Abstract
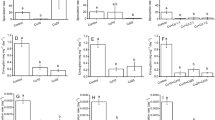
The response of Potamogeton crispus L. breakdown to controlled doses of different levels of chlorine and chlorine + ammonia was investigated over two years in outdoor experimental streams. In 1985, downstream riffles of 2 streams were dosed (observed in-stream concentrations) at ca. 10 µg/L Total Residual Chlorine (TRC), one stream at 64 µg/L TRC and one stream at 230 µg/L TRC. Two control streams were not dosed and the upstream riffles of each stream served as within stream controls. In 1986, the downstream riffle of one stream was dosed at 70 µg/L TRC and a second stream was dosed at 200 µg/L TRC. Four streams were also dosed with 2.5 mg/L NH3-N: one stream with no chlorine, one stream with ca. 10 µg/L TRC, one with 56 µg/L TRC, and one with 150 µg/L TRC. A seventh stream was dosed for 2 h at 2000 µg/L TRC and 2.5 mg/L ammonia and then allowed to recover (recovery stream). Each year, litter decomposition (degree day k values) was measured during two 35 day trials (Jun–Jul and Aug–Sep). In 1985, when streams were dosed with chlorine alone, decomposition was significantly reduced with the high (230 µg/L TRC) chlorine dose. Downstream decomposition was 27% (Jun–Jul) and 59% (Aug–Sep) of the upstream (control) rate. No other chlorine effects were found during this period. In Jun–Jul 1986, there was significantly lower decomposition in the downstream dosed sites of the 200 µg/L TRC alone stream, the 146 µg/L TRC + ammonia stream and the recovery stream; downstream decay rates were (respectively) 56%, 42% and 64% of the upstream control sites. No other up-down pairs were different in July 1986. In Aug–Sep, all three streams with chlorine + ammonia (6, 56 and 146 µg/L TRC + 2,5 mg/L ammonia) and the 70 µg/L TRC alone stream had significantly lower decomposition rates in the downstream dosed sites. For these streams, downstream decay rates ranged from 46% (high chlorine + ammonia) to 73% (low chlorine + ammonia) of the upstream control rates. No other up-down pairs were different during this trial. Up and downstream sites of the stream dosed with 2.5 mg/L ammonia alone were nearly identical for both trials (< 3% difference). These results indicate that TRC at less than 250 µg/L can significantly reduce litter decomposition and strongly suggest that addition of ammonia to chlorinated water can increase the toxic effect of chlorine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur, J. W., R. W. Andrew, V. R. Mattson, D. T. Olson, G. E. Glass, B. J. Halligan & C. T. Walbridge, 1975. Comparative toxicity of sewage effluent disinfection to freshwater aquatic life. EPA-600/3–75–012, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C.
Brooks, A. S. & J. M. Bartos, 1984. Effects of free and combined chlorine and exposire duration on rainbow trout, channel catfish, and emerald shiners. Trans. am. Fish. Soc. 113: 786–793.
Brungs, W. A., 1973. Effects of residual chlorine on aquatic life. J. Wat. Pollut. Cont. Fed. 45: 2180–2193.
Cairns, J., 1984. Are single species toxicity tests alone adequate for estimating environmental hazard? Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 4: 259–273.
Cairns, J. & B. R. Niederlehner, 1987. Problems associated with selecting the most sensitive species for toxicity testing. Hydrobiologia 153: 87–94.
Cummins, K. W., 1973. Trophic relations of aquatic insects. Ann. Rev. Ent. 18: 183–206.
Harter, H. L., 1960. Tables of range and studentized range. Ann. Math. Stat. 31: 1122–1147.
Hedtke, S. F. & J. W. Arthur, 1985. Evaluation of a site-specific water quality criterion for pentachlorophenol using outdoor experimental streams. In R. M. Cadwell, R. Purdy & R. C. Balmer (eds.), Aquatic toxicology and hazard assessment: seventh symposium. American Society for Testing and Materials, Special Technical Publication No. 695, Philadelphia, PA: 551–564.
