Abstract
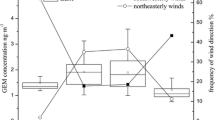
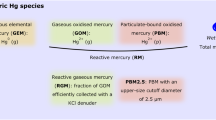
Exports of atmospheric mercury (Hg) from continental East Asia, a major Hg emitter in the globe, have been reported by several studies in neighboring countries such as Japan and Korea. Nonetheless, studies concerning this topic in Southeast Asia (SEA) countries are still limited. Accordingly, gaseous elemental mercury (GEM) has been measured from Can Thanh High School (CTHS), a suburban coastal site in southern Vietnam to study its characterization and discover the evidence of Hg trans-boundary transport from regional sources (e.g., East Asia). Data collected in July, August, and October 2022 were used in this study, and the overall GEM concentration was 1.61 ± 0.32 ng m-3. The GEM levels were higher in October than in July and August, potentially due to the discrepancy in air mass transport patterns induced by tropical monsoon and source origins of Hg. MERRA-2, backward trajectories, and CALIPSO images revealed the trans-boundary air pollution from continental East Asia to southern Vietnam, evidenced by significantly elevated (> 30%) atmospheric Hg concentrations as well as other air pollutants when the plume arrived at CTHS. Furthermore, our results also imply that atmospheric Hg exported from East Asia could influence large areas in SEA, suggesting the need for more studies in various SEA countries in the upcoming future. This study illustrated the influence of regional Hg emissions on local atmospheric Hg pollution and provided data to improve knowledge of the Hg biogeochemical cycle in SEA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariya PA, Amyot M, Dastoor A, Deeds D, Feinberg A, Kos G, Poulain A, Ryjkov A, Semeniuk K, Subir M, Toyota K (2015) Mercury physicochemical and biogeochemical transformation in the atmosphere and at atmospheric interfaces: a review and future directions. Chem Rev 115(10):3760–3802. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500667e
Babu SR, Nguyen LSP, Sheu GR, Griffith SM, Pani SK, Huang HY, Lin NH (2022) Long-range transport of La Soufrière volcanic plume to the western North Pacific: influence on atmospheric mercury and aerosol properties. Atmos Environ 268:118806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118806
Chen C, Qin X, Li H, Li H, Liu C, Fu M, Wang X, Huo J, Duan Y, Fu Q, Huang K, Deng C (2023) Atmospheric mercury in a developed region of eastern China: interannual variation and gas-particle partitioning. Heliyon 9:19786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19786
Dat ND, Nguyen LSP, Vo TDH, Do TTL, Tran ATK, Hoang NTT (2023) Pollution characteristics, associated risks, and possible sources of heavy metals in road dust collected from different areas of a metropolis in Vietnam. Environ Geochem Health 45:7889–7907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01696-4
Dat ND, Truong MT, Nguyen LSP, Tran ATK, Duc NM, Vo TDH, Sheu GR (2023) Street dust mercury levels among different land-use categories in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam: source apportionment and risk estimation. Atmos Pollut Res 14:101623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2022.101623
Do TTL, Griffith SM, Tseng WT, Lin NH (2021) Long-term trend of wintertime precipitation chemistry at a remote islet site influenced by anthropogenic emissions from continental East Asia. Atmos Environ 262:118626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118626
Draxler RR, Rolph GD (2013) HYSPLIT (Hybrid single-particle lagrangian integrated trajectory) model access via noaa arl ready. NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Silver Spring MD. http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php
Driscoll CT, Mason RP, Chan HM, Jacob DJ, Pirrone N (2013) Mercury as a global pollutant: sources, pathways, and effects. Environ Sci Technol 47:4967–4983. https://doi.org/10.1021/es305071v
Evers DC, Han YJ, Driscoll CT, Kamman NC, Goodale WM, Lambert KF, Holsen TM, Chen CY, Clair TA, Butler TJ (2007) Biological mercury hotspots in the Northeastern United States and Southeastern Canada. Bioscience 57:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1641/B570107
