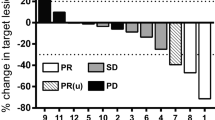
Summary
Immunological parameters were evaluated in patients treated with cytokine-mediated immunotherapy (CMI) consisting of low doses of recombinant human interferon α2a (rIFNα) and recombinant human interleukin-2 (rIL-2) administered either concomitantly or sequentially by subcutaneous self-injections in an outpatient setting. Twenty-six patients with hematological malignancies and 2 metastatic melanoma patients in a progressive stage were enrolled in this clinical trial. Of the 26 patients, 24 were at a stage of minimal residual disease, including 14 patients who had received autologous bone marrow transplantation (ABMT) 2–5 months previously, 7 chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and 3 acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients. Two patients (1 CML and 1 mult. myeloma) were treated at a stage of progressive disease. Non-MHC-restricted cytotoxicity directed against natural-killer(NK)-resistant (Daudi) and NK-sensitive (K562) target cells was assessed before, during and after CMI, either in fresh peripheral blood samples (spontaneous activity) or after in vitro rIL-2 activation (induced activity). Spontaneous killing activity was low prior to treatment, but increased upon termination of treatment in 10/15 evaluated cycels. rIL-2-activated cytotoxicity in vitro was markedly elevated in 8/12 and 6/8 patients after one and two cycles, respectively, of sequential treatment, as well as in 3/8 CML and 5/6 patients after one and two cycles, respectively, of concomitant treatment Activation of the T cell mitogenic response was demonstrated in 6/9 patients after concomitant CMI, while no such effect was observed throughout a sequential treatment in lymphoma and leukemia patients after ABMT. Although a direct correlation between immune stimulation and the in vivo antitumor response cannot yet be determined, our clinical observations support a beneficial therapeutic effect in a substantial number of patients. These results indicated that the ambulatory CMI protocol of rIL-2 and rIFNα could stimulate the host defense immune system and may be helpful in mediating the in vivo antitumor response in patients with minimal residual disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler A, Chervenick PA, Whiteside TL, Lotzova E, Herberman RB (1988) Interleukin 2 induction of lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) activity in the peripheral blood and bone marrow of acute leukemia patients: I. Feasibility of LAK generation in adult patients with active disease and in remission. Blood 71: 709
Atzpodien J, Korfer A, Franks CR, Poliwoda H, Kirchner H (1990) Home therapy with recombinant interleukin-2 and interferon-a2b in advanced human malignancies. Lancet 335: 1509
Blaise D, Viens P, Olive D, Stoppa AM, Gabert J, Pourreau CN, Attal M, Gaspard MH, Mannoni P, Jasmin C, Palmer P, Franks C, Michel G, Mawas C, Baume D, Philips T, Maraninchi D. Recombinant interleukin-2 (rIL-2) after autologous bone marrow transplantation (BMT): a pilot study in 19 patients (1991) Eur Cytokine Met 2: 121
Borzy MS, Ridgway D (1989) Prolonged defects of interleukin-2 production, responsiveness and receptor expression in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 73: 1608
Boyum A (1968) Separation of leukocytes from blood and bone marrow. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 21 [Suppl 97]: 77
Brund MJ, Tarnowski D, Davatelis V (1986) Interaction of recombinant interferons with recombinant interleukin-2: differential effects on natural killer cell activity and interleukin-2-activated killer cells. Int J Cancer 37: 787
Chang WC, Fujimiya Y, Casteel N, Pattengale P (1989) Natural killer cell immunodeficiency in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia: III. Defective interleukin-2 production by T-helper and natural killer cells. Int J Cancer 43: 591
Dabholkar M, Advani S, Tatake R, Gangal S (1986) Natural and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in chronic myeloid leukemia patients in remission. Leukemia Res 10: 203
Dabholkar M, Tatake R, Amin K, Advani S, Gangal S (1989) Modulation of natural killer and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity by interferon and interleukin 2 in chronic myeloid leukemia patients in remission. Oncology 46: 123
Dutcher JP, Creekmore S, Weiss GR, Margolin K, Markowitz AB, Roper M, Parkinson D, Ciobanu N, Fisher RI, Boldt DDH, Doroshow JH, Rayner AA, Hawkins M, Atkins M (1989) A phase II study of interleukin-2 and lymphokine-activated killer cells in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma. J Clin Oncol 7: 477
