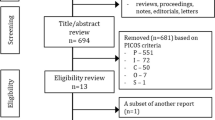
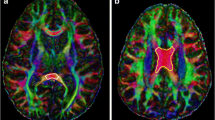
Abstract
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) can detect subtle manifestations of white matter (WM) injury following paediatric radiotherapy, which may be a potential biomarker for cognitive changes. This study aimed to synthesise the relationships between DTI indices and cognitive changes following paediatric radiotherapy through systematic review and meta-analysis. PubMed and Scopus electronic databases were used to identify eligible studies. Quality assessment was performed using the National Institute of Health (NIH) Quality Assessment Tool for Observational Cohort and Cross-Sectional Studies. Information on demographics, DTI changes, and associations to cognitive outcomes were extracted. Meta-analyses were performed on DTI changes in specific anatomical locations. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were followed in the preparation of this report. Eighteen studies were included (median study size: 21; range 18–146). 17/18 studies showed significant cognitive decline following irradiation. Meta-analyses found significant cognitive changes within patient’s group of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL; standard mean differences [SMD] = −0.075, P = 0.01) and brain tumours (BT; SMD = −1.037, P ≤ 0.001) compared to control/baseline. Both groups also had significantly lower fractional anisotropy (FA) scores in the corpus callosum (ALL: SMD = −0.979, P = 0.002; BT: SMD = −1.025, P < 0.001). Decreased FA was consistently associated with cognitive decline. Correlation on WMFA integrity to cognitive domains was statistically significant (Z = 9.86, P < 0.001) with a large effect size (r = 0.52). White matter tract integrity of the corpus callosum measured with FA has the potential to be a biomarker for radiotherapy-related cognitive decline. Inclusion of DTI in follow-up imaging should be encouraged.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yahya N, Manan HA (2021) Neurocognitive impairment following proton therapy for paediatric brain tumour: a systematic review of post-therapy assessments. Support Care Cancer 29:3035–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-020-05808-z
Schulte F, Kunin-Batson AS, Olson-Bullis BA et al (2019) Social attainment in survivors of pediatric central nervous system tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis from the Children’s Oncology Group. J Cancer Surviv 13(6):921–931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-019-00808-3
Saatci D, Thomas A, Botting B, Sutcliffe AG (2019) Educational attainment in childhood cancer survivors: a meta-analysis. Arch Dis Child. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2019-317594
Frost MH, Sloan JA (2002) Quality of life measurements: a soft outcome—or is it? Am J Manag Care 8:S574–S579
Yahya N, Manan HA (2021) Diffusion tensor imaging indices to predict cognitive changes following adult radiotherapy. Eur J Cancer Care 30(1):e13329. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecc.13329
Makale MT, McDonald CR, Hattangadi-Gluth JA, Kesari S (2016) Mechanisms of radiotherapy-associated cognitive disability in patients with brain tumours. Nat Rev Neurol 13(1):52–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2016.185
Ryan NP, Genc S, Beauchamp MH et al (2017) White matter microstructure predicts longitudinal social cognitive outcomes after paediatric traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Psychol Med 48(4):679–691. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0033291717002057
Rogalski E, Stebbins GT, Barnes CA et al (2012) Age-related changes in parahippocampal white matter integrity: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Neuropsychologia 50(8):1759–1765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.03.033
Fünfschilling U, Supplie LM, Mahad D et al (2013) Glycolytic oligodendrocytes maintain myelin and long-term axonal integrity. Nature 485:517–521
Lee Y, Morrison BM, Li Y et al (2012) Oligodendroglia metabolically support axons and contribute to neurodegeneration. Nature 487:443–448
Filley CM, Fields RD (2016) White matter and cognition: making the connection. J Neurophysiol 116(5):2093–2104. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00221.2016
Lawrence YR, Li XA, el Naqa I et al (2010) Radiation dose–volume effects in the brain. Int J Radiat Oncol 76(3):20–S7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.02.091
Kassubek R, Gorges M, Westhoff MA, Ludolph AC, Kassubek J, Müller HP (2017) Cerebral microstructural alterations after radiation therapy in high-grade glioma: a diffusion tensor imaging-based study. Front Neurol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2017.00286