Feng X, Li P, Fu X, Wang X, Zhang H, Lin CJ (2022) Mercury pollution in China: implications on the implementation of the Minamata Convention. Environ Sci Process Impacts 24:634–648. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2em00039c
Fu X, Feng X (2015) Variations of atmospheric total gaseous mercury concentrations for the sampling campaigns of 2001/2002 and 2009/2010 and implications of changes in regional emissions of atmospheric mercury. Bull Miner Petrol Geochem 34:242–249
Fu X, Zhang H, Yu B, Wang X, Lin CJ, Feng XB (2015) Observations of atmospheric mercury in China: a critical review. Atmos Chem Phys 15:9455–9476. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-9455-2015
Fu X, Yang X, Tan Q, Ming L, Lin T, Lin J, Li X, Feng X (2018) Isotopic composition of gaseous elemental mercury in the marine boundary layer of East China Sea. J Geophys Res Atmos 123(14):7656–7669. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD028671
Gelaro R, McCarty W, Súarez MJ, Todling R, Molod A, Takacs L, Randles CA, Darmenov A, Bosilovich MG, Reichle R, Wargan K, Coy L, Cullather R, Draper C, Akella S, Buchard V, Conaty A, da Silva AM, Gu W, Kim GK, Koster R, Lucchesi R, Merkova D, Nielsen JE, Partyka G, Pawson S, Putman W, Rienecker M, Schubert SD, Sienkiewicz M, Zhao B (2017) The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J Clim 30:5419–5454. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0758.1
Hien TT, Chi NDT, Nguyen NT, Takenaka N, Huy DH (2019) Current status of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in Vietnam’s most populous city. Ho Chi Minh City Aerosol and Air Quality Res 19(10):2239–2251. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2018.12.0471
Huang HY, Wang SH, Huang WX, Lin NH, Chuang MT, da Silva AM, Peng CM (2020) Influence of synoptic-dynamic meteorology on the long-range transport of Indochina biomass burning aerosols. J Geophys Res Atmos 125:e2019JD031260. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD031260
Hung WT, Lu CH, Sarah Shrestha B, Lin HC, Lin CA, Grogan D, Hong J, Ahmadov R, James E, Joseph E (2020) The impacts of transported wildfire smoke aerosols on surface air quality in New York State: a case study in summer 2018. Atmos Environ 227:117415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117415
Khue VHN, Hang NTT (2021) Air pollution emission inventory of thermal power plants in South-East and South-West areas, and proposed solutions to reduce emissions. VNUHCM J Earth Sci Environ 5(SI1):SI122–SI136. https://doi.org/10.32508/stdjsee.v5iSI1.577
Kushner DS, Lopez TM, Wallace KL, Damby DE, Kern C, Cameron CE (2023) Estimates of volcanic mercury emissions from Redoubt Volcano, Augustine Volcano, and Mount Spurr eruption ash. Front Earth Sci 11:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2023.1054521
Le PV, Phan-Van T, Mai KV, Tran DQ (2019) Space–time variability of drought over Vietnam. Int J Climatol 39:5437–5451. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6164
Lin NH, Tsay SC, Maring HB, Yen MC, Sheu GR, Wang SH et al (2013) An overview of regional experiments on biomass burning aerosols and related pollutants in Southeast Asia: from BASEASIA and the Dongsha experiment to 7-SEAS. Atmos Environ 78:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.04.066
Lin H, Tong Y, Yu C, Chen L, Yin X, Zhang Q, Kang S, Luo L, Schauer J, de Foy B, Wang X (2022) First observation of mercury species on an important water vapor channel in the southeastern tibetan Plateau. Atmos Chem Phys 22:2651–2668. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-22-2651-2022
Lin CC, Macrohon JKE, Brimblecombe P, Adyanis LN, Yeh CF, Lai CH, Wang LC (2023) Atmospheric mercury speciation and concentration at the urban and industrial sites in Taiwan over a three-year period. Atmos Environ 313:120070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2023.120070
