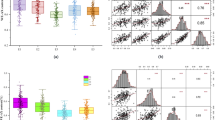
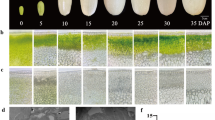
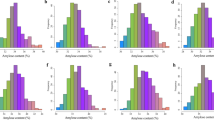
Abstract
Key message
QTL map** for fiber-related traits and elucidation of a stable and novel QTL affecting seed lignin content, cellulose content and seed oil content.
Abstract
Dissection of the genetic networks for fiber biosynthesis is important for improving the seed oil content and meal value of Brassica napus. In this study, the genetic basis of seed fiber biosynthesis in B. napus was investigated via quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis using a doubled haploid population derived from ‘KenC-8’ crossed with ‘N53-2.’ Seed lignin content (LC), cellulose content (CC) and hemicellulose content (HC) were significantly negatively correlated with seed oil content (OC). Co-localization QTLs among LC, CC, HC and OC on A09 were found with contributions ranging from 9.87 to 48.50%. Seven co-localization QTLs involved in the fiber component and OC were further verified by bulked segregant analysis (BSA). The unique QTL uqA9-12 might be a real and new QTL that was commonly identified by QTL map** and BSA and simultaneously affected LC, CC and OC with opposite additive effects. A potential regulatory network controlling seed fiber biosynthesis was constructed to dissect the complex mechanism of seed fiber and oil accumulation, and numerous candidate genes were identified in the fiber-related QTL regions. These results provided an enrichment of QTLs and potential candidates for fiber biosynthesis, as well as useful new information for understanding the complex genetic mechanism underlying rapeseed seed fiber accumulation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Arcade A, Labourdette A, Falque M, Mangin B, Chardon F, Charcosset A, Joets J (2004) BioMercator: integrating genetic maps and QTL towards discovery of candidate genes. Bioinformatics 20:2324–2326
Badani AG, Snowdon RJ, Wittkop B, Lipsa FD, Baetzel R, Horn R, De Haro A, Font R, Lühs W, Friedt W (2006) Colocalization of a partially dominant gene for yellow seed colour with a major QTL influencing acid detergent fibre (ADF) content in different crosses of oilseed rape (Brassica napus). Genome 49:1499–1509
Behnke N, Suprianto E, Möllers C (2018) A major QTL on chromosome C05 significantly reduces acid detergent lignin (ADL) content and increases seed oil and protein content in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 131:2477–2492
Chao H, Wang H, Wang X, Guo L, Gu J, Zhao W, Li B et al (2017) Genetic dissection of seed oil and protein content and identification of networks associated with oil content in Brassica napus. Sci Rep 7:46295
Chen Y, Qi L, Zhang X, Huang J, Wang J, Chen H, Ni X et al (2013) Characterization of the quantitative trait locus OilA1 for oil content in Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 26:2499–2509
Cheng X, **a MS, Zeng MX, Gu MJ, Yang MY, Xu J, Liu L et al (2016) Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with oil content and development of near isogenic lines for stable qOC-A10 in Brasscia napus L. Can J Plant Sci 96:423–432
Delourme R, Falentin C, Huteau V, Clouet V, Horvais R, Gandon B, Specel S et al (2006) Genetic control of oil content in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 113:1331–1345
Desprez T, Juraniec M, Crowell EF, Jouy H, Pochylova Z, Parcy F, Höfte H, Gonneau M, Vernhettes S (2007) Organization of cellulose synthase complexes involved in primary cell wall synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15572–15577
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L (2010) MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 15:573–581
Fornalé S, Rencoret J, García-Calvo L, Encina A, Rigau J, Gutiérrez A, Del Río JC, Caparros-Ruiz D (2016) Changes in cell wall polymers and degradability in Maize mutants lacking 3′- and 5′-O-methyltransferases involved in lignin biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol 58:240–255
Fu FY, Liu LZ, Chai YR, Chen L, Yang T, ** MY, Ma AF, Yan XY, Zhang ZS, Li JN (2007) Localization of QTLs for seed color using recombinant inbred lines of Brassica napus in different environments. Genome 50:840–854
Gigolashvili T, Berger B, Mock HP, Müller C, Weisshaar B, Flügge UI (2007) The transcription factor HIG1/MYB51 regulates indolic glucosinolate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 50:886–901
Guo L, Devaiah SP, Narasimhan R, Pan X, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Wang X (2012) Cytosolic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases interact with phospholipase Dδ to transduce hydrogen peroxide signals in the Arabidopsis response to stress. Plant Cell 24:2200–2212
Jiang C, Shi J, Li R, Long Y, Wang H, Li D, Zhao J et al (2014) Quantitative trait loci that control the oil content variation of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 127:957–968
Liang Y, Liang Y, Li J, Chen L (2002) Difference between yellow and black seed coat in B. napus. Chin J Oil Crop Sci 24:13–18
Liu L, Stein A, Wittkop B, Sarvari P, Li J, Yan X, Dreyer F, Frauen M, Friedt W, Snowdon RJ (2012) A knockout mutation in the lignin biosynthesis gene CCR1 explains a major QTL for acid detergent lignin content in Brassica napus seeds. Theor Appl Genet 124:1573–1586