Fidler IJ, Heicappell R, Saiki I, Grutter G, Horsberger MA, Nuesch J (1987) Direct anti-proliferative effects of recombinant human interferon a B/D hybrids on human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 47: 2020
Foa R, Guarini A, Tos AG, Cardona S, Fierro MT, Meloni G, Tosti S, Mandelli F, Gavosto F (1991) Peripheral blood and bone marrow immunophenotypic and functional modifications induced in acute leukemia patients treated with interleukin 2: evidence of in vivo lymphokine activated killer cell generation. Cancer Res 51: 964
Fujimiya Y, Bakke A, Chang WC, Linker-Isreli M, Udis B, Horowitz D, Pattengale PK (1986) Natural killer-cell immunodeficiency in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia: I. Analysis of the defect using monoclonal antibodies HNK-1 (Leu-7) and B73.1. Int J Cancer 37: 639
Gastl G, Marth C, Leiter E, Gattringer C, Mayer I, Daxenbichler G, Flener R, Huber C (1985) Effects of human recombinant a2 arg-interferon and g-interferon on human breast cancer cell lines: dissociation of antiproliferative activity and induction of HLA-DR antigen expression. Cancer Res 45: 2957
Gottlieb DJ, Prentic HG, Heslop HE, Bello-Fernandez C, Bianchi AC, Galazka AR, Brenner MK (1989) Effects of recombinant interleukin-2 administration on cytotoxic function following high-dose chemoradiotherapy for hematological malignancy. Blood 74: 2335
Grimm EA, Mazumder A, Zhang HZ, Rosenberg SA (1982) Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon lysis of natural killer-resistant fresh solid tumor cells by interleukin 2-activated autologous human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med 155: 1823
Hauch M, Gazzola MV, Small T, Bordignon C, Barnett L, Cunningham I, Malaspinia HC, O'Reilly RJ, Keever CA (1990) Anti-leukemia potential of interleukin-2 activated natural killer cells after bone marrow transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 75: 2250
Herberman RB, Ortaldo JR (1981) Natural killer cells: their role in defenses against disease. Science 214: 24
Herberman RB, Hiserodt J, Vujanovic N, Balch C, Lotzova E, Bolhuis R, Golub S, Lanier LL, Phillips JH, Riccardi C, Ritz J, Santoni A, Schmidt RE, Uchida A (1987) Lymphokine-activated killer cell activity. Immunol Today 8: 178
Hercend T, Takvorian T, Nowill A, Tantravahi R, Moingeon P, Anderson KC, Murray C, Bohuon C, Ythier A, Ritz J (1986) Characterization of natural killer cells with antileukemic activity following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 67: 722
Hersey P, Bolhuis R (1987) “Nonspecific” MHC-unrestricted killer cells and their receptors. Immunol Today 8: 233
Heslop HE, Gottlieb DJ, Bianchi AC, Meager A, Prentice HG, Mehta AB, Hoffbrand AV, Brenner MK (1989) In vivo induction of gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor by interleukin-2 infusion following intensive chemotherapy or autologous marrow transplantation. Blood 74: 1374
Higuchi CM, Thompson JA, Cox T, Lindgren CG, Bruckner CD, Fefer A (1989) Lymphokine-activated killer function following autologous bone marrow transplantation for refractory hematological malignancies. Cancer Res 49: 5509
Hirsh M, Lipton A, Harvey H, Givant E, Hopper K, Jones G, Zeffren J, Levitt D (1990) Phase I study of interleukin-2 and interferon alfa-2a as outpatient therapy for patients with advanced malignancy. J Clin Oncol 8: 1657
Krigel RL, Padavic-Shaller KA, Rudolph AR, Litwin S, Konrad M, Bradley EC, Comis RL (1988) A phase I study of recombinant interleukin 2 plus recombinant b-interferon. Cancer Res 48: 3875
Lee KH, Talpaz M, Rothberg JM, Murray JL, Papadopoulos N, Plager C, Benjamin R, Levitt D, Gutterman J (1989) Concomitant administration of recombinant human interleukin-2 and recombinant interferon a-2A in cancer patients: a phase I study. J Clin Oncol 7: 1726
Lotzova E, Savary CA, Herberman RB (1987) Induction of NK cell activity against fresh human leukemia in culture with interleukin 2. J Immunol 138: 2718
Mackinnon S, Hows JM, Goldman JM (1990) Induction of in vitro graft-versus-leukemia activity following bone marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 76: 2037
Mehta B, Advani S, Nadkarni J (1989) Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity correlated with histological classification and prognosis. Oncology 46: 323
Morecki S, Nabet C, Ackerstein A, Schlesinger M, Slavin S (1991) The effect of in-vitro T lymphocyte depletion on generation of IL-2 activated cytotoxic cells. Bone Marrow Transplant 7: 269
Nagler A, Greenberg PL. Lanier LL, Phillips JH (1988) The effects of recombinant interleukin 2-activated natural killer cells on autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic progenitors. J Exp Med 168: 47
Nagler A, Ackerstein A, Naparstek E, Ben-Neriah S, Barak V, Slavin S (1991) Concomitant treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia with recombinant human interleukin-2 and interferon-a2a (in press)
