Abstract
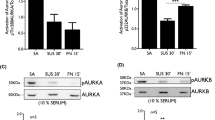
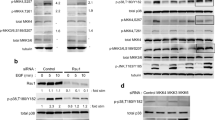
The type-I plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1), the primary inhibitor of both tissue-type and urokinase-type plasminogen activators (t-PA, u-PA), is the primary regulator of plasminogen activation and possibly of extracellular proteolysis. In anchorage-dependent cells, the PAI-1 gene is regulated by cell adhesion. PAI-1 gene expression is induced more evidently in cells that adhered to the culture plate than in those that did not adhere. In this study, we further demonstrate that the PAI-1 gene expression associated with cell adhesion is elicited through the activation of MEK and p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase (MAPK; ERK) signal pathways. We found that the MEK inhibitors, PD98059 and U0126, inhibited the induction of PAI-1 gene and protein expression during cell adhesion, PD98059 also inhibited the adhesion of cells to the culture plate, and cell adhesion elicited the kinase activities of MEK and ERK. In addition, we illustrate that two transcription response elements, the serum response element (SRE) and the hypoxia response element (HRE), which exist in the PAI-1 promoter, might be correlated with PAI-1 gene expression during cell adhesion. We discovered that the binding ability of nucleoproteins to both SRE and HRE was enhanced by cell adhesion and was dependent on MEK. Based on these results, we suggest that both MEK and ERK are involved in the induction of PAI-1 gene expression during cell adhesion. Furthermore, the subsequent downstream molecules, Elk-1 and HIF-1, may also participate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aplin AE, Short SM, Juliano RL. Anchorage-dependent regulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade by growth factors is supported by a variety of integrin alpha chains. J Biol Chem 274:31223–31228;1999.
Aplin AE, Stewart SA, Assoian RK, Juliano RL. Integrin-mediated adhesion regulates ERK nuclear translocation and phosphorylation of Elk-1. J Cell Biol 153:273–281;2001.
Banfi C, Eriksson P, Giandomenico G, Mussoni L, Sironi L, Hamsten A, Tremoli E. Transcriptional regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 gene by insulin: Insights into the signaling pathway. Diabetes 50:1522–1530;2001.
Blasi F. Proteolysis, cell adhesion, chemotaxis, and invasiveness are regulated by the u-PA-u-PAR-PAI-1 system. Thromb Haemost 82:298–304;1999.
Chen RH, Sarnecki C, Blenis J. Nuclear localization and regulation of ERK- and RSK-encoded protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol 12:915–927;1992.
Conese M, Nykjaer A, Petersen CM, Cremona O, Pardi R, Andreasen PA, Gliemann J, Christensen EI, Blasi F. Alpha-2 macroglobulin receptor/Ldl receptor-related protein (Lrp)-dependent internalization of the urokinase receptor. J Cell Biol 131:1609–1622;1995.
Cubellis MV, Wun TC, Blasi F. Receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of urokinase is caused by its specific inhibitor PAI-1. EMBO J 9:1079–1085;1990.
Deng G, Curriden SA, Wang S, Rosenberg S, Loskutoff DJ. Is plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 the molecular switch that governs urokinase receptor-mediated cell adhesion and release? J Cell Biol 134:1563–1571;1996.
Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E. Integrin signaling. Science 285:1028–1032;1999.
Gille HA, Sharrocks D, Shaw PE. Phosphorylation of transcription factor p62TCF by MAP kinase stimulates ternary complex formation at c-fos promoter. Nature 358:414–417;1992.
Gorlach A, Diebold I, Schini-Kerth VB, Berchner-Pfannschmidt U, Roth U, Brandes RP, Kietzmann T, Busse R. Thrombin activates the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 signaling pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells: Role of the p22 (phox)-containing NADPH oxidase. Circ Res 89:47–54;2001.
Hill CS, Wynne J, Treisman R. The Rho family GTPases RhoA, Rac1, and CDC42Hs regulate transcriptional activation by SRF. Cell 81:1159–1170;1995.
Jonathan S, Christian OG. Technical Report CBIL-TR-1997-1001-v0.0 TESS: Transcription Element Search Software on the WWW. URL: http://www.cbil.upenn.edu/tess; 1997.
Kanse SM, Kost C, Wilhelm OG, Andreasen PA, Preissner KT. The urokinase receptor is a major vitronectin-binding protein on endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res 224:344–353;1996.
Kjoller L, Kanse SM, Kirkegaard T, Rodenburg KW, Ronne E, Goodman SL, Preissner KT, Ossowski L, Andreasen PA. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 represses integrin- and vitronectin-mediated cell migration independently of its function as an inhibitor of plasminogen activation. Exp Cell Res 232:420–429;1997.
Kobayashi N, Nakano S, Mita S, Kobayashi T, Honda T, Tsubokou Y, Matsuoka H. Involvement of Rho-kinase pathway for angiotensin II-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene expression and cardiovascular remodeling in hypertensive rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301:459–466;2002.
Kortenjann M, Thomae O, Shaw PE. Inhibition of v-raf-dependent c-fos expression and transformation by a kinase-defective mutant of the mitogen-activated protein kinase Erk2. Mol Cell Biol 14:4815–4824;1994.
