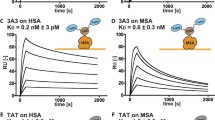
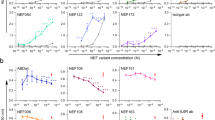
Abstract
Affinity proteins based on small scaffolds are currently emerging as alternatives to antibodies for therapy. Similarly to antibodies, they can be engineered to have high affinity for specific proteins. A potential problem with small proteins and peptides is their short in vivo circulation time, which might limit the therapeutic efficacy. To circumvent this issue, we have engineered bispecificity into an albumin-binding domain (ABD) derived from streptococcal Protein G. The inherent albumin binding was preserved while the opposite side of the molecule was randomized for selection of high-affinity binders. Here we present novel ABD variants with the ability to bind to the epidermal growth factor receptor 3 (ErbB3). Isolated candidates were shown to have an extraordinary thermal stability and affinity for ErbB3 in the nanomolar range. Importantly, they were also shown to retain their affinity to albumin, hence demonstrating that the intended strategy to engineer bispecific single-domain proteins against a tumor-associated receptor was successful. Moreover, competition assays revealed that the new binders could block the natural ligand Neuregulin-1 from binding to ErbB3, indicating a potential anti-proliferative effect. These new binders thus represent promising candidates for further development into ErbB3-signaling inhibitors, where the albumin interaction could result in prolonged in vivo half-life.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weiner LM, Surana R, Wang S (2010) Monoclonal antibodies: versatile platforms for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 10(5):317–327. doi:10.1038/nri2744
Scott AM, Wolchok JD, Old LJ (2012) Antibody therapy of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 12(4):278–287. doi:10.1038/nrc3236
Lofblom J, Frejd FY, Stahl S (2011) Non-immunoglobulin based protein scaffolds. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22(6):843–848. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2011.06.002
Gebauer M, Skerra A (2009) Engineered protein scaffolds as next-generation antibody therapeutics. Curr Opin Chem Biol 13(3):245–255. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.04.627
Gilbreth RN, Koide S (2012) Structural insights for engineering binding proteins based on non-antibody scaffolds. Curr Opin Struct Biol 22(4):413–420. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2012.06.001
Zahnd C, Kawe M, Stumpp MT, de Pasquale C, Tamaskovic R, Nagy-Davidescu G, Dreier B, Schibli R, Binz HK, Waibel R, Pluckthun A (2010) Efficient tumor targeting with high-affinity designed ankyrin repeat proteins: effects of affinity and molecular size. Cancer Res 70(4):1595–1605. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2724
Schmidt MM, Wittrup KD (2009) A modeling analysis of the effects of molecular size and binding affinity on tumor targeting. Mol Cancer Ther 8(10):2861–2871. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0195
Kontermann RE (2009) Strategies to extend plasma half-lives of recombinant antibodies. BioDrugs 23(2):93–109. doi:10.2165/00063030-200923020-00003
Kratz F, Elsadek B (2012) Clinical impact of serum proteins on drug delivery. J Control Release 161(2):429–445. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.11.028
Anderson CL, Chaudhury C, Kim J, Bronson CL, Wani MA, Mohanty S (2006) Perspective–FcRn transports albumin: relevance to immunology and medicine. Trends Immunol 27(7):343–348. doi:10.1016/j.it.2006.05.004
Stork R, Campigna E, Robert B, Muller D, Kontermann RE (2009) Biodistribution of a bispecific single-chain diabody and its half-life extended derivatives. J Biol Chem 284(38):25612–25619. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.027078
Hopp J, Hornig N, Zettlitz KA, Schwarz A, Fuss N, Muller D, Kontermann RE (2010) The effects of affinity and valency of an albumin-binding domain (ABD) on the half-life of a single-chain diabody-ABD fusion protein. Protein Eng Des Sel 23(11):827–834. doi:10.1093/protein/gzq058
Hutt M, Farber-Schwarz A, Unverdorben F, Richter F, Kontermann RE (2012) Plasma half-life extension of small recombinant antibodies by fusion to immunoglobulin-binding domains. J Biol Chem 287(7):4462–4469. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.311522
Unverdorben F, Färber-Schwarz A, Richter F, Hutt M, Kontermann RE (2012) Half-life extension of a single-chain diabody by fusion to domain B of staphylococcal Protein A. Protein Eng Des Sel 25(2):81–88. doi:10.1093/protein/gzr061
Dennis MS, ** H, Dugger D, Yang R, McFarland L, Ogasawara A, Williams S, Cole MJ, Ross S, Schwall R (2007) Imaging tumors with an albumin-binding Fab, a novel tumor-targeting agent. Cancer Res 67(1):254–261. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2531
