Abstract
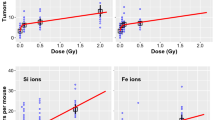
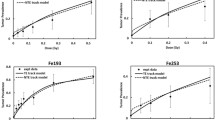
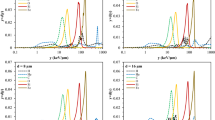
Stochastic radiation effects following exposure to heavy ions and other high linear energy transfer (LET) radiation in space are a matter of concern when the long-term consequences of space flights are considered. This paper is an overview of the relevant literature, emphasizing uncertainties entailed from estimates of relative biological effectiveness (RBE) for different experiment end-points, making the choice of a single weighting factor for the prediction of cancer risk in man extremely difficult. Life-span-shortening studies in mice exposed to heavy ions and ongoing large-scale experiments in monkeys exposed to protons suggest that RBEs for all cancers are lower than 5. This does not exclude a much higher RBE for rare tumors such as brain tumors in monkeys or promoted Harderian gland tumours in mice at LET >80 keV/µm. Skin cancer studies in rats exposed to neon or argon resulted in similar RBE. Exposure to fission neutrons led to high RBE in all species, not excluding values much higher than 20 for specific cancers such as lung tumors in mice and all cancers in rats. The estimate of maximal RBE is, however, extremely dependent on the hypothesis made on the shape of the dose-response curves in the lower range of doses. These results suggest that neutrons may be the most hazardous component of high-LET radiation. There is only limited evidence from cancer experiments that LET >150 keV/µm results in highly decreased efficiency, but this has been found for bone cancer induction following exposure to fission fragments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth EJ, Prioleau JC, Mahlmann LJ (1987) Skyhook Project: Progress Report, Berkeley, pp 133–138
Batchelor AL, Jenner TJ, Cobb LM (1983) Further experiments to study whether localized fission fragment irradiation of rat lung causes tumours. Phys Med Biol 28:475–483
Broerse J (1981) Tumor induction in rhesus monkeys after total body irradiation with x-rays and fission neutrons. Int J Radiat Biol 40:671–678
Broerse J (1986) Tumor induction in experimental animals after neutron and x-irradiation in radiation carcinogenesis and DNA alterations. In: Burns JF, Upton AC, Silini G (eds) Life sciences, Vol 124. Plenum Press, London, pp 27–50
Burns FJ, Albert RE (1980) Dose response for skin tumors induced by single and split doses of argon ions. Biological and Medical Research with Accelerated Heavy Ions at the Bevalac University of California
Burns FJ, Albert RE (1986) Dose-response for radiation-induced cancer in rat skin. In: Burns FJ, Upton AC, Silini G (eds) Radiation carcinogenesis and DNA alterations. Life sciences, vol 124. Plenum Press, London, pp 51–70
Chameaud J, Masse R, Lafuma J (1984) Influence of radon daughter exposure at low doses on occurrence of lung cancer in rats. Radiat Prot Dosim 7:385–388
Felber M, Burns FJ, Garte SJ (1992) Amplification of thec-myc on-cogene in radiation-induced rat skin tumors as a function of linear energy transfer and dose. Radiat Res 131:297–301
Fry RJM, Powers-Risius P, Alpen EL, Ainsworth EJ (1985) High-LET radiation carciogenesis. Radiat Res 104: 188–195
Masse R, Morlier JP, Morin M, Chameaud J, Bredon P, Lafuma J (1992) Animals exposed to radon. Radiat Prot Dosim 45:603–609
Mays CW, Lloyd RD, Taylor GN, Shabestari LR, Angus W, Atherton DR, Gillett NA (1989) Fission fragment RBE for bone sarcoma induction. Radiat Res 119:432–442
Morin M, Lafuma J (1988) Cancers radio-induits chez le rat. Rapport CEA - R 5462-1998
Morlier JP, Morin M, Chameaud J, Masse R, Bottard S, Lafuma J (1992) Importance du débit de dose sur l'apparition des cancers chez le rat après inhalation de radon. CR Acad Sci 315:463–466
NCRP Report No 104 (1990) The relative biological effectiveness of radiations of different qualities. National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements. Bethesda, MD
Ullrich RL (1982) Lung tumor in mice. In: Neutron carcinogenesis (Broerse J, Gerber GB (eds) EUR 8084, Euratom, Luxembourg, pp 43–55
Ullrich RL (1984) Tumor induction in BALB/c mice after fractionated or protracted exposure to fission spectrum neutrons. Radiat Res 97:587–597
UNSCEAR (1993) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. 1993 Report to the General Assembly, with scientific annexes. United Nations, New York
Wood DH (1991) Long-term mortality and cancer risk in irradiation rhesus monkeys. Radiat Res 126:132–140
Wood DH, Yochmowitz MG, Salmon YL (1986) Lifetime effects of single event proton exposures in rhesus monkeys. In: Life-span radiation effects studies in animals: what can they tell us? Proceedings of Hanford Life Science Symposium 1983, CONF-830951, National Technical Information Service, Springfield, Virginia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masse, R. RBE for carcinogenesis following exposure to high LET radiation. Radiat Environ Biophys 34, 223–227 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209746
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209746