Abstract
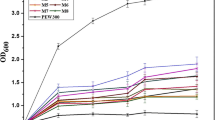
Antibacterial peptides have received increasing attention as a new pharmaceutical substance. But the molecular mechanism of lysis is still poorly understood. CMIV gene and mutant CMIV gene in GST fusion system were expressed. After cleaving with different cleavage reagents, the peptide with an excess of N-terminus and with an un-amidated C-terminus stopped the activity while the peptide with an excess Asn at the C-terminus had the activity level the same as natural CMIV. The results showed that the terminal structure of cecropin CMIV played an important role in its biological activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Shuangquan, Qu **anming, Qi Zhenwu, Insect immunity and the applied prospect of cecropin CHN,J. Biochem., 1987, 3(1): 11.
Boman, H. G., Faye, I., Hofsten, V. P. et al., On the primary structures of lysozyme, cecropins and attacins from hyalophora cecropia,Dev. Comp. Immuml., 1985, 9: 551.
Christensen, B., Fink, J., Merrifield, R. B. et al., Channel-forming properties of cecropins and related model compounds incorporated into planar lipid membranes,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1988, 85: 5072.
**e Wei, Dou Fei, Wu Haihong et al., Fusion expression of a mutant cecropin CMIV gene inE. coli, Science in China (in Chinese), Ser.C, 1997, 27: 278.
Sambrook, J., Fritish, E. F., Maniatis, T.,Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Mand, 2nd Ed., New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989.
Smith, D. B., Johnson, K. S., Single-step purification of peptides expressed inE. coli as a fusion with S-transferase,Gene, 1988, 67: 31.
Chang, J.-Y., Thrombin specificity requirement for apolar amino acids adjacent to the thrombin cleavage site of polypeptide substrate,Eur. J. Biochem., 1985, 151: 217.
Helmann, S., vonJagow, G., Tircine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of protein in the range from 1 to 100 kDa,Anal. Biochem., 1987, 166: 368.
Hultmark, D., Engstrom, A., Bennich, H. et al., Insect immunity: isolation and structure of cecropin D and four minor antibacterial component from cecropin pupae,Eur. J. Biochem., 1982, 127: 207.
Wang Liang, Wu Haihong, Dou Fei et al., High-level expression of cecropin CMIV in E.coli from a fusion construct containing the human tumor necrosis factor,Biochemistry and Mokcdar Biology Intenurtiod, 1997, 41: 1051.
Boman, H. G., Faye, I., Gudmundsson, G. H. et al., Cell-free immunity in cecropia: a model system for antibacterial proteins,Eur. J. Biochem., 1991, 201: 23.
Andreu, D., Merrifield, R. B., Steiner, H. et al., N-terminal analogs of cecropin A: synthesis, antibacterial activity and conformational properties,Biochem., 1985, 24: 1683.
Yuki Nakajima, Qu **anming, Shunji Natori, Interaction between liposomes and sarcotoxin IA, a potent antibacterial protein of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly),J. Bio. Chem., 1987, 262(4): 1665.
Wu Yingya, Liu Feipeng, Zhou Tianhong et al., Expression of cecropin fused with bFGF in yeast,Progress in Biology Engineer (in Chinese), 1998, 18(5): 11.
Loraine, S., Kushol, G., Jeffrey, N. W., The concentration-dependent membrane activity of cecmpin,Biochcm., 1997, 36: 11452.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project supported by the Jiangsu Province Applied Research Project.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dou, F., **e, W., Dong, X. et al. The terminal structure plays an important role in the biological activity of cecropin CMIV. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 42, 494–500 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02881773
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02881773