Abstract
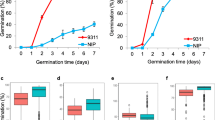
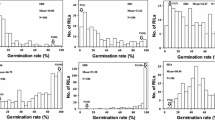
Seed dormancy in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) is one of the most important parameters affecting malting. Seed dormancy is quantitatively inherited and variously influenced by the environment. The objectives of the present study were to determine the genome location and effects of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) involved in the expression of seed dormancy in a barley cross between two varieties derived from different germplasm pools. Using a doubled-haploid population of 107 lines of the cross between the malting types Triumph (two-row, dormant) and Morex (six-row, non-dormant), seed dormancy phenotypic data sets from five environments and a 147-marker linkage map were developed in order to perform QTL analyses with simple interval map** and simplified composite interval map** procedures. Two different types of variables were considered for seed dormancy characterization: (1) level of dormancy induced during seed development, which was indirectly measured as germination percentage at 3 days and 7 days, GP3 and GP7 respectively; (2) rate of dormancy release in the course of a period after seed harvest (after-ripening). Different mechanisms of genetic control were detected for these two types of dormancy-related traits. A major and consistent dormancy QTL near the centromere on chromosome 7(5H) was associated with the establishment of dormancy during seed development and accounted for 52% and 33% of the variability for GP3 and GP7, respectively. Two other QTLs located in the vicinity of the vrs1 locus on chromosome 2(2H) and near the long arm telomere on chromosome 7(5H) explained 9% and 19% of variation, respectively, for the rate of dormancy release during after-ripening. Likewise, seed dormancy was assessed in an F2 population derived from the cross between two dormant types of distinct germplasm groups, Triumph (European, two-row, malt) and Steptoe (North American, six-row, feed), which showed similar but not identical genetic control for dormancy. Interestingly, there is remarkable dormancy QTL conservation in both regions on chromosome 7(5H) identified in this study and among other barley map** populations. These widely conserved QTLs show potential as targets for selection of a moderate level of seed dormancy in breeding programs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOSA (1988) Association of Official Seed Analysis for testing seeds. J Seed Technol 12
Ayoub M, Symons SJ, Edney MJ, Mather DE (2002) QTLs affecting kernel size and shape in a two-rowed by six-rowed barley cross. Theor Appl Genet 105:237–247
Becker J, Heun M (1995) Barley microsatellites: allele variation and map**. Plant Mol Biol 27:835–845
Buraas T, Skinnes H (1984) Genetic investigations on seed dormancy in barley. Hereditas 101:235–244
Costa JM, Corey A, Hayes PM, Jobet C, Kleinhofs A, Kopisch-Obusch A, Kramer SF, Kudrna D, Li M, Riera-Lizarazu O, Sato K, Szucs P, Too**da T, Vales MI, Wolfe RI (2001) Molecular map** of the Oregon Wolfe barleys: a phenotypically polymorphic doubled-haploid population. Theor Appl Genet 103:415–424
EBC (1987) European brewery convention. Analytica EBC, 4th edn. Brauerei und Gertränke Rundschau, Zurich
Foley ME (2001) Seed dormancy: an update on terminology, physiological genetics, and quantitative trait loci regulating germinability. Weed Sci 49:305–317
Franckowiack J (1997) Revised linkage maps for morphological markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Barley Genet Newsl 26:9–21
Gao W, Clancy JA, Han F, Prada D, Kleinhofs A, Ullrich SE (2003) Molecular dissection of a dormancy QTL region near the chromosome 7(5H) L telomere in barley. Theor Appl Genet 107:552–559
Han F, Ullrich SE, Clancy JA, Jitkov V, Kilian A, Romagosa I (1996) Verification of barley seed dormancy loci via linked molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 92:87–91
Han F, Ullrich SE, Clancy JA, Romagosa I (1999) Inheritance and fine map** of a major barley seed dormancy QTL. Plant Sci 143:113–118
Karakousis A, Kretschmer J, Manning S, Chalmers K, Langridge P (1996) The Australian barley genome map** project. Available on-line at: http://greengenes.cit.cornell.edu/WaiteQTL
King RW (1989) Physiology of sprouting resistance. In: Derera NF (ed) Pre-harvest field sprouting of cereals. CRC Press, New York, pp 27–55
Kleinhofs A, Kilian A, Saghai-Maroof MA, Biyashev RM, Hayes PM, Chen FQ, Lapitan N, Fenwick A, Blake TK, Kanazin V, Ananiev E, Dahleen L, Kudrna D, Bollinger J, Knapp SJ, Liu B, Sorrells M, Heun M, Franckowiack JD, Hoffman D, Skadsen R, Steffenson BJ (1993) A molecular, isozyme and morphological map of barley genome. Theor Appl Genet 86:705–712
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincon SE, Newburg L (1987) mapmaker: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Marquez-Cedillo LA, Hayes PM, Jones BL, Kleinhofs A, Legge WG, Rossnagel BG, Sato K, Ullrich SE, Wesenberg DM (2000) NABGMP: QTL analysis of malting quality in barley based on the doubled-haploid progeny of two elite North American varieties representing different germplasm groups. Theor Appl Genet 101:173–184
Oberthur L, Blake TK, Dyer WE, Ullrich SE (1995) Genetic analysis of seed dormancy QTL in reciprocal backcross populations. Available on-line at: J Agric Genomics http://www.ncrg.org/jag/papers95/paper596/index595.html
Qi X, Lindhout P (1997) Development of AFLP markers in barley. Mol Gen Genet 254:330–336
Ramsay L, Macaulay M, Degli-Ivanissevich S, MacLean K, Cardle L, Fuller J, Edwards KJ, Tuvesson S, Morgante M, Massari A, Maestri E, Marmiroli N, Sjakste T, Ganal M, Powell W, Waugh R (2000) A simple sequence repeat-based linkage map of barley. Genetics 156:1997–2005
Romagosa I, Han F, Clancy JA, Ullrich SE (1999) Individual locus effects on dormancy during seed development and after-ripening in barley. Crop Sci 39:74–79
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KA, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
SAS Institute (2001) SAS user’s guide statistics, ver. 8. SAS Institute, Cary, N.C.
