Abstract
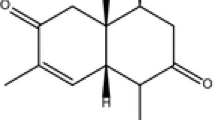
Isoalantolactone, a major constituent ofInula racemosa (Compositae) was tested for its antimicrobial action against five bacteria, six human and six plant pathogenic fungi. The lactone showed absolute toxicities at 500 μg/mL against 3 soil borne phytopathogenic fungi (Gaeumannomyces graminis var.tritici, Rhizoctonia cerealis andPhytophthora capsici) with the MICs determined to be 100, 100 and 300 μg/mL, respectively. At the MICs, isoalantolactone exhibited its fungistatic nature of toxicity. The lowest fungicidal concentrations of the lactone toG graminis var.tritici, R cerealis andP. capsici were shown to be 150, 150 and 350 μg/mL, respectively. Moreover, isoalantolactone displayed weaker antibacterial activities againstBacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas fluorecense, Sarcina lentus andStaphylococcus aureus with MICs of 125, 425, 150, 150 and 100 μg/mL, respectively. The investigation disclosed the strong inhibition of isoalantolactone to the phytopathogenic fungi, raising a possibility that the lactone could be considered as a starting point for the project aiming at the development of new fungicide(s).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shashikant, V. S., Sahai, Y. N., Trends in Environmental Pollution and Pesticide Toxicology, New Delhi: Jagmander Book Agency, 1989, 375.
Spotts, R. A., Cervantes, L. A., Population pathogenicity and benomyl resistance ofBotrytis spp.Penicillium spp. andMucor piriformis in packing house, Plant Disease, 1986, 70: 106.
Jiangsu College of New Medicine, A Comprehensive Dictionary of the Traditional Chinese Medicines (Zhong Yao Da Ci Dian), Shanghai: Shanghai People’s Press, 1977, 81.
Kirtikar, K. R., Basu, B. D., Indian Medicinal Plants, Dehradun: M/S Bisan Singh Mahendra Pal Sirgh, 1975.
Mahadevan, A., Biochemical Aspects of Plant Disease Resistance, Part I: Preformed Inhibitory Substances Prohibition, New Delhi: Today and Tomorrow’s Printers and Publishers, 1982.
Mishra, A. K., Dubey, N. K., Evaluation of some essential oils for their toxicity against fungi causing deterioration of stored food commodities, Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1994, 60 (3): 1001.
Wain, R. L., Chemical aspects of plant disease resistance, in Natural Products and the Protection of Plants (ed. Marini-Bettalo, G. B.), New York: Elsevier Scientific Publishing Co., 1977, 483.
Ruzicka, L., Pieth, P., Polyterpene und polyterpenoid LV2. Zur Kenntnis der Alantolactone, Kelvetica Chemica Acta, 1993, 14: 1090.
Tan, R. X., Tang, H. Q., Hu, J. et al., Lignans and sesquiterpene lactones fromArtemisia sieversiana andInula racemosa, Phytochemistry, 1998, 49(2): 157.
Thomson, D. P., Fungitoxic activity of essential oil components on food storage fungi, Mycologia, 1989, 81(1): 151.
Booth, C., Introduction to general methods, in Methods in Microbiology, Vol. 4, New York: Academic Press, 1989, 36.
Sedha, R. K., Dhillon, R. S., Sodhi, B. S. et al., Effect of λ methylene-γ-lactones containing essential oil of Mungbean-Rhiboium interaction, Indian Journal of Ecology, 1992, 19: 32.
Picman, A. K., Schmeider, E. F., Inhibition of fungal growth by selected sesquiterpene lactones, Biochemistry System Ecology, 1993, 21: 307.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Mishra, A.K., He, B. et al. Antimicrobial activities of isoalantolactone, a major sesquiterpene lactone ofInula racemosa . Chin.Sci.Bull. 46, 498–501 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03187267
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03187267