Neil JJ, Shiran SI, McKinstry RC, Schefft GL, Snyder AZ, Almli CR, Akbudak E, Aronovitz JA, Miller JP, Lee BC, Conturo TE (1998) Normal brain in human newborns: apparent diffusion coefficient and diffusion anisotropy measured by using diffusion tensor MR imaging. Radiology 209:57–66
Suzuki Y, Matsuzawa H, Kwee IL, Nakada T (2003) Absolute eigenvalue diffusion tensor analysis for human brain maturation. NMR Biomed 16:257–260
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339:b2535. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2535
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M et al (2015) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P)2015 statement. Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000100. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100
Wallace BC, Dahabreh IJ et al (2012) Closing the gap between methodologists and end-users: R as a computational back-end. J Stat Softw 49(5):1–15
Suurmond R, van Rhee H, Hak T (2017) Introduction, comparison and validation of Meta-Essentials: a free and simple tool for meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods 8(4):537–553. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1260
Partanen M, Bouffet E, Laughlin S et al (2018) Early changes in white matter predict intellectual outcome in children treated for posterior fossa tumours. Neuroimage Clin 20:697–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2018.09.005
Glass JO, Ogg RJ, Hyun JW, Harreld JH et al (2017) Disrupted development and integrity of frontal white matter in patients treated for pediatric medulloblastoma. Neuro-Oncology. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nox062
Redmond KJ, Hildreth M, Sair HI et al (2018) Association of neuronal injury in the genu and body of corpus callosum after cranial irradiation in children with impaired cognitive control: a prospective study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 101(5):1234–1242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.04.037
Rueckriegel SM, Bruhn H, Thomale UW, Driever PH (2015) Cerebral white matter fractional anisotropy and tract volume as measured by MR imaging are associated with impaired cognitive and motor function in pediatric posterior fossa tumor survivors. Pediatr Blood Cancer 62:1252–1258. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.25485
Follin C, Svärd D, van Westen D et al (2019) Microstructural white matter alterations associated to neurocognitive deficits in childhood leukemia survivors treated with cranial radiotherapy—a diffusion kurtosis study. Acta Oncol 58(7):1021–1028. https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2019.1571279
Schuitema I, Deprez S, Van Hecke W et al (2013) Accelerated aging, decreased white matter integrity, and associated neuropsychological dysfunction 25 years after pediatric lymphoid malignancies. J Clin Oncol 31:3378–3388. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2012.46.7050
Edelmann MN, Krull KR, Liu W et al (2014) Diffusion tensor imaging and neurocognition in survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Brain 137:2973–2983. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awu230
Moxon-Emre I, Farb NAS, Oyefiade AA et al (2019) Facial emotion recognition in children treated for posteriro fossa tumours and typically develo** children: a divergence or predictors. Neuroimage Clin 23:101886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101886
Aukema EJ, Caan MWA, Oudhuis N et al (2009) White matter fractional anisotropy correlated with speed of processing and motor speed in young childhood cancer survivors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74(3):837–843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.08.060
King TZ, Wang L, Mao H (2015) Disruption of white matter integrity in adult survivors of childhood brain tumors: correlated with long-term intellectual outcomes. PLoS ONE 10(7):e131744. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0131744
Khong PL, Leung L, Fung A et al (2006) White matter anisotropy in post-treatment childhood cancer survivors: preliminary evidence of association with neurocognitive function. J Clin Oncol 24:884–890. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.02.4505
Smith KM, King TZ, Jayakar R, Morris RD (2014) Reading skill in adult survivors of childhood brain tumor: a theory-based neurocognitive model. Neuropsychology 28(3):448–458. https://doi.org/10.1037/neu0000056
Aleksonis HA, Wier R, Pearson MM et al (2019) Associations among diffusion tensor imaging and neurocognitive function in survivors of pediatric brain tumor: a pilot study. Appl Neuropsychol Child. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622965.2019.1613993
Palmer SL, Glass JO, Li Y et al (2012) White matter integrity is associated with cognitive processing in patients treated for posterior fossa brain tumor. Neuro-Oncology 14(9):1185–1193. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nos154
