Abstract
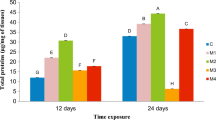
In this work, we propose to evaluate the effect of agriculture intensification under greenhouses on the biochemical and transcriptomic responses of the earthworms Eisenia andrei. This work was conducted on two sites in Téboulba and Sahline (Monastir governorate) and a control site in an experimental plot that is undergoing organic farming. For this purpose, the earthworms Eisenia andrei were exposed to the soils during 7 and 14 days. The physicochemical properties of the soils were analyzed. The biochemical biomarkers of metallothioneins (MTs) and malondialdehyde (MDA) accumulations were also assessed. Moreover, the gene expression level of the MTs was analyzed. The results of our study revealed a significant trace element accumulation accompanied by a high level of MDA and MT proteins. Moreover, a significant expression of the MT gene was observed in earthworms exposed to the soils from Sahline and Téboulba. Hence, this work reveals that intensive agriculture can affect the biological responses of earthworms and consequently, the soil’s biofertility.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banni M, Dondero F, Jebali J, Guerbej H et al (2007) Assessment of heavymetal contamination using real-time PCR analysis of mussel metallothionein mt10 and mt20 expression: a validation along the Tunisian coast. Biomarkers 12:369–383
Bonanomi G, De Filippis F, Cesarano G et al (2016) Organic farming induces changes in soil microbiota that affect agro-ecosystem functions. Soil Biol Biochem 103:327–336
Bouché MB (1972) Lombriciens de France. Ecologie et systématique. vol. 72. I.N.R.A (2)
Boughattas I, Hattab S, Boussetta H et al (2016) Biomarker responses of Eisenia andrei to a polymetallic gradient near a lead mining site in North Tunisia. Environ Pollut 218:530–541
BradfordM.M, (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Brulle F, Mitta G, Leroux R et al (2007) The strong induction of metallothionein gene following cadmium exposure transiently affects the expression of many genes in Eisenia fetida: A trade-off mechanism? Comp Biochem Physiol -. C Toxicol Pharmacol 144:334–341
Calisi A, Lionetto MG, De Lorenzis E et al (2014) Metallothionein induction in the coelomic fluid of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris following heavy metal exposure: A short report. Biomed Res Int 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/109386
Calisi A, Lionetto MG, Schettino T (2009) Pollutant-induced alterations of granulocyte morphology in the earthworm Eisenia foetida. Ecotox Environ Safe 72(5):1369–1377
Cluzeau D, Guernion M, Chaussod R et al (2012) Integration of biodiversity in soil quality monitoring: baselines for microbial and soil fauna parameters for different land-use types. Eur J Soil Biol 49:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2011.11.003
Dallinger R (1996) Metallothionein research in terrestrial invertebrates: synopsis and perspectives. Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 113(2):125–133
Dedeke GA, Owagboriaye F, Adebambo A, Ademolu K (2016) Earthworm metallothionein production as biomarker of heavy metal pollution in abattoir soil. Appl Soil Ecol 104:42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.02.013
Dedeke GA, Owagboriaye F, Ademolu K, Olujimi O, Aladesida A (2018) Comparative assessment on mechanism underlying renal toxicity of commercial formulation of roundup herbicide and glyphosate alone in male albino rat. Int J Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1177/1091581818779553
Demuynck S, Grumiaux F, Mottier V et al (2006) Metallothionein response following cadmium exposure in the oligochaete Eisenia fetida. Comp Biochem Physiol - C Toxicol Pharmacol 144:34–46. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2006.05.004
Drahansky M, Paridah M, Moradbak A et al (2016) We are IntechOpen, the world ’ s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists TOP 1%. ntech i:13. doi:https://doi.org/10.5772/57353
Eickhout B, van Meijl H, Tabeau A, van Rheenen T (2007) Economic and ecological consequences of four European land use scenarios. Land use policy 24:562–575
Flohre A, Rudnick M, Traser G et al (2011) Does soil biota benefit from organic farming in complex vs. simple landscapes? Agric Ecosyst Environ 141:210–214
Furst A, Nguyen Q (1989) Cadmium-lnduced Metallothionein. Biol Trace Elem Res 2:81–85
