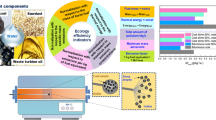
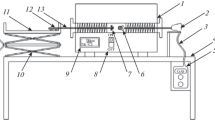
Abstract
Most industrial waste (mainly from raw-materials processing) consists of materials with relatively high calorific value. Their direct combustion to produce thermal and electrical energy is environmentally undesirable. An alternative approach is to convert the waste to slurry fuel, by forming suspensions in water. In the present work, the benefits of this approach are assessed by comparing the characteristics of slurry combustion with those of coal and fuel-oil combustion. The following factors are taken into account in the assessment: the ignition time delay; the minimum ignition temperature; the duration of combustion; the maximum combustion temperature; the heat of combustion; and the emissions of sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides. The cost of the components is also considered. The assessment shows that the effectiveness of the fuel suspensions may be as much as 50 times that of coal. Predictions show that thermal and electrical energy generation by the combustion of the proposed slurry fuels in industrial regions could supply up to 10% of annual energy requirements.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
BP Statistical Review of World Energy, London: British Petroleum, 2017.
Key World Energy Statistics, Paris: Int. Energy Agency, 2017.
Tracking Clean Energy Progress, Paris: Int. Energy Agency, 2017.
Qu, W., Xu, L., Qu, G., et al., The impact of energy consumption on environment and public health in China, Nat. Hazards, 2017, vol. 87, no. 2, pp. 675–697.
Shang, Y., Sun, Z., Cao, J., et al., Systematic review of Chinese studies of short-term exposure to air pollution and daily mortality, Environ. Inst., 2013, vol. 54, pp. 100–111.
Gaffney, J.S. and Marley, N.A., The impacts of combustion emissions on air quality and climate—From coal to biofuels and beyond, Atmos. Environ., 2009, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 23–36.
Saidur, R., Abdelaziz, E.A., Demirbas, A., et al., A review on biomass as a fuel for boilers, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2011, vol. 15, no. 5, pp. 2262–2289.
Zhou, C., Liu, G., Fang, T., and Lam, P.K.S., Investigation on thermal and trace element characteristics during co-combustion biomass with coal gangue, Bioresour. Technol., 2015, vol. 175, pp. 454–462.
Zhao, X., Zhu, W., Huang, J., et al., Emission characteristics of PCDD/Fs, PAHs and PCBs during the combustion of sludge-coal water slurry, J. Energy Inst., 2015, vol. 88, no. 2, pp. 105–111.
Strizhak, P.A. and Vershinina, K.Y., Maximum combustion temperature for coal-water slurry containing petrochemicals, Energy, 2017, vol. 120, pp. 34–46.
Li, D., Wu, D., Xu, F., et al., Literature overview of Chinese research in the field of better coal utilization, J. Clean. Prod., 2018, vol. 185, pp. 959–980.
Wang, H., Liu, S., Li, X., et al., Morphological and structural evolution of bituminous coal slime particles during the process of combustion, Fuel, 2018, vol. 218, pp. 49–58.
Liu, J., Wang, R., **, J., et al., Pilot-scale investigation on slurrying, combustion, and slagging characteristics of coal slurry fuel prepared using industrial waste liquid, Appl. Energy, 2014, vol. 115, pp. 309–319.
Vershinina, K.Yu. and Strizhak, P.A., Ignition of coal suspensions based on water of different quality, Coke Chem., 2016, vol. 59, no. 11, pp. 437–440.
Zhang, K., Cao, Q., **, L., et al., A novel route to utilize waste engine oil by blending it with water and coal, J. Hazard Mater., 2017, vol. 332, pp. 51–58.
Volynkina, E.P., Analysis of the state and problems of technological waste recycling in Russia, Vestn. Sib. Gos. Ind. Univ., 2017, no. 2, p. 20.
Dmitrienko, M.A. and Strizhak, P.A., Coal-water slurries containing petrochemicals to solve problems of air pollution by coal thermal power stations and boiler plants: an introductory review, Sci. Total Environ., 2018, vols. 613–614, pp. 1117–1129.
Armesto, L., Bahillo, A., Cabanillas, A., et al., Co-combustion of coal and olive oil industry residues in fluidized bed, Fuel, 2003, vol. 82, no. 8, pp. 993–1000.
Bhuiyana, A.A., Blicblau, A.S., Islam, A.K.M.S., and Naser, J., A review on thermo-chemical characteristics of coal/biomass co-firing in industrial furnace, Energy Inst., 2018, vol. 91, no. 1, pp. 1–18.
Mei, Y., Liu, R., and Zhang, L., Influence of industrial alcohol and additive combination on the physicochemical characteristics of bio-oil from fast pyrolysis of pine sawdust in a fluidized bed reactor with hot vapor filter, Energy Inst., 2016, vol. 90, no. 6, pp. 923–932.
Vershinina, K.Y., Kuznetsov, G.V., and Strizhak, P.A., Sawdust as ignition intensifier of coal water slurries containing petrochemicals, Energy, 2017, vol. 140, pp. 69–77.
Valiullin, T.R., Vershinina, K.Yu., Lyrshchikov, S.Yu., and Shevyrev, S.A., Ignition of fuel based on filter cake, Coke Chem., 2017, vol. 60, no. 3, pp. 127–132.
Nyashina, G.S., Kuznetsov, G.V., and Strizhak, P.A., Energy efficiency and environmental aspects of the combustion of coal-water slurries with and without petrochemicals, J. Clean. Prod., 2017, vol. 172, pp. 1730–1738.
Dmitrienko, M.A., Nyashina, G.S., and Strizhak, P.A., Environmental indicators of the combustion of prospective coal water slurry containing petrochemicals, J. Hazard. Mater., 2017, vol. 338, pp. 148–159.
Dmitrienko, M.A., Strizhak, P.A., and Tsygankova, Y.S., Technoeconomic analysis of prospects of use of organic coal-water fuels of various component compositions, Chem. Petrol. Eng., 2017, vol. 53, nos. 3–4, pp. 195–202.
Zhou, H., Ren, T., and Yang, Y., Impact of OFA on combustion and NOx emissions of a large-scale laboratory furnace fired by a heavy-oil swirl burner, Appl. Therm. Eng., 2015, vol. 90, pp. 994–1006.
Abdul Jameel, A.G., Han, Y., Brignoli, O., et al., Show more heavy fuel oil pyrolysis and combustion: kinetics and evolved gases investigated by TGA-FTIR, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol., 2017, vol. 127, pp. 183–195.
Funding
Financial support was provided by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project 18-43-700001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by B. Gilbert
About this article
Cite this article
Kuznetsov, G.V., Nyashina, G.S., Valiullin, T.R. et al. Benefits of Slurry Fuels Based on Industrial Wastes. Coke Chem. 62, 422–432 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068364X19090047
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068364X19090047