Abstract
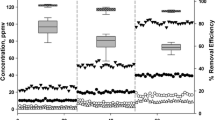
Experiments were carried out to quantify the mineralization and distribution of pentachlorophenol (PCP) by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium, and distribution of its transformation products into water-soluble, solvent-soluble, sorbed, and volatile fractions in liquid cultures. Water-soluble and solvent-soluble products from 14C-PCP transformation were first measured under oxygen limited conditions. Results indicated that after 12 days, 15% of 14C was recovered in methylene chloride, and less than 1% was water soluble. Sorption to the fungal mat reached a maximum of 16% 14C after 9 days incubation and declined to 5% at day 12. However, recovery of 14C within the system was only 30% at day 12. To improve the mass balance of the system, polyurethane foam was placed inside the culture flask to trap volatile products of PCP transformation. Results showed that after 12 days incubation of 14C-PCP with the fungus, 82% of the 14C added was volatilized. GC/MS analysis demonstrated that pentachloroanisole (PCA) was the only volatile product of PCP transformation. Sorption of 14C to the fungal mat was reversible to some extent. Chemical mass balance results in this experiment were near 100%. In the final experiment, the polyurethane volatile trap was placed outside the culture flask to assess the impact of the continuous removal of volatiles from the flask head space on mineralization. Increased 14CO2 production was observed when the polyurethane volatile trap was placed outside the culture flask compared with placement inside the flask.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bollag JM, Liu SY (1985) Copolymerization of halogenated phenols and syringic acid. Pesticide Biochem Physiol 23:261–272
Coulter C, Hamilton JTG, Harper DB (1993) Evidence of the existence of independent chloromethane and S-adenosyl methionine-utilizing system for methylation in Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:1461–1466
Crosby DG (1981) Environmental chemistry of pentachlorophenol. Pure Appl Chem 53:1052–1080
Cserjesi AJ, Johnson EL (1972) Methylation of pentachlorophenol by Trichoderma virgatum. Can J Microbiol 13:45–49
Guo H, Chang H, Joyce TW, Glaser J (1990) Degradation of chlorinated phenols and guaiacols by the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. In: Kirk TK, Chang HM (eds) Biotechnology in pulp and paper manufacture, applications, and fundamental investigations. Butterworth-Heinemann, Stoneham, MA
Harper DG, Busvell JA, Kennedy JT, Hamilton JTG (1990) Chloromethane, methyl donor in veratryl alcohol biosynthesis in Phanerochaete chrysosporium and other lignin-degrading fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:3450–3457
Kang G (1993) Biodegradation of organopollutants in bench scale bioreactors using the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. PhD dissertation, Civil and Environmental Engineering, Utah State University, Logan, UT, 206 pp
Kang G, Stevens DK (1994) Degradation of pentachlorophenol in bench scale bioreactors using the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Haz Waste Haz Mat 11:397–410
Kirk TK, Schultz E, Connors WJ, Lorenz LF, Zeikus JG (1978) Influence of culture parameters on lignin metabolism by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Microbiol 117:277–285
Lamar RT, Glaser JA, Kirk KT (1990a) Fate of pentachlorophenol (PCP) in sterile soils inoculated with the white-rot basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysoporium: Mineralization, volatilization, and depletion of PCP. Soil Biol Biochem 22:433–440
Lamar RT, Larsen MJ, Kirk KT (1990b) Degradation of pentachlorophenol by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Applied Environ Microbiol 56:3519–3526
Lin JE, Wang HY, Hickey RF (1990) Degradation kinetics of pentachlorophenol by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:1125–1134
Marinucci AC, Bartha R (1979) Apparatus for monitoring the mineralization of volatile 14C-labeled compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol 38:1020–1022
McGinnis GD (1982) Biological and photochemical degradation of PCP and creosote. Mississippi State University, prepared for Forest Products Laboratory, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Madison, WI, 95 pp
Mileski GJ, Bumpus JA, Jurek MA, Aust SD (1988) Biodegradation of pentachlorophenol by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2885–2889
Murthy NBK, Kaufman DD, Fries F (1979) Degradation of pentachlorophenol (PCP) in aerobic and anaerobic soil. J Environ Sci Health B14:1–14
Schwarzenbach RP, Gschwend PM, Imboden DM (1993) Environmental Organic Chemistry. John Wiley and Sons, NY, 681 pp
Sims RC, Sims JL, Hansen SG (1991) Soil Transport and Fate Database 2.0 and Model Management System. Utah State University, Logan, UT
Whelan G, Sims RC (1992) Oxidation of recalcitrant organics in subsurface systems. Haz Waste Haz Mat 9:245–265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly: Graduate Research Assistant, Civil and Environmental Engineering, Utah State University, Logan, Utah, 84322, USA
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badkoubi, A., Stevens, D.K. & Murarka, I.P. Quantification of pentachlorophenol transformation product distribution in the presence of Phanerochaete chrysosporium . Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 30, 1–8 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00211322
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00211322