Padovani L, André N, Constine LS, Muracciole X (2012) Neurocognitive function after radiotherapy for paediatric brain tumours. Nat Rev Neurol 8:578–588. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2012.182
Ajithkumar T, Price S, Horan G, Burke A, Jefferies S (2017) Prevention of radiotherapy-induced neurocognitive dysfunction in vors of paediatric brain tumours: the potential role of modern imaging and radiotherapy techniques. Lancet Oncol 18:e91–e100
Tsang DS, Kim L, Liu ZA et al (2020) Intellectual changes after radiation for children with brain tumors: which brain structures are most important? Neuro-Oncology 23(3):487–197. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noaa217
Palmer SL, Reddick WE, Glass JO et al (2010) Regional white matter anisotropy and reading ability in patients treated for pediatric embryonal tumors. Brain Imaging Behav 4:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-010-9092-1
Duc NM (2020) The role of diffusion tensor imaging metrics in the discrimination between cerebellar medulloblastoma and brainstem glioma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.28468
Connor M, Karunamuni R, McDonald C et al (2017) Regional susceptibility to dose-dependent white matter damage after brain radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 123(2):209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2017.04.006
Chen HF, Huang LL, Li HY et al (2020) Microstructural disruption of the right inferior fronto-occipital and inferior longitudinal fasciculus contributes to WMH-related cognitive impairment. CNS Neurosci Ther 26:576–588. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13283
Sorg SF, Schiehser DM, Bondi MW et al (2016) White matter microstructural compromise is associated with cognition but not posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms in military veterans with traumatic brain injury. J Head Trauma Rehabil 31:297–230
McKenna BS, Theilmann RJ, Sutherland AN et al (2015) Fusing functional MRI and diffusion tensor imaging measures of brain function and structure to predict working memory and processing speed performance among inter-episode bipolar patients. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 21:330–341
Tuladhar AM, van Norden AG, de Laat KF et al (2015) White matter integrity in small vessel disease is related to cognition. Neuroimage Clin 7:518–524
de Groot JC, de Leeuw FE, Oudkerk M et al (2000) Cerebral white matter lesions and cognitive function: the Rotterdam Scan Study. Ann Neurol 47:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1002/1531-8249(200002)47:2〈145:aid-ana3〉3.3.co;2‑g
Scantlebury N, Strother D, Bouffet E et al (2016) White matter and information processing speed following treatment with cranial-spinal radiation for pediatric brain tumor. Neuropsychology 30(4):425–438. https://doi.org/10.1037/neu0000258
Brinkman TM, Reddick WE, Luxton J et al (2012) Cerebral white matter integrity and executive function in adult survivors of childhood medulloblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 14:iv25–iv36. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nos214
Voon NS, Manan HA, Yahya N (2021) Cognitive Decline following Radiotherapy of Head and Neck Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of MRI Correlates. Cancers 13(24):6191. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246191
Voon NS, Lau FN, Zakaria R et al (2021) MRI-based brain structural changes following radiotherapy of Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a systematic review. Cancer Radiother 25(1):62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canrad.2020.07.008
Ding Z, Zhang H, Lv XF et al (2018) Radiation-induced brain structural and functional abnormalities in presymptomatic phase and outcome prediction. Hum Brain Mapp 39(1):407–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23852
Law N, Bouffet E, Laughlin S et al (2011) Cerebello-thalamo-cerebral connections in pediatric brain tumor patients: impact on working memory. Neuroimage 56:2238–2248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.03.06
Yahya N, Manan HA (2019) Utilisation of diffusion tensor imaging in Intracranial radiotherapy and radiosurgery planning for white matter dose optimization: a systematic review. World Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.06.027
O’Sullivan M, Morris RG, Huckstep B et al (2004) Diffusion tensor MRI correlates with executive dysfunction in patients with ischaemic leukoaraiosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75(3):441–447. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2003.014910
Turken A, Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Bammer R et al (2008) Cognitive processing speed and the structure of white matter pathways: convergent evidence from normal variation and lesion studies. Neuroimage 42(2):1032–1044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.03.057