Kutz SM, Hordines J, McKeown-Longo PJ, Higgins PJ. TGF-beta1-induced PAI-1 gene expression requires MEK activity and cell-to-substrate adhesion. J Cell Sci 114:3905–3914;2001.
Kwaan HC, Wang J, Svoboda K, Declerck PJ. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 may promote tumour growth through inhibition of apoptosis. Br J Cancer 82:1702–1708;2000.
Lee CC, Shyu KG, Lin S, Wang BW, Liu YC, Chang H. Cell adhesion regulates the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene expression in anchorage-dependent cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 291:185–190;2002.
Lenormand P, Sardet C, Pages G, L'Allemain G, Brunet A, Pouyssegur J. Growth factors induce nuclear translocation of MAP kinases (p42mapk and p44mapk) but not of their activator MAP kinase kinase (p45 mapkk) in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 122:1079–1088;1993.
Lin S, Huang HC, Chen LL, Lee CC, Huang TS. GL331 induces down-regulation of cyclin D1 expression via enhanced proteolysis and repressed transcription. Mol Pharmacol 60:768–774;2001.
Lin TH, Chen Q, Howe A, Julinano RL. Cell anchorage permits efficient signal transduction between Ras and its downstream kinases. J Biol Chem 272:8849–8852;1997.
Lin S, Wang W, Wilson GM, Yang X, Brewer G, Holbrook NJ, Gorospe M. Down-regulation of cyclin D1 expression by prostaglandin A2 is mediated by enhanced cyclin D1 mRNA turnover. Mol Cell Biol 20:7903–7913;2000.
Lopez S, Peiretti F, Morange P, Laouar A, Fossat C, Bonardo B, Huberman E, Juhan-Vague I, Nalbone G. Activation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 synthesis by phorbol esters in human promyelocyte HL-60 — Roles of PKCβ and MAPK p42. Thromb Haemost 81:415–422;1999.
Loskutoff KJ, Sawdey M, Mimuro J, Coller B. Progress in Hemostasis and Thrombosis, ed 9. Philadelphia, Saunders, 87–115;1989.
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1982.
Marais R, Wynne J, Treisman R. The SRF accessory protein Elk-1 contains a growth factor-regulated transcriptional activation domain. Cell 73:381–393;1993.
Miyamoto S, Teramoto H, Gutkind JS, Yamada KM. Integrins can collaborate with growth factors for phosphorylation of receptor tyrosine kinases and MAP kinase activation: Roles of integrin aggregation and occupancy of receptors. J Cell Biol 135:1633–1642;1996.
Nykjaer A, Conese M, Christensen EI, Olson D, Cremona O, Gliemann J, Blasi F. Recycling of the urokinase receptor upon internalization of the uPA:serpin complexes. EMBO J 16:2610–2620;1997.
Palmier D, Lee JW, Juliano RL, Church FC. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and -3 increase cell adhesion and motility of MDA-MB-435 breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 277:40950–40957;2002.
Renshaw MW, Ren XD, Schwartz MA: Growth factor activation of MAP kinase requires cell adhesion. EMBO J 16:5592–5599;1997.
Richard DE, Berra E, Gothie E, Roux D, Pouyssegur J. p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases phosphorylate hypoxia-inducible factor 1(HIF-1) and enhance the transcriptional activity of HIF-1. J Biol Chem 274:32631–32637;1999.
Ryan MP, Kutz SM, Higgins PJ. Complex regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) gene expression by serum and substrate adhesion. Biochem J 314:1041–1046;1996.
Schneiderman J, Loskutoff DJ. Plasminogen activator inhibitors. Trends Cardiovasc Med 1:99–102;1991.
Schwartz MA, Schaller MD, Ginsberg MH. Integrins: Emerging paradigms of signal transduction. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 11:549–599;1995.
Short SM, Boyer JL, Juliano RL. Integrins regulate the linkage between upstream and downstream events in G-protein-coupled receptor signaling to mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 275:12970–12977;2000.
Sprengers ED, Kluft C. Plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood 69:381–387;1987.
Stefansson S, Lawrence DA. The serpin PAI-1 inhibits cell migration by blocking integrin alpha V beta 3 binding to vitronectin. Nature 383:441–443;1996.
Takeda K, Ichiki T, Tokunou T, Iino N, Fujii S, Kitabatake A, Shimokawa H, Takeshita A. Critical role of Rho-kinase and MEK/ERK pathways for angiotensin II-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 gene expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21:868–873;2001.
Fink T, Kazlauskas A, Poellinger L, Ebbesen P, Zachar V. Identification of a tightly regulated hypoxia-response element in the promoter of human plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Blood 99:2077–2083;2002.
Webb DJ, Thomas KS, Gonias SL. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 functions as a urokinase response modifier at the level of cell signaling and thereby promotes MCF-7 cell growth. J Cell Biol 152:741–751;2001.
Whitmarsh AJ, Shore P, Sharrocks AD, Davis RJ. Integration of MAP kinase signal transduction pathways at the serum response element. Science 269:403–407;1995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, H., Shyu, KG., Lin, S. et al. The plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene is induced by cell adhesion through the MEK/ERK pathway. J Biomed Sci 10, 738–745 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02256326
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02256326