Tolmachev V, Orlova A, Pehrson R, Galli J, Baastrup B, Andersson K, Sandstrom M, Rosik D, Carlsson J, Lundqvist H, Wennborg A, Nilsson FY (2007) Radionuclide therapy of HER2-positive microxenografts using a 177Lu-labeled HER2-specific Affibody molecule. Cancer Res 67(6):2773–2782. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1630
Andersen JT, Pehrson R, Tolmachev V, Daba MB, Abrahmsen L, Ekblad C (2011) Extending half-life by indirect targeting of the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) using a minimal albumin-binding domain. J Biol Chem 286(7):5234–5241. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.164848
Wunder A, Stehle G, Schrenk HH, Hartung G, Heene DL, Maier-Borst W, Sinn H (1998) Antitumor activity of methotrexate-albumin conjugates in rats bearing a Walker-256 carcinoma. Int J Cancer 76(6):884–890. doi:10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19980610)76:6<884:aid-ijc19>3.0.co;2-2
Stehle G, Sinn H, Wunder A, Schrenk HH, Stewart JC, Hartung G, Maier-Borst W, Heene DL (1997) Plasma protein (albumin) catabolism by the tumor itself-implications for tumor metabolism and the genesis of cachexia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 26(2):77–100
Jain RK (1988) Determinants of tumor blood flow: a review. Cancer Res 48(10):2641–2658
Burger AM, Hartung G, Stehle G, Sinn H, Fiebig HH (2001) Pre-clinical evaluation of a methotrexate–albumin conjugate (MTX-HSA) in human tumor xenografts in vivo. Int J Cancer 92(5):718–724
Subramanian GM, Fiscella M, Lamouse-Smith A, Zeuzem S, McHutchison JG (2007) Albinterferon alpha-2b: a genetic fusion protein for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Nat Biotechnol 25(12):1411–1419. doi:10.1038/nbt1364
Metzner HJ, Weimer T, Kronthaler U, Lang W, Schulte S (2009) Genetic fusion to albumin improves the pharmacokinetic properties of factor IX. Thromb Haemost 102(4):634–644. doi:10.1160/TH09-04-0255
Flisiak R, Flisiak I (2010) Albinterferon-alpha 2b: a new treatment option for hepatitis C. Expert Opin Biol Ther 10(10):1509–1515. doi:10.1517/14712598.2010.521494
Alm T, Yderland L, Nilvebrant J, Halldin A, Hober S (2010) A small bispecific protein selected for orthogonal affinity purification. Biotechnol J 5(6):605–617. doi:10.1002/biot.201000041
Nilvebrant J, Alm T, Hober S, Lofblom J (2011) Engineering bispecificity into a single albumin-binding domain. PLoS ONE 6(10):e25791. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025791
Makrides SC, Nygren PA, Andrews B, Ford PJ, Evans KS, Hayman EG, Adari H, Uhlen M, Toth CA (1996) Extended in vivo half-life of human soluble complement receptor type 1 fused to a serum albumin-binding receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277(1):534–542
Ahmad JN, Li J, Biedermannova L, Kuchar M, Sipova H, Semeradtova A, Cerny J, Petrokova H, Mikulecky P, Polinek J, Stanek O, Vondrasek J, Homola J, Maly J, Osicka R, Sebo P, Maly P (2012) Novel high-affinity binders of human interferon gamma derived from albumin-binding domain of Protein G. Proteins 80(3):774–789. doi:10.1002/prot.23234
Linhult M, Binz HK, Uhlen M, Hober S (2002) Mutational analysis of the interaction between albumin-binding domain from streptococcal Protein G and human serum albumin. Protein Sci 11(2):206–213. doi:10.1110/ps.02802
Kraulis PJ, Jonasson P, Nygren PA, Uhlen M, Jendeberg L, Nilsson B, Kordel J (1996) The serum albumin-binding domain of streptococcal Protein G is a three-helical bundle: a heteronuclear NMR study. FEBS Lett 378(2):190–194
Cramer JF, Nordberg PA, Hajdu J, Lejon S (2007) Crystal structure of a bacterial albumin-binding domain at 1.4 A resolution. FEBS Lett 581(17):3178–3182. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.06.003
Citri A, Skaria KB, Yarden Y (2003) The deaf and the dumb: the biology of ErbB-2 and ErbB-3. Exp Cell Res 284(1):54–65
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2(2):127–137. doi:10.1038/35052073
Baselga J, Swain SM (2009) Novel anticancer targets: revisiting ERBB2 and discovering ERBB3. Nat Rev Cancer 9(7):463–475. doi:10.1038/nrc2656
Schoeberl B, Pace EA, Fitzgerald JB, Harms BD, Xu L, Nie L, Linggi B, Kalra A, Paragas V, Bukhalid R, Grantcharova V, Kohli N, West KA, Leszczyniecka M, Feldhaus MJ, Kudla AJ, Nielsen UB (2009) Therapeutically targeting ErbB3: a key node in ligand-induced activation of the ErbB receptor-PI3 K axis. Sci Signal 2 (77): ra31 doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000352
Carlsson J (2012) Potential for clinical radionuclide-based imaging and therapy of common cancers expressing EGFR-family receptors. Tumor Biol 33(3):653–659. doi:10.1007/s13277-011-0307-x
Linggi B, Carpenter G (2006) ErbB-4 s80 intracellular domain abrogates ETO2-dependent transcriptional repression. J Biol Chem 281(35):25373–25380. doi:10.1074/jbc.M603998200
