Abstract
Particle-wall collision is a complex liquid-solid coupling matter approximating to a chaotic state. Previous research mainly focused on the issues of particle trajectory and near-wall flow field, but the particle-wall collision mechanism and contact effects are unclear. To address this, a coupled computational fluid dynamics and discrete element method (CFD-DEM) modeling method is proposed. Firstly, flow field profiles are acquired by the CFD method as the initial motion conditions. Then, the particles are regarded as rigid bodies, and the data interactions between CFD and DEM are implemented by calculating for interaction force and void fraction. The results show that there are radial texture phenomena on the particle trajectories caused by the flowing interference; the central region has the lowest velocity and can be regarded as the rigid core of a Rankine vortex; if inlet diameter is 20 mm, the contacting distribution with rotating superposition can reach the best uniformity; the higher viscosity can carry more particles, and the transporting ability of the fluid medium is improved; the uniform contact effects can be more easily performed by the low viscosity fluid. This research can offer theoretical relevance to the modeling for multi-phase particle fluid, and provide technical support for flow regulation in the areas of fluid-based processing, turbine blade erosion, and reactor wall abrasion.
中文概要
目的
颗粒-壁面冲击碰撞是**似混沌运动的液固耦合问 题。针对传统建模方法难以描述颗粒-壁面碰撞运 动过程所涉及的壁面效应问题,本文旨在提出一 种液固耦合建模方法,以揭示流固耦合条件下的 颗粒-壁面接触规律,探讨碰撞过程中环境变量 (流道结构和流体粘度)对碰撞壁面效应的作用 机理;得到在约束及非约束空间流场中,流体粘度与颗粒-壁面碰撞行为的内在联系,为流体光整 加工、轮机叶片及反应器内壁面磨损所涉及的流 场调控提供技术支持。
创新点
1. 建立适用于液固两相流的计算流体力学和离散 单元法(CFD-DEM)耦合动力学模型;2. 通过 捕捉颗粒-壁面碰撞点分布,得到不同流道结构及 流体粘度下的颗粒-壁面作用范围;3. 建立无量纲 化材料去除方程,探明非约束及约束空间流场内 流体粘度对材料去除分布的影响。
方法
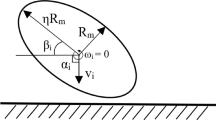
1. 将颗粒视为理想刚体,对流体运动及颗粒运动 分别进行建模,通过求解流体对颗粒的作用力以 及网格单元内流体体积分数实现两者之间的交 互耦合,进而得到流场内颗粒的运动规律;2. 采 用软球接触模型描述颗粒-壁面碰撞过程,进而得 到不同流道结构及流体粘度下的颗粒-壁面碰撞 落点分布;3. 计算颗粒-壁面冲击速度及冲击压 力,通过无量纲化材料去除方程,得到约束空间 及非约束空间内不同流体粘度下的工件表面材 料去除分布。
结论
1. 流道结构及流体粘度会极大影响颗粒-壁面碰撞 落点分布;在本文算例中,为获得均匀的工件加 工效果,应采用较低粘度流体,并使抛光盘做周 期性自转运动。2. 随着流体粘度的升高,流体输 运颗粒的能力增**,在非约束空间内的颗粒对壁 面的碰撞冲击越剧烈,但在约束空间内的碰撞作 用力减弱;在本文算例中,为获得更为均匀的材 料去除分布,应采用较低粘度流体。3. 借助粒子 图像测速法得到了壁面处颗粒速度分布,并与模 拟结果进行对比,验证了建模方法的有效性。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao, Z.C., Cheung, C.F., 2014. Theoretical modelling and analysis of the material removal characteristics in fluid jet polishing. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 89:158–166. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2014.09.008
Chen, G.J., Zhang, Y.J., Yang, Y.S., 2013. Modelling the unsteady melt flow under a pulsed magnetic field. Chinese Physics B, 22(12):124703. http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/22/12/124703
Gao, H., Guo, L.J., Zhang, X.M., 2002. Liquid–solid separation phenomena of two-phase turbulent flow in curved pipes. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 45(25):4995–5005. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0017-9310(02)00207-7
Guala, M., Stocchino, A., 2007. Large-scale flow structures in particle-wall collision at low Deborah numbers. European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids, 26(4):511–530. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechflu.2006.10.004
Hu, G.M., 2010. Analysis and Simulation of Granular System by Discrete Element Method Using EDEM. Wuhan University of Technology Press, Wuhan, China, p.145–146 (in Chinese).
Ji, S.M., Weng, X.X., Tan, D.P., 2012a. Analytical method of softness abrasive two-phase flow field based on 2D model of LSM. Acta Physica Sinica, 61(1):010205 (in Chinese).