Mao H, Cheng I, Zhang L (2016) Current understanding of the driving mechanisms for spatiotemporal variations of atmospheric speciated mercury: a review. Atmos Chem Phys 16:12897–12924. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-12897-2016
Marumoto K, Hayashi M, Takami A (2015) Atmospheric mercury concentrations at two sites in the Kyushu Islands, Japan, and evidence of long-range transport from East Asia. Atmos Environ 117:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.07.019
Morton-Bermea O, Schiavo B, Salgado-Martínez E, Almorín-Ávila MA, Hernández-Álvarez E (2021) Gaseous elemental mercury (GEM) in the Mexico City Metropolitan Area. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 107:514–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03293-6
Morton-Bermea O, Hernández-Álvarez E, Ordoñez-Godínez SL, Montes-Ávila I (2023) Mercury, platinum, antimony and other trace elements in the atmospheric. environment of the Urban Area of Mexico City: Use of Ficus benjamina as biomonitor. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106:665–669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-03080-9
Nguyen LSP, Sheu GR (2019) Four-year measurements of wet mercury deposition at a tropical mountain site in central Taiwan. Aerosol Air Qual Res 19:2043–2055. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2019.05.0250
Nguyen LSP, Sheu GR, Lin DW, Lin NH (2019) Temporal changes in atmospheric mercury concentrations at a background mountain site downwind of the East Asia continent in 2006–2016. Sci Total Environ 686:1049–1056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.425
Nguyen LSP, Zhang L, Lin DW, Lin NH, Sheu GR (2019) Eight-year dry deposition of atmospheric mercury to a tropical high mountain background site downwind of the east Asian continent. Environ Pollut 225:113128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113128
Nguyen LSP, Huang HY, Lei TL, Bui TT, Wang SH, Chi KH, Sheu GR, Lee CT, Ou-Yang CF, Lin NH (2020) Characterizing a landmark biomass-burning event and its implication for aging processes during long-range transport. Atmos Environ 241:117766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117766
Nguyen LSP, Sheu GR, Chang SC, Lin NH (2021) Effects of temperature and relative humidity on the partitioning of atmospheric oxidized mercury at a highaltitude mountain background site in Taiwan. Atmos Environ 261:118572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118572
Nguyen LSP, Sheu GR, Hsiao TC, Lee CT, Chang SC, Lin NH (2021) Relationships between atmospheric mercury and optical properties of spring outflow aerosols from Southeast Asia. Atmos Pollut 12:101178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2021.101178
Nguyen LSP, Nguyen KT, Griffith SM, Sheu GR, Yen MC, Chang SC, Lin NH (2022) Multiscale temporal variations of atmospheric mercury distinguished by the Hilbert–Huang transform analysis reveals multiple El Nino Southern oscillation links. Environ Sci Technol 56:1423–1432. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c03819
Nguyen LSP, Chang JHW, Griffith SM, Hien TT, Kong SSK, Le HN, Huang HY, Sheu GR, Lin NH (2022) Trans-boundary air pollution in a southeast Asian megacity: case studies of the synoptic meteorological mechanisms and impacts on air quality. Atmos Pollut Res 13:101366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2022.101366
Nguyen LSP, Hien TT, Truong MT, Chi NDT, Sheu GR (2022) Atmospheric particulate-bound mercury (PBM10) in a Southeast Asia megacity: sources and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 307:135707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135707
Nguyen LSP, Pham TDH, Tran AN, To TH (2023) Investigating and optimizing a method to determine atmospheric mercury for application in Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam. VNUHCM J Nat Sci 7(1):2552–2560. https://doi.org/10.32508/stdjns.v7i1.1256
Nguyen LSP, Pham TDH, Truong MT, Tran AN (2023) Characteristics of total gaseous mercury at a tropical megacity in Vietnam and influence of tropical cyclones. Atmos Pollut Res 14(8):101813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2023.101813