Gabriel D, Roschewitz I, Tscharntke T et al (2006) Beta diversity at different spatial scales: plant communities in organic and conventional agriculture. Ecol app 16(5):2011–2021
Galay-Burgos M, Spurgeon DJ, Weeks JM et al (2003) Develo** a new method for soil pollution monitoring using molecular genetic biomarkers. Biomarkers 8:229–239
Gao M, Taylor MK, Callaham Jr. MA (2016) Do non-native earthworms influence trophic dynamics in experimental soil ecosystems? International Visitors Program Science Leadership Forum, Washington, DC
Hattab S, Boughattas I, Boussetta H et al (2015) Transcriptional expression levels and biochemical markers of oxidative stress in the earthworm Eisenia andrei after exposure to 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 122:76–82
Hattab S, Hattab S, Flores-Casseres ML et al (2016) Characterisation of lead-induced stress molecular biomarkers in Medicago sativa plants. Environ Exp Bot 123:1–12
Headey D, Jayne TS (2014) Adaptation to land constraints: is Africa different? Food Policy 48:18–33
Homa J, Stürzenbaum SR, Kolaczkowska E (2016) Metallothionein 2 and heat shock protein 72 protect allolobophora chlorotica from cadmium but not nickel or copper exposure: body malformation and coelomocyte functioning. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 71:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-016-0276-6
Jankowski KJ, Neill C, Davidson EA et al (2018) Deep soils modify environmental consequences of increased nitrogen fertilizer use in intensifying Amazon agriculture. Sci Rep 8:1–11. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31175-1
Kammenga J, Laskowski R (2000) Demographic approaches in Ecotoxicology: state of the art. Wiley, Chichester
Kammenga JE, Dallinger R, Donker MH et al (2000) Biomarkers in terrestrial invertebrates for soil risk assessment. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 164:93–147
Lanno R, Wells J, Conder J, Bradham K, Basta N (2004) The bioavailability of chemicals in soil for earthworms. Ecotox Environ safe 57:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.200418292
Lecoeur S, Videmann B, Berny P (2004) Evaluation of metallothionein as a biomarker of single and combined Cd/Cu exposure in Dreissena polymorpha. Environ Res 94:184–191
Livingstone DR, Martinez PG, Michel X, Narbonne JF et al (1990) Oxyradical production as a pollution-mediated mechanism of toxicity in the common mussel, Mytilus edulis L., and other molluscs. Funct Ecol 4:415. https://doi.org/10.2307/2389604
Loveland P, Webb J (2003) Is there a critical level of organic matter in the agricultural soils of temperate regions: A review. Soil Tillage Res 70:1–18
Lukkari T, Taavitsainen M, Soimasuo M et al (2004) Biomarker responses of the earthworm Aporrectodea tuberculata to copper and zinc exposure: Differences between populations with and without earlier metal exposure. Environ Pollut 129:377–386
Margoum C, Malessard C, Gouy V (2006) Investigation of various physicochemical and environmental parameter influence on pesticide sorption to ditch bed substratum by means of experimental design. Chemosphere 63:1835–1841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.10.032
Mkhinini M, Boughattas I, Bousserhine N, Banni M (2019) Biochemical and transcriptomic response of earthworms Eisenia andrei exposed to soils irrigated with treated wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:2851–2863. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3794-0
Mkhinini M, Boughattas I, Alphonse V et al (2019) Effect of treated wastewater irrigation in East Central region of Tunisia (Monastir governorate) on the biochemical and transcriptomic response of earthworms Eisenia andrei. Sci Total Environ 647:1245–1255
Monga C, Lin JY, Otsuka K, Place F (2014) Land Tenure and Agricultural Intensification in Sub-Saharan Africa. Oxford Handb Africa Econ
Moolenaar SW, Lexmond TM, Van Der Zee SEATM (1997) Calculating heavy metal accumulation in soil: A comparison of methods illustrated by a case-study on compost application. Agric Ecosyst Environ 66:71–82. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8809(97)00087-X
Morgan JE, Morgan AJ (1999) The accumulation of metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn and Ca) by two ecologically contrasting earthworm species (Lumbricus rubellus and Aporrectodea caliginosa): Implications for ecotoxicological testing. Appl Soil Ecol 13:9–20
Naidu R, Rengasamy P, Sumner ME (1995) Australian sodic soils: Distribution, properties and management. CSIRO Australia, East Melbourne