Oshimi K, Oshimi Y, Akutsu M, Takei Y, Saito H, Okada M, Mizoguchi H (1986) Cytotoxicity of interleukin 2-activated lymphocytes for leukemia and lymphoma cells. Blood 68: 938
Pawelec G, Schneider E, Ehninger G, Rehbein A, Schmidt H (1989) Partial correction of defective generation of lymphokine-activated killer cells in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia after in vivo treatment with interferon a (Wellferon). Cancer Immunol Immunother 29: 63
Petrie A (1978) Linear regression and correlation: In: Lecture notes on medical statistics. Blackwell London, p 102
Phillips JH, Genlo BT, Myers WW, Rayner AA, Lanier LL (1987) In vivo and in vitro activation of natural killer cells in advanced cancer patients undergoing combined recombinant interleukin-2 and LAK cell therapy. J Clin Oncol 5: 1933
Pillai MR, Balaram P, Padmanabhan TK, Abraham T, Nair K (1989) Interleukin 2 and alpha interferon induced in vitro modulation of spontaneous cell mediated cytotoxicity in patients with cancer of the uterine cervix undergoing radiotherapy. Acta Oncol 28: 39
Quesada JR, Reuben J, Manning JT, Hersh EM, Gutterman JU (1984) Alpha interferon for induction of remission in hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med 310: 15
Rajaram N, Tatake RJ, Advani SH, Naik SL, Gangal SG (1990) Natural killer and lymphokine-activated killer cell functions in chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Immunol Immunother 31: 44
Rettie JE, Gottlieb D, Heslop HE, Leger O, Drexler HG, Hazlehurst G, Hoffbrand AV, Brenner MK (1989) Endogenously generated activated killer cells circulate after autologous and allogeneic bone marrow transplantation but not after chemotherapy. Blood 73: 1351
Robertson MJ, Ritz J (1990) Biology and clinical relevance of human natural killer cells. Blood 76: 2421
Rosenberg SA (1988) Immunotherapy of cancer using interleukin 2. Immunol Today 9: 58
Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Muul LM, Chang AE, Avis FP, Leitman S, Linehan WM, Robertson CN, Lee RE, Rubin JT, Seipp CA, Simpson CG, White DE (1987) A progress report on the treatment of 157 patients with advanced cancer using lymphokine-activated killer cells and interleukin-2 or high-dose interleukin-2 alone. N Engl J Med 316: 889
Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Yang JC, Aebersold PM, Linehan MW, Siepp CA, White DE (1989) Experience with the use of high dose interleukin-2 in the treatment of 652 cancer patients. Ann Surg 210: 474
Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Yang JC, Linehan WM, Seipp C, Calabro S, Karp SE, Sherry RM, Steinberg S, White DE (1989) Combination therapy with interleukin-2 and alpha-interferon for the treatment of patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 7: 1863
Roth MS, Bunn PA, Foon KA (1988) Interferon therapy for lymphoproliferative disorders. Cancer Treat Res 38: 231
Smith KA (1988) Interleukin-2: inception, impact and implication. Science 240: 1169
Soiffer R, Murray C, Cochran K, Ish C, Wang E, Ritz J (1990) Selective expansion of NK cells in patients given low dose recombinant IL-2 after BMT (abstract). Blood 76 [Suppl 1]: 220a
Sugarman BJ, Aggarwal BB, Hass PE, Figari IS, Palladino MA, Shepard HM (1985) Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science 230: 943
Talpaz M, Kantarjian HM, McCredie KB, Keating MJ, Trujillo J, Gutterman J (1987) Clinical investigation of human alpha interferon in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 69: 1280
Urba WJ, Steis RG, Longo DL, Kopp WC, Maluish AE, Marcon L, Nelson DL, Stevenson HC, Clark JW (1990) Immunomodulatory properties and toxicity of interleukin 2 in patients with cancer. Cancer Res 50: 185
Voogt PJ, Falkenburg JHF, Fibbe WE, Veenhof WFJ, Hamilton M, Van Krimpen BA, Bolhuis RLH (1989) Normal hematopoietic progenitor cells and malignant lymphohematopoietic cells show different susceptibility to direct cell-mediated MHC-non-restricted lysis by T cell receptor-/CD−, T cell receptor+/CD3+ and T cell receptor ab+/CD3 lymphocytes. J Immunol 142: 1774
Yabuhara A, Kawai H (1990) A recycling defect as characteristic of natural killer cells in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Res 28: 572
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morecki, S., Revel-Vilk, S., Nabet, C. et al. Immunological evaluation of patients with hematological malignancies receiving ambulatory cytokine-mediated immunotherapy with recombinant human interferon-α2a and interleukin-2. Cancer Immunol Immunother 35, 401–411 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01789019
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01789019