Summary
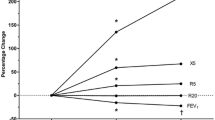
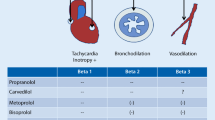
Twelve subjects with chronic obstructive lung disease and a partially reversible obstruction received increasing single doses of bopindolol (1, 2, 4, and 8 mg), pindolol (7.5, 15, and 30 mg), and atenolol (50 and 100 mg). Resting heart rate and blood pressure were reduced in a dose-dependent fashion. The actions of the drugs on lung function were assessed by whole body plethysmography. Pindolol did not influence mean airway resistance (R aw). Bopindolol (1, 2 and 4 mg) and atenolol (50 mg) exhibited a neutral effect on meanR aw. Atenolol (100 mg) and to a lesser extent bopindolol (8 mg) induced a long-lasting increase in mean Raw.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Raw :
-
airway resistance
- HR:
-
heart rate
References
Aellig WH (1982) Clinical pharmacological experiments with bopindolol (LT 31-200): a long acting β-adrenoceptor blocking drug with partial agonist activity. Br J Clin Pharmacol 13:267–268
Dorow P (1982) Influence of intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (isa) during β-adrenoceptor blockade in asthmatics. Br J Clin Pharmacol 13:321S–323S
Formgren H (1976) The effect of metoprolol and practolol on lung function and blood pressure in hypertensive asthmatics. Br J Clin Pharmacol 3:1007–1014
Hulthén UL, Brummelen P van, Amann FW, Buehler FR (1983) Antihypertensive efficacy of the new long-acting β-blocker bopindolol as related to age. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 5:426–429
Kochar AS, Barman R (1982) Letter to the editor. Eur J Respir Dis 63:591
Opie LH (1980) Drugs and the heart. I. Beta-blocking agents. Lancet I:693–698
Platzer R, Galeazzi RL, Niederberger W, Rosenthaler J (1984) Simultaneous modeling of bopindolol kinetics and dynamics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 36:5–13
Ruffin RE, McLutyre ELM, Latimer KM et al. (1982) Assessment of β-adrenoceptor antagonists in asthmatic patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 13:325S–335S
Schiess W, Welzel D, Gugler R (1984) Double-blind comparison of once-daily bopindolol, pindolol, and atenolol in essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 27:529–534
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorow, P., Schiess, W. Bopindolol, pindolol, and atenolol in patients with chronic obstructive lung disease. Klin Wochenschr 64, 366–369 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01728185
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01728185