Hermanutz, R. O., S. F. Hedtke, J. W. Arthur, R. W. Andrew, K. N. Allen & J. C. Helgen, 1987. Ammonia effects on microinvertebrates and fish in outdoor experimental streams. Envir. Pollut. 47: 249–283.
Hermanutz, R. O., K. N. Allen & S. F. Hedtke, in press. Toxicity and fate of total residual chlorine in outdoor experimental streams. In R. L. Jolley et al. (eds.), Water Chlorination.
Karr, J. R., 1987. Biological monitoring and environmental assessment: a conceptual framework. Envir. Management. 11: 249–256.
Karr, J. R., R. C. Heidinger & E. H. Helmer, 1985. Effets of chlorine and ammonia from waste water treatment facilities on biotic integrity. J. Wat. Pollut. Cont. Fed. 57: 912–915.
Lee, G. F. & R. A. Jones, 1986. Water quality hazard assessment for domestic wastewaters. In H. L. Bergman, R. A. Kimerle & A. W. Maki (eds.), Environmental Hazard Assessment of Effluents. Pergamon Press, NY: 228–246.
Mackay, R. J. & K. E. Kersey, 1985. A preliminary study of aquatic insect communities and leaf decomposition in acid streams near Dorset, Ontario. Hydrobiologia 122: 3–11.
Minshall, G. W., 1978. Autotrophy in stream ecosystems. BioScience 28: 767–771.
Mulholland, P. J.,A. V. Palumbo, J. W. Elwood & A. D. Rosemond, 1987. Effects of acidification on leaf decomposition in streams. J. N. am. Benthol. Soc. 6: 147–158.
Newbold, J. D., J. W. Elwood, M. S. Schulze, R. W. Stark & J. C. Barmeier, 1983. Continuous ammonium enrichment of a woodland stream: uptake kinetics, leaf decomposition, and nitrification. Freshwat. Biol. 13: 193–204.
Newman, R. M., J. A. Perry E. Tam & R. L. Crawford, 1987. Effects of chronic chlorine exposure on litter processing in outdoor experimental streams. Freshwat. Biol. 18:415–428.
Osborne, L. L., 1985. Response of Sheep River, Alberta, macroinvertebrate communities to discharge of chlorinated municipal sewage effluent. In R. L. Jolley et al. (eds), Water chlorination chemistry, environmental impact and health effects, volume 5. Lewis Publishers, Chelsea, Michigan: 481–492.
Paller, M. H., W. M. Lewis, R. C. Heidinger & L. J. Wawronowicz, 1983. Effects of ammonia and chlorine on fish in streams receiving secondary discharges. J. Wat. Pollut. Cont. Fed. 55: 1087–1097.
Perry, J. A., N. H. Troelstrup, M. Newsom & B. Shelley, 1987. Whole ecosystem manipulation experiments: the search for generality. Wat. Sci. Tech. 19: 55–71.
Stout, R. J. & W. E. Cooper, 1983. Effect of p-cresol on leaf decomposition and invertebrate colonization in experimental outdoor streams. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 40: 1647–1657.
Thurston, R. V., R. C. Russo, R. J. Luedtke, C. E. Smith, E. L. Meyun,C. Chakoumakos, K. C. Wang & C. J. D. Brown, 1984. Chronic toxicity of ammonia to rainbow trout. Trans. am. Fish. Soc. 113: 56–73.
Webster, J. R. & E. F. Benfield, 1986. Vascular plant breakdown in freshwater ecosystems. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 17: 567–594.
Wilkinson, L., 1987. SYSTAT: the system for statistics. SYSTAT Inc., Evanston, IL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
currently at the Department of Fisheries and Wildlife
currently at the Department of Fisheries and Wildlife
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newman, R.M., Perry, J.A. The combined effects of chlorine and ammonia on litter breakdown in outdoor experimental streams. Hydrobiologia 184, 69–78 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00014303
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00014303