Liu L, Qu C, Wittkop B, Yi B, ** of seed fibre QTL in Brassica napus L. PLoS ONE 8:e83052
Liu J, Osbourn A, Ma P (2015) MYB transcription factors as regulators of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. Mol Plant 8:689–708
Newman LJ, Perazza DE, Juda L, Campbell MM (2004) Involvement of the R2R3-MYB, AtMYB61, in the ectopic lignification and dark-photomorphogenic components of the det3 mutant phenotype. Plant J 37:239–250
Persson S, Paredez A, Carroll A, Palsdottir H, Doblin M, Poindexter P, Khitrov N, Auer M, Somerville CR (2007) Genetic evidence for three unique components in primary cell-wall cellulose synthase complexes in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15566–15571
Qu C, Fu F, Lu K, Zhang K, Wang R, Xu X, Wang M, Lu J, Wan H, Zhanglin T, Li J (2013) Differential accumulation of phenolic compounds and expression of related genes in black- and yellow-seeded Brassica napus. J Exp Bot 64:2885–2898
Raboanatahiry N, Chao H, Guo L, Gan J, **ang J, Yan M, Zhang L et al (2017) Synteny analysis of genes and distribution of loci controlling oil content and fatty acid profile based on QTL alignment map in Brassica napus. BMC Genom 18:776
Richmond TA, Somerville C (2000) The cellulose synthase superfamily. Plant Physiol 124:495–498
Rius SP, Casati P, Iglesias AA, Gomez-Casati DF (2008) Characterization of Arabidopsis lines deficient in GAPC-1, a cytosolic NAD-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Plant Physiol 148:1655–1667
Rotmistrovsky K, Jang W, Schuler GD (2004) A web server for performing electronic PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 32:108–112
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504
Shi J, Li R, Qiu D, Jiang C, Long Y, Morgan C, Bancroft I, Zhao J, Meng J (2009) Unraveling the complex trait of crop yield with quantitative trait loci map** in Brassica napus. Genetics 182:851–861
Simbaya J, Slominski BA, Rakow G, Campbell LD, Downey RK, Bell JM (1995) Quality characteristics of yellow-seeded Brassica seed meals-protein, carbohydrates, and dietary fiber components. J Agric Food Chem 43:2062–2066
Snowdon RJ, Wittkop B, Rezaidad A, Hasan M, Lipsa F, Stein A, Friedt W (2010) Regional association analysis delineates a sequenced chromosome region influencing antinutritive seed meal compounds in oilseed rape. Genome 53:917–928
Stein A, Wittkop B, Liu L, Obermeier C, Friedt W, Snowdon RJ (2013) Dissection of a major QTL for seed colour and fibre content in Brassica napus reveals colocalization with candidate genes for phenylpropanoid biosynthesis and flavonoid deposition. Plant Breed 132:382–389
Sun F, Fan G, Hu Q, Zhou Y, Guan M, Tong C et al (2017) The high-quality genome of Brassica napus cultivar ‘ZS11’ reveals the introgression history in semi-winter morphotype. Plant J 92:452–468
Thimm O, Bläsing O, Gibon Y, Nagel A, Meyer S, Krüger P, Selbig J, Müller LA, Rhee SY, Stitt M (2004) Mapman: a user-driven tool to display genomics data sets onto diagrams of metabolic pathways and other biological processes. Plant J 37:914–939
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2012) Windows QTL cartographer 2.5. Department of statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh
Wang X, Wang H, Long Y, Li D, Yin Y, Tian J, Chen L, Liu L, Zhao W, Zhao Y, Yu L, Li M (2013) Identification of QTLs associated with oil content in a high-oil Brassica napus cultivar and construction of a high-density consensus map for QTLs comparison in B. napus. PLoS ONE 8:e80569
Wang J, Jian H, Wei L, Qu C, Xu X, Lu K, Qian W, Li J, Li M, Liu L (2015a) Genome-wide analysis of seed acid detergent lignin (ADL) and hull content in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). PLoS ONE 10:e0145045
Wang X, Wang H, Long Y, Liu L, Zhao Y, Tian J, Zhao W, Li B, Chen L, Chao H, Li M (2015b) Dynamic and comparative QTL analysis for plant height in different developmental stages of Brassica napus L. Theor Appl Genet 128:1175–1192
Wittkop B, Snowdon RJ, Friedt W (2009) Status and perspectives of breeding for enhanced yield and quality of oilseed crops for Europe. Euphytica 170:131–140
Zou C, Wang PX, Xu YB (2016) Bulked sample analysis in genetics, genomics and crop improvement. Plant Biotechnol J 14:1941–1955
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2015CB150205), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31671721) and New Century Talents Support Program of the Ministry of Education of China (NCET110172).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LM carried out the QTL analysis and wrote the manuscript. HC and HL analyzed the data. LC, WZ and BL participated in the field experiment. HW, LZ and BW provided helpful suggestions for the manuscript. ML designed, led and coordinated the overall study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standards
The authors declare that the experiments comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Additional information
Communicated by Heiko C. Becker.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, L., Chao, H., Chen, L. et al. Stable and novel QTL identification and new insights into the genetic networks affecting seed fiber traits in Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 132, 1761–1775 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03313-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03313-4