Ji, S.M., Zhong, J.Q., Tan, D.P., 2012b. Distribution and dynamic characteristic of particle group with different concentration in structural flow passage. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 28(4): 45–53 (in Chinese).
**, Y.F., Wan, Y., Zhang, B., et al., 2017. Modeling of the chemical finishing process for polylactic acid parts in fused deposition modeling and investigation of its tensile properties. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 240:233–239. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.10.003
Kotrocz, K., Mouazen, A.M., Kerenyi, G., 2016. Numerical simulation of soil-cone penetrometer interaction using discrete element method. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 125:63–73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2016.04.023
Kowsari, K., Nouraei, H., Samareh, B., et al., 2016. CFDaided prediction of the shape of abrasive slurry jet micromachined channels in sintered ceramics. Ceramics International, 42(6):7030–7042. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.01.091
Kruggel-Emden, H., Simsek, E., Rickelt, S., 2007. Review and extension of normal force models for the discrete element method. Powder Technology, 171(3):157–173. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2006.10.004
Ku, X.K., Lin, J.Z., 2008. Motion and orientation of cylindrical and cubic particles in pipe flow with high concentration and high particle to pipe size ratio. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A, 9(5):664–671. http://dx.doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A071463
Li, C., 2012. Study of Near Wall Area Micro-cutting Mechanism and Control Method for Softness Abrasive Flow Finishing. PhD Thesis, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China (in Chinese).
Lopez, A., Nicholls, W., Stickland, M.T., et al., 2015. CFD study of Jet Im**ement Test erosion using Ansys Fluent® and OpenFOAM®. Computer Physics Communications, 197:88–95. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2015.07.016
Mansouri, A., Arabnejad, H., Karimi, S., et al., 2015. A combined CFD/experimental methodology for erosion prediction. Wear, 332:1090–1097. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2014.11.025
Nguyen, N.Y., Tian, Y.B., Zhong, Z.W., 2014. Modeling and simulation for the distribution of slurry particles in chemical mechanical polishing. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 75(1):97–106. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6132-9
Ren, C.J., Wang, J.D., Song, D., et al., 2011. Determination of particle size distribution by multi-scale analysis of acoustic emission signals in gas-solid fluidized bed. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 12(4):260–267. http://dx.doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1000396
Sun, Q.C., Wang, G.Q., 2009. An Introduction to the Mechanics of Granular Materials. Science Press, Bei**g, China, p.33–34 (in Chinese).
Tan, D.P., Zhang, L.B., 2014. A WP-based nonlinear vibration sensing method for invisible liquid steel slag detection. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 202:1257–1269. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.06.014
Tan, D.P., Ji, S.M., Li, P.Y., et al., 2010. Development of vibration style ladle slag detection methods and the key technologies. Science China Technological Sciences, 53(9):2378–2387. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-4073-6
Tan, D.P., Li, P.Y., Ji, Y.X., et al., 2013. SA-ANN-based slag carry-over detection method and the embedded WME platform. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 60(10):4702–4713. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2012.2213559
Tan, D.P., Ji, S.M., Fu, Y.Z., 2015. An improved soft abrasive flow finishing method based on fluid collision theory. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 85(5):1261–1274.
Tan, D.P., Yang, T., Zhao, J., et al., 2016. Free sink vortex Ekman suction-extraction evolution mechanism. Acta Physica Sinica, 65(5):054701 (in Chinese).
Wan, S., Ang, Y.J., Sato, T., et al., 2014. Process modeling and CFD simulation of two-way abrasive flow machining. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 71(5):1077–1086. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5550-4
Wang, T., Wan, Y., Kou, Z.J., et al., 2016. Construction of a bioactive surface with micro/nano-topography on titanium alloy by micro-milling and alkali-hydrothermal treatment. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine, 230(12):1086–1095. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0954411916675382
Wu, X.C., Wu, Y.C., Zhang, C.C., et al., 2013. Fundamental research on the size and velocity measurements of coal powder by trajectory imaging. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 14(5):377–382. http://dx.doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1200233
Zhang, K., **ing on the substrate during suspension plasma spraying. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 17(9):733–744. http://dx.doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1500203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51375446 and 51575494) and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. LR16E050001 and LZ14E050001)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, Sm., Ge, Jq. & Tan, Dp. Wall contact effects of particle-wall collision process in a two-phase particle fluid. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 18, 958–973 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1700039
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1700039
Keywords
- Wall contact effects
- Computational fluid dynamics and discrete element method (CFD-DEM)
- Particle-wall collision
- Two-phase particle fluid