Huang X, Gao L, Wang S, McManaman JL, Thor AD, Yang X, Esteva FJ, Liu B (2010) Heterotrimerization of the growth factor receptors erbB2, erbB3, and insulin-like growth factor-i receptor in breast cancer cells resistant to herceptin. Cancer Res 70(3):1204–1214. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3321
Sergina NV, Rausch M, Wang D, Blair J, Hann B, Shokat KM, Moasser MM (2007) Escape from HER-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy by the kinase-inactive HER3. Nature 445(7126):437–441. doi:10.1038/nature05474
Foreman PK, Gore M, Kobel PA, Xu L, Yee H, Hannum C, Ho H, Wang SM, Tran HV, Horowitz M, Horowitz L, Bhatt RR (2012) ErbB3 inhibitory surrobodies inhibit tumor cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 11(7):1411–1420. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0068
Grovdal LM, Kim J, Holst MR, Knudsen SL, Grandal MV, van Deurs B (2012) EGF receptor inhibitors increase ErbB3 mRNA and protein levels in breast cancer cells. Cell Signal 24(1):296–301. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.09.012
Vaught DB, Stanford JC, Young C, Hicks DJ, Wheeler F, Rinehart C, Sanchez V, Koland J, Muller WJ, Arteaga CL, Cook RS (2012) HER3 is required for HER2-induced preneoplastic changes to the breast epithelium and tumor formation. Cancer Res 72(10):2672–2682. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3594
Amin DN, Sergina N, Lim L, Goga A, Moasser MM (2012) HER3 signalling is regulated through a multitude of redundant mechanisms in HER2-driven tumour cells. Biochem J 447(3):417–425. doi:10.1042/BJ20120724
Ruther U (1982) pUR 250 allows rapid chemical sequencing of both DNA strands of its inserts. Nucleic Acids Res 10(19):5765–5772
Kronqvist N, Malm M, Gostring L, Gunneriusson E, Nilsson M, Hoiden Guthenberg I, Gedda L, Frejd FY, Stahl S, Lofblom J (2011) Combining phage and staphylococcal surface display for generation of ErbB3-specific affibody molecules. Protein Eng Des Sel 24(4):385–396. doi:10.1093/protein/gzq118
Nilsson B, Moks T, Jansson B, Abrahmsen L, Elmblad A, Holmgren E, Henrichson C, Jones TA, Uhlen M (1987) A synthetic IgG-binding domain based on staphylococcal Protein A. Protein Eng 1(2):107–113
Johansson MU, Frick IM, Nilsson H, Kraulis PJ, Hober S, Jonasson P, Linhult M, Nygren PA, Uhlen M, Bjorck L, Drakenberg T, Forsen S, Wikstrom M (2002) Structure, specificity, and mode of interaction for bacterial albumin-binding modules. J Biol Chem 277(10):8114–8120. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109943200
Gulich S, Linhult M, Nygren P, Uhlen M, Hober S (2000) Stability towards alkaline conditions can be engineered into a protein ligand. J Biotechnol 80(2):169–178
Hulme EC, Trevethick MA (2010) Ligand binding assays at equilibrium: validation and interpretation. Br J Pharmacol 161(6):1219–1237. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00604.x
Hosse RJ, Rothe A, Power BE (2006) A new generation of protein display scaffolds for molecular recognition. Protein Sci 15(1):14–27. doi:10.1110/ps.051817606
Gostring L, Malm M, Hoiden-Guthenberg I, Frejd FY, Stahl S, Lofblom J, Gedda L (2012) Cellular effects of HER3-specific affibody molecules. PLoS ONE 7(6):e40023. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0040023
Lejon S, Frick IM, Bjorck L, Wikstrom M, Svensson S (2004) Crystal structure and biological implications of a bacterial albumin-binding module in complex with human serum albumin. J Biol Chem 279(41):42924–42928. doi:10.1074/jbc.M406957200
Holt LJ, Basran A, Jones K, Chorlton J, Jespers LS, Brewis ND, Tomlinson IM (2008) Anti-serum albumin domain antibodies for extending the half-lives of short-lived drugs. Protein Eng Des Sel 21(5):283–288. doi:10.1093/protein/gzm067
Dennis MS, Zhang M, Meng YG, Kadkhodayan M, Kirchhofer D, Combs D, Damico LA (2002) Albumin binding as a general strategy for improving the pharmacokinetics of proteins. J Biol Chem 277(38):35035–35043. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205854200
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Swedish Research Council (VR), the Knut and Alice Wallenberg foundation (KAW), and the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences (KVA). Prof. Per-Åke Nygren is acknowledged for scientific advice and helpful discussion.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Johan Nilvebrant and Mikael Astrand contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nilvebrant, J., Åstrand, M., Löfblom, J. et al. Development and characterization of small bispecific albumin-binding domains with high affinity for ErbB3. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 70, 3973–3985 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-013-1370-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-013-1370-9