Summary
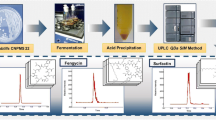
A gradient analytical HPLC system was developed to assay titers of the three major components of the aridicin (Ardacin) complex produced byKibdelosporangium aridum (SK&F AAD-216). The separation was performed on a Beckman Ultrasphere column using a gradient of acetonitrile (26–43%) in 0.1 M pH 3.2 phosphate buffer with UV detection at 220 nm. The gradient system was necessary to analyze all three major factors within a reasonable recycle time (14 min) without interference by front eluting impurities. The assay was linear from 12 to 200 μg/ml (multipleR 2=0.998), with a standard deviation for retention time of 1.4%. A SepPAK isolation scheme was developed to assay samples in complex matrices such as fermentation broths. Using this assay as a monitor, fermentation medium optimization increased the total titers of the three factors from approximately 5 μg/ml to over 200 μg/ml. The optimal medium contained glucose, beet molasses and methyl oleate. The latter substrate was particularly effective in enhancingproducation 10-fold, presumably by enhancing the supply of acetly-CoA. This is a biosynthetic precursor of both dihydroxyphenylglycine, present in the nucleus, and the acyl side chains present on the amino-glucuronic acids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boeck, L.D., F.P. Mertz and G.M. Clem. 1985. A41030, a complex of novel glycopeptide antibiotics produced by a strain ofStreptomyces virginiae. J. Antibiot. 38:1–8.
Boeck, L.D., F.P. Mertz, R.K. Wolter and C.E. Higgins. 1984. N-demethyl vancomycin, a novel antibiotic produced by a strain ofNocardia orientalis taxonomy and fermentation. J. Antibiot. 37 (5):446–453.
Boeck, L.D. and W.M. Stark. 1983. Actaplanin, a complex of new glycopeptide antibiotics-Fermentation. Dev. Ind. Microbiol. 25:505–514.
DePhillips, P.A., A.J. Giovenella, S.F. Grappel, R.D. Hedde, P.W. Jeffs, L.B. Killmer, T.O. Lindsey, L.J. Nisbet, G.D. Roberts, K.M. Snader and R.D. Sitrin. 1985. Isolation, structural studies and biological evaluation of the major and minor components of the aridicin (AAD-216) complex. Abstr. 790, 25th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Minneapolis, MN, October 1985, American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC.
Sylvester. 1956–57. Ristocetin, microbiological properties. Antibiotic. Ann., 687–692.
Hammond, S.J., M.P. Williamson, D.H. Williams, L.D. Boeck and G.G. Marconi. 1982. On the biosynthesis of the antibiotic vancomycin. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun., 344–345.
Hearn, M. 1983. High Performance Liquid Chromatography of Peptides. In: High-Performance Liquid Chromatography: Advances and Perspectives (Horvath, Cs., ed.), Vol 3, p. 88, Academic Press, New York.
Hearn, M., F. Regnier, and T. Wehr (eds). 1983. High Performance Liquid Chromatography of Proteins and Peptides. Academic Press, New York.
Jeffs, P.W., G.W. Chan, R.D. Sitrin, N. Holder, G.D. Roberts, C. De Brosse. 1985. The structure of the glycolipid components pf the aridicin antibiotic complex. J. Org. Chem. 50: 1726–1731.
Jeffs, P.W., L. Mueller, C. DeBrosse, S.L. Heald and R. Fisher. 1986. The structure of aridicin A. An integrated approach employing 2D NMR, energy minimization and distance contraints. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 108:3063–3075.
Kunstmann, M.P., L.A. Mitscher, J.N. Porter, A.J. Shay and M.A. Darken. 1968. LL-AV290, A new antibiotic. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 242–245.
Mertz, F.P. and L.E. Doolin. 1973. The effect of inorganic phosphate on the biosynthesis of vancomycin. Can. J. Microbiol. 19:263–270.
Pittenger, R.C. and R.B. Brigham. 1956.Streptomyces orientalis, n. sp., the source of Vancomycin. Antibiot. Chemother. 6:642–647.
Shearer, M.C., P. Actor, B.A. Bowie, S.F. Grappel, C.H. Nash, D.J. Newman, Y.K. Oh, C.H. Pan and L.J. Nisbet. 1985. Aridicins, novel glycopeptide antibiotics. I. Taxonomy, production and biological activity. J. Antibiot. 38: 555–560.
Sitrin, R.D., G.W. Chan, F. Chapin, A.J. Giovenella, S.F. Grappel, P.W. Jeffs, L. Phillips, K.M. Snader and L.J. Nisbet. 1986. Aridicins, novel glycopeptide antibiotics: III. Preparation, characterization, and biological activities of aglycone derivatives. J. Antibiot. 39:68–75.
Sitrin, R.D., G.W. Chan, J.J. Dingerdissen, W. Holl, J.R.E. Hoover, J.R. Valenta, L. Webb and K.M. Snader. 1985. Aridicins, novel glycopeptide antibiotics. II. Isolation and chemical characterization. J. Antibiot. 38:561–571.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, C.H., Chan, G., Nisbet, L.J. et al. Analytical HPLC of the aridicin glycopeptide complex and its application to fermentation development. Journal of Industrial Microbiology 1, 303–310 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569308
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569308