Obrist D, Kirk JL, Zhang L, Sunderland EM, Jiskra M, Selin NE (2018) A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: changes of emissions, climate, and land use. Ambio 47(2):116–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-017-1004-9
Qiu Y, Gai P, Yue F, Zhang Y, He P, Kang H, Yu X, Chen J, **e Z (2022) Potential factors impacting PM2.5-Hg during haze evolution revealed by mercury isotope: emission sources and photochemical processes. Atmos Res 277:106318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2022.106318
Sheu GR, Lin NH, Lee CT, Wang JL, Chuang MT, Wang SH, Chi KH, Ou-Yang CF (2013) Distribution of atmospheric mercury in northern Southeast Asia and South China Sea during Dongsha experiment. Atmos Environ 78:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.07.002
Sheu GR, Nguyen LSP, Truong MT, Lin DW (2019) Characteristics of atmospheric mercury at a suburban site in northern Taiwan and influence of trans-boundary haze events. Atmos Environ 214:116827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.116827
Streets DG, Horowitz HM, Lu Z, Levin L, Thackray CP, Sunderland EM (2019) Global and regional trends in mercury emissions and concentrations, 2010–2015. Atmos Environ 201:417–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.12.031
Tang Y, Wang S, Wu Q, Liu K, Wang L, Li S, Gao W, Zhang L, Zheng H, Li Z, Hao J (2018) Recent decrease trend of atmospheric mercury concentrations in East China: the influence of anthropogenic emissions. Atmos Chem Phys 18:8279–8291. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-8279-2018
Tang Y, Wu Q, Wang S, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Qiao F (2023) Enhanced daytime atmospheric mercury in the marine boundary layer in the South oceans. Sci Total Environ 892:164691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164691
UN Environment (2019) Global mercury assessment 2018. UN Environment Programme, Chemicals and health branch Geneva, Switzerland. https://www.unep.org/resources/publication/global-mercury-assessment-2018
UNEP (2013) UNEP: Global mercury assessment: sources, emissions, releases and environmental transport. UNEP Chemicals Branch, Geneva
Vardè M, Barbante C, Barbaro E, Becherini F, Bonasoni P, Busetto M, Calzolari F, Cozzi G, Cristofanelli P, Dallo F, De Blasi F, Feltracco M, Gabrieli J, Gambaro A, Maffezzoli N, Morabito E, Putero D, Spolaor A, Cairns WRL (2022) Characterization of atmospheric total gaseous mercury at a remote high-elevation site (Col Margherita Observatory, 2543 m a.s.l.) in the Italian Alps. Atmos Environ 271:118917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118917
Wang SH, Hung WT, Chang SC, Yen MC (2016) Transport characteristics of Chinese haze over Northern Taiwan in winter, 2005–2014. Atmos Environ 126:76–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.11.043
Winker DM, Vaughan MA, Omar A, Hu Y, Powell KA, Liu Z, Hunt WH, Young SA (2009) Overview of the CALIPSO mission and CALIOP data processing algorithms. J Atmos Ocean Technol 26:2310–2323. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JTECHA1281.1
Wu Q, Li G, Wang S, Liu K, Hao J (2018) Mitigation options of atmospheric hg emissions in China. Environ Sci Technol 52:12368–12375
Yin X, Kang S, de Foy B, Ma Y, Tong Y, Zhang W, Wang X, Zhang G, Zhang Q (2018) Multi-year monitoring of atmospheric total gaseous mercury at a remote high-altitude site (Nam Co, 4730 m a.s.l.) in the inland Tibetan Plateau region. Atmos Chem Phys 18:10557–10574. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-10557-2018
Funding
The authors thank the Ho Chi Minh Department of Science and Technology for financial support in this research under Grant No. 39/2021/HĐ-QKHCN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, L.S.P., Hien, T.T. Long-Range Atmospheric Mercury Transport from Across East Asia to a Suburban Coastal Area in Southern Vietnam. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 112, 14 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-023-03842-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-023-03842-1