Abstract
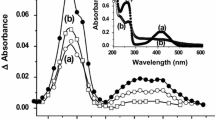
Using the electron pulse radiolytic techniques, the reactions between hydroxyl radical and tea polyphenol four constituents epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), epicatechin gallate (ECG), epigallocatechin (EGC) and epicatechin (EC) have been investigated in detail, their corresponding rate constants for scavenging hydroxyl radicals have been determined to be 1.5 × 1010, 1.4 × 1010, 9.7 × 109and 9.2 x 109 dm3-mol−1-s−1, respectively. On the basis of their structures and transient absorption spectra, the OH adducts of EGCG and ECG undergo unimolecular elimination of gallate group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zheng, R. L.,Free Radical Biology (in Chinese), Bei**g: Higher Educational Press, 1992, 1–46.
Floyd, R. A., Role of oxygen free radicals in carcinogenesis and brain ischemia,FASEB J., 1990, 4: 2587.
Lin, N. Y., Radioprotection and radiosensitization mechanisms and application,Radiat. Phys. Chem., 1986, 28: 211.
Zhou, Y. C., Zheng, R. L., Phenolic compounds and an analog as superoxide anions scavengers and antioxidants,Biochem. Pharmacol., 1991, 42: 1177.
O’Neill, P., Chapman, P. W., Potential repair of free radical adducts of dGMP and dG by a series of reductants, A pulse radiolytic study,Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 1985, 47, 71.
Yao, S. D., Sheng, S. G., Cai, J. H. et al., Nanosecond pulse radiolysis studies in China,Radiat. Phys. Chem., 1995, 46: 105.
Swallow, A. J., Applications of pulse radiolysis to the study of aqueous organic systems, inThe Study of Fast Processes and Transient Species by Electron Pulse Radiolysis (eds. Baxendale, J. H., Busi, F.), Reidel: Dordrecht, 1982, 241–266.
Adams, G. E., Michael, B. D., Pulse radiolysis of henzoquinone and hydroquinone: Semiquinone formation by water elimination from trihydroxycyclohexadienyl radicals,Trans. Faraday Soc., 1967, 63: 1171.
Land, E. J., Ebert, M., Pulse radiolysis studies of aqueous phenol: Water elimination from dihydroxycyclohexadienyl radicals to form phenoxyl,Trans. Faraday Soc., 1967, 63: 1181.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 39130050)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Yao, S., Lin, W. et al. Reactions of tea polyphenol four constituents with hydroxyl radical: A pulse radiolytic study. Sc. China Ser. B-Chem. 41, 295–300 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879710
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879710