Sayed-Tabatabaei BE, Komatsuda T, Takaiwa F, Graner A (1999) DNA sequencing and primer designing for RFLP clones evenly distributed in the barley genome. Barley Genet Newsl 28:15–18
Simpson GM (1990) Seed dormancy in grasses. Cambridge University Press, New York
Takeda K (1996) Varietal variation and inheritance of seed dormancy in barley. In: Noda K, Mares DJ (eds) Proc 7th Int Symp Pre-harvest Sprouting Cereals. Center for Academic Societies of Japan, Osaka, pp 205–212
Tanksley SD (1993) Map** polygenes. Annu Rev Genet 27:205–233
Thomas WT, Powell W, Swanston JS, Ellis RP, Chalmers KJ, Barua UM, Jack P, Lea V, Forster BP, Waugh R, Smith DB (1996) Quantitative trait loci for germination and malting quality characters in a spring barley cross. Crop Sci 36:265–273
Tinker NA, Mather DE (1995) mqtl: software for simplified composite interval map** of QTL in multiple environments. Available on-line at: J Agric Genomics http://www.ncrg.org/jag/papers95/paper295/index295.html
Tinker NA, Mather DE, Rossnagel BG, Kasha KJ, Kleinhofs A, Hayes PM, Falk DE, Ferguson T, Shugar LP, Legge WG, Irvine RB, Choo TM, Briggs KG, Ullrich SE, Franckowiack JD, Blake TK, Graf RJ, Dofing SM, Shagai-Maroof MA, Scoles GJ, Hoffman D, Dahleen LS, Kilian A, Chen F, Biyashev RM, Kudrna DA, Steffenson BJ (1996) Regions of the genome that affect agronomic performance in two-row barley. Crop Sci 36:1053–1062
Ullrich SE, Hayes PM, Dyer WE, Blake TK, Clancy JA (1993) Quantitative trait locus analysis of seed dormancy in “Steptoe” barley. In: Walker-Simmons MK, Reid JL (eds) Proc 6th Int Symp Pre-harvest Sprouting Cereals. Am Assoc Cereal Chemist, St Paul, Minn., pp 136–145
Ullrich SE, Han F, Blake TK, Oberthur L, Dyer WE, Clancy JA (1995) Seed dormancy in barley: genetic resolution and relationship to other traits. In: Noda K, Mares DJ (eds) Proc 7th Int Symp Pre-harvest Sprouting Cereals. Center for Academic Societies of Japan, Osaka, pp 157–163
Ullrich SE, Han F, Gao W, Prada D, Clancy JA, Kleinhofs A, Romagosa I, Molina-Cano JL (2002) Summary of QTL analyses of the seed dormancy trait in barley. Barley Newsl 45:39–41. Available on-line at: http://wheat.pw.usda.gov/ggpages/BarleyNewsletter/45/Proceedings1.htm
Vos P, Hogers M, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Le T, Hornes M, Frijiters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Vadim Jitkov and Mellissa Dugger for assistance in the field. The financial support of the Comisión Interministerial de Ciencia y Tecnología (Competitive Grants AGF98-0251-C03–01 and AGF99-1024), which funded the Spanish teams, and of the North American Barley Genome Project through USDA-CSREES Special Grant Contract no. C0203A-02, Project 4206 and the Washington State Agricultural Research Center Project 1006 to the USA team are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Langridge
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prada, D., Ullrich, S.E., Molina-Cano, J.L. et al. Genetic control of dormancy in a Triumph/Morex cross in barley. Theor Appl Genet 109, 62–70 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1608-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1608-x