Chan JK, Ng IO, Fung A, Wong J. Adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation using extended right lobe grafts. Ann Surg 1997; 226:261.
Wachs ME, Bak TE, Karrer FM, Everson GT, Shrestha R, Trouillot TE, Mandell MS, Steinberg TG, Kam I. Adult living donor liver transplantation using a right hepatic lobe. Transplantation 1998; 66:1313.
Fan ST, Lo CM, Liu CL. Technical refinement in adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation using right lobe graft. Ann Surg 2000; 231:126.
Inomata Y, Uemoto S, Asonuma K, Egawa H. Right lobe graft in living donor liver transplantation. Transplantation 2000; 69:258.
Surman OS. The ethics of partial-liver donation. N Engl J Med 2002; 346(14):1038.
Yamaoka Y, Morimoto T, Inamoto T, Tanaka A, Honda K, Ikai I, Tanaka K, Ichimiya M, Ueda M, Shimahara Y. Safety of the donor in living-related liver transplantation- an analysis of 100 parental donors. Transplantation 1995; 59(2):224.
Suh KS, Kim SH, Kim SB, Lee HJ, Lee KU. Safety of right lobectomy in living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 2002; 8(10):910.
Lo CM. Complications and long-term outcome of living liver donors: a survey of 1,508 cases in five Asian centers. Transplantation 2003; 75(3):S12.
Nishizaki T, Ikegami T, Hiroshige S, Hashimoto K, Uchiyama H, Yoshizumi T, Kishikawa K, Shimada M, Sugimachi K. Small graft for living donor liver transplantation. Ann Surg 2001; 233:575.
Shimada M, Shiotani S, Ninomiya M, Terashi T, Hiroshige S, Minagawa R, Soejima Y, Suehiro T, Sugimachi K. Characteristics of liver grafts in living donor liver transplantation: comparison between right and left lobe grafts. Arch Surg 2002; 137:1174.
Urata K, Kawasaki S, Matsunami H, Hashikura Y, Ikegami T, Ishizone S, Momose Y, Komiyama A, Makuuchi M. Calculation of child and adult standard liver volume for liver transplantation. Hepatology 1995; 21:1317.
Hiroshige S, Nishizaki T, Soejima Y, Hashimoto K, Ohta R, Miyagawa R, Shimada M, Honda H, Hashizume M, Sugimachi K. Beneficial effects of 3-dimensional visualization on hepatic vein reconstruction in living donor liver transplantation using right lobe graft. Transplantation 2001; 72:1993.
Starzl TE, Putnam CW, Groth CG, et al. Alopecia, ascites, and incomplete regeneration after 85 to 90 percent liver resection. Am J Surg 1975; 129:587.
Ku Y, Fukumoto T, Nishida T, et al. Evidence that portal vein decompression improves survival of carnine quarter orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation 1995; 10:1388.
Boillot O, Delafosse B, Mechet I, Boucaud C, Pouyet M. Small-for-size partial liver graft in an adult recipient; a new transplant technique. Lancet 2002; 359(9304):406.
Altaca G, Scigliano E, Guy SR, Sheiner PA, Reich DJ, Schwartz ME, Miller CM, Emre S. Persistent hypersplenism early after liver transplant: the role of splenectomy. Transplantation 1997; 64(10):1481.
Cescon M, Sugawara Y, Takayama T, Seyama Y, Sano K, Imamura H, Makuuchi M. Role of splenectomy in living-donor liver transplantation for adults. Hepatogastroenterol 2002; 49:721.
Smith CM, Davies DB, McBride MA. Liver transplantation in the United States: a report from the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network. Clin Transpl 2000; 19.
Humar A. Adult living donor transplants: which portion of the liver to use. Liver Transplant 2003; 9:634.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Miss Rie Nakao for her assistance in preparing this manuscript. This study was supported, in part, by a grant-in-aid for scientific research (No. 13357011) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Shimada, M., Ijichi, H., Yonemura, Y. et al. Is graft size a major risk factor in living-donor adult liver transplantation?. Transpl Int 17, 310–316 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00147-004-0720-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00147-004-0720-9