Deprez S, Amant F, Yigit R et al (2011) Chemotherapy-induced structural changes in cerebral white matter and its correlation with impaired cognitive functioning in breast cancer patients. Hum Brain Mapp 32(3):480–493. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.21033
Welzel T, Niethammer A, Mende U et al (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging screening of radiation-induced changes in the white matter after prophylactic cranial irradiation of patients with small cell lung cancer: first results of a prospective study. Am J Neuroradiol 29(2):379–383. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0797
Duan F, Cheng J, Jiang J et al (2016) Whole-brain changes in white matter microstructure after radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273(12):4453–4459
Agbahiwe H, Rashid A, Horska A et al (2017) A prospective study of cerebral frontal lobe, and temporal lobe volume and neuropsychological performance in children with primary brain tumors treated with cranial radiation. Cancer 123(1):161–168. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30313
Bradshaw M, Wefel J (2014) The neuropsychology of oncology. In: Parsons M, Hammeke T (eds) Clinical neuropsychology: a pocket handbook for assessment, 3rd edn. American Psychological Association, Washington DC, pp 313–337
Moxon-Emre I, Bouffet E, Taylor MD et al (2014) Impact of craniospinal dose, boost volume, and neurologic complications on intellectual outcome in patients with medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol 32:1760–1768
Moxon-Emre I, Bouffet E, Taylor MD et al (2016a) Vulnerability of white matter to insult during childhood: evidence from patients treated for medulloblastoma. J Neurosurg Pediatr 18:29–40
Yahya N, Manan H (2020) Neurocognitive impairment following proton therapy for paediatric brain tumour: a systematic review of post-therapy assessments. Support Care Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-020-05808-z
Schagen SB, Muller MJ, Boogerd W et al (2002) Late effects of adjuvant chemtherapy on cognitive function: a follow-up study in breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol 13(9):1387–1397
Winocur G, Vardy J, Binns MA, Kerr L, Tannock I (2006) The effects of the anti-cancer drugs, methotrexate and 5‑fluorouracil, on cognitive function in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85(1):66–75
Uh J, Merchant TE, Conklin HM et al (2021) Diffusion tensor imaging-based analysis of baseline neurocognitive function and post-treatment white matter changes in pediatric patients with craniopharyngioma treated with surgery and proton therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 109(2):515–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.08.060
Hunsche S, Moseley ME, Stoeter P, Hedehus M (2001) Diffusion-tensor MR imaging at 1.5 and 3.0 T: initial observations. Radiology 221:550–556
Sjoerd BV, Derek KJ, Max AV, Alexander L (2011) Partial volume effect as a hidden covariate in DTI analyses. Neuroimage 55:1566–1576
Wheeler-Kingshot CAM, Cercignani M (2009) About “axial” and “radial” diffusivities. Magn Reson Med 61(5):1255–1260. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.21965
Watts R, Thomas A, Filippi CG, Nickerson JP, Freeman K (2014) Potholes and molehills: bias in the diagnostic performance of diffusion-tensor imaging in concussion. Radiology 272(1):217–223. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.14131856
Thomas C, Ye FQ, Irfanoglu MO et al (2014) Anatomical accuracy of brain connections derived from diffusion MRI tractography is inherently limited. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(46):16574–16579. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1405672111
Funding
This work was funded by the Ministry of Higher Learning (Malaysia) – Fundamental Research Grant (FRGS/1/2021/SS03/UKM/02/1) to NY and HAM and the National University of Malaysia under grants FF-2020-013 to HAM, NAY and NSV and GP-2021-K017963 to NAY.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, literature search and data analysis were performed by Noor Shatirah Voon, Noorazrul Yahya and Hanani A. Manan. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Noor Shatirah Voon and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
N.S. Voon, H.A. Manan and N. Yahya declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Availability of data and material
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voon, N.S., Manan, H.A. & Yahya, N. Diffusion tensor imaging indices as biomarkers for cognitive changes following paediatric radiotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Strahlenther Onkol 198, 409–426 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-022-01905-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-022-01905-6