Ndayibagira A, Sunahara GI, Yves Robidoux P (2007) Rapid isocratic HPLC quantification of metallothionein-like proteins as biomarkers for cadmium exposure in the earthworm Eisenia andrei. Soil Biol Biochem 39:194–201. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.07.008
Negri A, Potocki W, Iwanicki A et al (2013) Expression and display of Clostridium difficile protein FliD on the surface of Bacillus subtilis spores. J Med Microbiol 62:1379–1385
Olsen SR (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate (No. 939). US Dept. of Agriculture
Orebiyi EO, Awomeso JA, Idowu OA, Martins et al (2010) Assessment of pollution hazards of shallow well water in Abeokuta and environs, southwest, Nigeria. Amer J Environ Sci 6(1):50–56
Otsuka K, Place F (2014) Changes in Land Tenure and Agricultural Intensification in Sub-Saharan Africa. WIDER Working Paper 2014/051
Roesijadi G (1996) Metallothionein and its role in toxic metal regulation. Comp Biochem Physiol C 113(2):117–123
Sanchez-Hernandez JC (2006) Earthworm biomarkers in ecological risk assessment. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 188:85–126. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-32964-2_3
Sciences M, Kingdom U (1996) Effects of Metal-Contaminated Soils on the Growth, Sexual Development, and Early Cocoon Production of the Earthworm Eisenia fetida, with Particular Reference to Zinc. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 95:86–95
Stürzenbaum SR, Kille P, Morgan AJ (1998) The identification, cloning and characterization of earthworm metallothionein. FEBS Lett 431:437–442
Suriya J, Bharathiraya S, Sekar V, Rajasekaran R (2012) Metallothionein induction and antioxidative responses in the estuarine Polychaeta Capitella capitata (Capitellidae). Asian Pac J Trop Biomed S1052–S1059
Tsyusko OV, Hardas SS, Shoults-Wilson WA, Starnes CP, Joice G et al (2012) Short-term molecular-level effects of silver nanoparticle exposure on the earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 171:249–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.08.003
Tumminello RA, Fuller-espie SL (2013) Heat stress induces ROS production and histone phosphorylation in celomocytes of Eisenia hortensis Abstract The effect of heat stress on celomocytes (leukocytes) from Eisenia hortensis was investigated by measuring the production of reactive oxygen spec. 50–57
Uwizeyimana H, Wang M, Chen W, Khan K (2018) Ecotoxicological effects of binary mixtures of siduron and Cd on mRNA expression in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Sci Total Environ 610–611:657–665. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.265
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N et al (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. (Genome Biol) 3:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034
Viarengo A, Ponzano E, Dondero F, Fabbri R (1997) A simple spectrophotometric method for metallothionein evaluation in marine organisms: An application to Mediterranean and Antarctic molluscs. Mar Environ Res 44:69–84. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-1136(96)00103-1
Wang X, Zhao X, Zhang Z et al (2016) Assessment of soil erosion change and its relationships with land use/cover change in China from the end of the 1980s to 2010. Catena 137:256–268. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.10.004
Weller SA, Simpkins SA, Stead DE et al (2002) Identification of Agrobacterium spp. present within Brassica napus seed by Taqman PCR - Implications for GM screening procedures. Arch Microbiol 178:338–343. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-002-0461-z
Woo S, Yum S, Kim DW, Park HS (2009) Transcripts level responses in a marine medaka (Oryzias javanicus) exposed to organophosphorus pesticide. Comp Biochem Physiol - C Toxicol Pharmacol 149:427–432. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.10.100
Zhen L, Cao SY, Cheng SK et al (2010) Arable land requirements based on food consumption patterns: case study in rural Guyuan District, Western China. Ecol Econ 69:1443–1453
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hattab, S., Boughattas, I., Mkhinini, M. et al. Impact of Intensive Farming on Soil Heavy Metal Accumulation and Biomarkers Responses of Earthworms Eisenia andrei. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 105, 559–564 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-03000-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-03000-x