Abstract
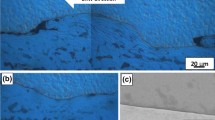
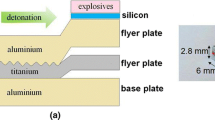
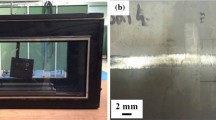
The residual deformation structures around the bonding interface in an explosively welded Ti/Ti clad material have been studied by optical microscopy and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The microstructures around the bonding interface in the clad material welded at flyer plate speed of 420 m/s were consistent with the deformation structures of pure titanium under conventional quasistatic deformation around ambient temperature, except for the development of c + a dislocations just near the bonding interface and the presence of {10-13} twinning. The latter has been newly observed in pure titanium. The deformation modes within 50 μm from the bonding interface in system IV were essentially the same as those in pure titanium under conventional quasistatic deformation at elevated temperatures. The {13-41} twinning has been newly confirmed experimentally and was defined as an active twinning mode under high strain rate and/or at elevated temperatures. The microstructural aspects of adiabatic shear band (ASB) were also described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Nishida, A. Chiba, K. Imamura, H. Minato, and J. Shudo:Metall. Trans. A., 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 735–42.
J. Dor-Ram, B.Z. Weiss, and Y. Komen:Acta Metall., 1979, vol. 27, pp. 1417–29.
E. Ganin, Y. Komen, and B.Z. Weiss:Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34, pp. 147–58.
M. Hammerschmidt and H. Kreye: inShock Waves and High-Strain-Rate Phenomena in Metals (Concepts and Applications), M.A. Meyers and L.E. Murr, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1981, pp. 961–73.
P.G. Partridge:Metall. Rev., 1967, vol. 12, 169–94.
N.E. Paton and W.A. Backofen:Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 2839–47.
R.A. Fishburn, W.T. Roberts, and D.V. Wilson:Met. Technol., 1976, vol. 3, pp. 310–22.
J.W. Christian:Theory of Transformations in Metals and Alloys, Pergamon Press, New York, NY, 1965, pp. 743–801.
M. Nishida and A. Chiba: Kumamoto University, Kumamoto, Japan, unpublished research, 1990.
G.B. Olson, J.F. Mescall, and M. Azrin: inShock Waves and High-Strain-Rate Phenomena in Metals (Concepts and Applications), M.A. Meyers and L.E. Murr, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1981, pp. 221–47.
S.P. Timothy:Acta Metall., 1987, vol. 35, pp. 301–06.
R.E. Winter:Phil. Mag., 1975, vol. 35, pp. 765–73.
Y. Me-Bar and D. Shechtman:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1989, vol. 58, pp. 181–88.
H.A. Grebe, H-R. Pak, and M.A. Meyers:Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, pp. 761–74.
M.A. Meyers and H-R. Pak:Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34, pp. 2493–99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
H. MINATO, formerly Graduate Student, Department of Materials Science and Resource Engineering, Kumamoto University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishida, M., Chiba, A., Ando, S. et al. Microstructural modifications in an explosively welded Ti/Ti clad material: II. Deformation structures around bonding interface. Metall Trans A 24, 743–750 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02656642
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02656642