Abstract
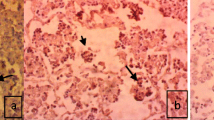
Pulmonary tissues from non-infected dogs, naturallyDirofilaria immitis-infected dogs and experimentally infected puppies, selectively necropsied after infection, were assessed using peroxidase-antiperoxidase (PAP) staining technology. Sequential sections of pulmonary tissue were PAP stained with anti-freshD. immitis serum, anti-paraffin processedD. immitis serum, anti-dog immunoglobulin (IgG, IgG Fc, IgM) sera and anti-dog complement (C3) serum, and examined for antibody, complement and forD. immitis antigen. The extent of alveolar septal thickening was positively correlated with infection status. Cellular infiltration was most evident surrounding obstructed areas whereD. immitis werein situ. Antigenic material (microfilariae, eggs, fragmented filariae) labelled by PAP was identified in the pulmonary arteries, alveolar capillaries and alveolar septa. Deposits of complement and IgG, presumably associated with immune complex formation, were also observed in some of the infected dogs. Identification of antigen, antibodies and complement associated with alveolar septal pathology suggested that immune mechanisms were active in its development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FW:
-
fresh worm
- PAP:
-
peroxidase-antiperoxidase
- PW:
-
processed worm
References
Abramowsky, C.R., Powers, K.G., Aikawa, M. and Swinehart, G., 1981.Dirofilaria immitis. 5. Immunopathology of filarial nephropathy in dogs.American Journal of Pathology,104, 1–12
Aikawa, M., Abramowsky, C.R., Power, K.G. and Furrow, R., 1981. Dirofilariasis IV. Glomerulonephropathy induced byDirofilaria immitis infection.American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene,30, 84–91
Atwell, R.B., Sutton, R.H. and Moodie, E.W., 1983. Preliminary report on the pulmonary pathology associated with subcutaneous injections ofDirofilaria immitis antigen.Veterinary Research Communications,6, 59–62
Atwell, R.B., Sutton, R.H. and Buoro, I.B.J., 1986. Early pulmonary lesions caused by deadDirofilaria immitis in dogs exposed to homologous antigens.British Journal of Experimental Pathology,67, 395–405
Casey, H.W. and Splitter, G.A., 1975. Membraneous glomerulonephritis in dogs infected withDirofilaria immitis.Veterinary Pathology,12, 111–117
Daniele, R.P., 1981. Immune complex injury of the lung.American Review of Respiratory Disease,124, 738–755
Howe, C., Lee, L.T., Harboe, A. and Haukenes, G., 1967. Immunochemical study of influenza virus and associated host tissue components.Journal of Immunology,98, 543–557
Leavitt, R.Y. and Fauci, A.S., 1986. Pulmonary vasculitis.American Review of Respiratory Disease,134, 149–166
Markwell, M.A.K., Haas, S.M., Bieber, L.L. and Tolbert, N.E., 1978. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples.Annals of Biochemistry,87, 206–210
Osborne, C.A., Hammer, R.F., O'Leary, T.P., Pomeroy, K.A., Jeraj, K., Barlough, J.E. and Vernier, R.L., 1981. Renal manifestations of canine dirofilariasis. In: G.F. Otto (ed),Proceedings of the Heartworm Symposium '80, (Veterinary Medicine Publishing Co., Bonner Springs), 67–92
Sternberger, L.A., 1979. The unlabelled antibody peroxidase-antiperoxidase (PAP) method.Immunocytochemistry, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York), 104–169
Tanaka, K.I. and Atwell, R.B., 1990. The optimal condition for peroxidase-anti-peroxidase staining of lung tissues in canine dirofilariasis.Japanese Journal of Veterinary Science,52, 447–451
Tanaka, K.I. and Atwell, R.B., 1991. Immunoperoxidase staining characteristics ofDirofilaria immitis in the dog.Research in Veterinary Science,50, 33–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, K.I., Atwell, R.B. Immunohistological observations on pulmonary tissues from dogs infected withDirofilaria immitis . Vet Res Commun 17, 109–117 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01839238
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01839238