Abstract
Background
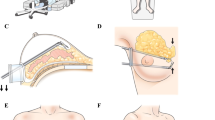
New surgical innovations of nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM), such as endoscopic NSM (E-NSM) or robotic NSM (R-NSM), were emerging. However, there was a lack of evidence comparing the effectiveness and safety in the management of breast cancer.
Methods
A case–control comparison study was conducted for patients with breast cancer underwent E-NSM or R-NSM with immediate prosthesis breast reconstruction (IPBR) from July 2010 to February 2019 at a single institution to compare the clinical outcomes, learning curve, patient-reported cosmetic results, and medical cost.
Results
A total of 91 E-NSM and 40 R-NSM procedures were retrieved and analyzed. The surgical margin involvement rate in both R-NSM (2.5%) and E-NSM (4.4%) procedures were relatively low (P = 0.52). The R-NSM group was associated with higher satisfaction rates in terms of scar appearance, scar length, and surgical wound position compared with the E-NSM group. Compared with E-NSM, the R-NSM operation time took longer (241 ± 61 vs. 215 ± 70 min, P = 0.01), less blood loss (32 ± 29 vs. 79 ± 62 ml, P < 0.01), and higher medical cost (10,587 ± 554 vs. 6855 ± 936 U.S. dollars, P < 0.01). There was no statistically significant difference in nipple ischemia/necrosis or overall complication between R-NSM and E-NSM. In the learning curve analysis, it took the 27th procedure in E-NSM and 10th procedure in R-NSM to decrease operation time significantly.
Conclusions
R-NSM was associated with higher wound-related satisfaction, lesser blood loss, and shorter learning curve compared with E-NSM, however, at the price of longer operation time and higher medical cost.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lai HW, Lin SL, Chen ST, Kuok KM, Chen SL, Lin YL, Chen DR, Kuo SJ. Single-axillary-incision endoscopic-assisted hybrid technique for nipple-sparing mastectomy: technique, preliminary results, and patient-reported cosmetic outcome from preliminary 50 procedures. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25(5):1340–9.
Tukenmez M, Ozden BC, Agcaoglu O, Kecer M, Ozmen V, Muslumanoglu M, Igci A. Videoendoscopic single-port nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate reconstruction. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2014;24(2):77–82.
Sakamoto N, Fukuma E, Higa K, Ozaki S, Sakamoto M, Abe S, Kurihara T, Tozaki M: Early results of an endoscopic nipple-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(12):3406–13.
Toesca A, Peradze N, Manconi A, Galimberti V, Intra M, Colleoni M, Bonanni B, Curigliano G, Rietjens M, Viale G et al: Robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy for the treatment of breast cancer: feasibility and safety study. Breast. 2017;31:51–6.
Sarfati B, Struk S, Leymarie N, et al. Robotic prophylactic nipple-sparing mastectomy with immediate prosthetic breast reconstruction: a prospective study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25(9):2579–86.
Lai HW, Chen ST, Lin SL, Chen CJ, Lin YL, Pai SH, Chen DR, Kuo SJ. Robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction with gel implant: technique, preliminary results and patient-reported cosmetic outcome. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26(1):42–52.
Fan LJ, Jiang J, Yang XH, Zhang Y, Li XG, Chen XC, Zhong L. A prospective study comparing endoscopic subcutaneous mastectomy plus immediate reconstruction with implants and breast conserving surgery for breast cancer. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009;122(24):2945–50.
Ito K, Kanai T, Gomi K, Watanabe T, Ito T, Komatsu A, Fujita T, Amano J. Endoscopic-assisted skin-sparing mastectomy combined with sentinel node biopsy. ANZ J Surg. 2008;78(10):894–8.
Lai HW, Chen ST, Chen DR, Chen SL, Chang TW, Kuo SJ, Kuo YL, Hung CS. Current trends in and indications for endoscopy-assisted breast surgery for breast cancer: results from a six-year study conducted by the Taiwan Endoscopic Breast Surgery Cooperative Group. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150310.
Lai HW, Wu HS, Chuang KL, Chen DR, Chang TW, Kuo SJ, Chen ST, Kuo YL. Endoscopy-assisted total mastectomy followed by immediate pedicled transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous (TRAM) Flap Reconstruction: Preliminary Results of 48 Patients. Surg Innov. 2015;22(4):382–9.
Hung CS, Chang SW, Liao LM, M, et al. The learning curve of endoscopic total mastectomy in Taiwan: a multi-center study. PLoS One. 2017;12(6):e0178251.
Ingram D. Is it time for breast cancer surgeons to embrace endoscopic-assisted mastectomy? ANZ J Surg. 2008;78(10):837–8.
Leff DR, Vashisht R, Yongue G, Keshtgar M, Yang GZ, Darzi A. Endoscopic breast surgery: where are we now and what might the future hold for video-assisted breast surgery? Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;125(3):607–25.
Abramovici L, Cartier C, Pierre G, Garrel R. Robot-assisted transaxillary thyroidectomy: surgical technique. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2015;132(3):153–6.
Alkatout I, Mettler L, Maass N, Ackermann J. Robotic surgery in gynecology. J Turkish German Gynecol Assoc. 2016;17(4):224–32.
Selber JC, Baumann DP, Holsinger FC. Robotic latissimus dorsi muscle harvest: a case series. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129(6):1305–12.
Toesca A, Peradze N, Galimberti V, et al. Robotic Nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction with implant: first report of surgical technique. Ann Surg. 2017;266(2):e28–30.
Sarfati B, Honart JF, Leymarie N, Rimareix F, Al Khashnam H, Kolb F: Robotic da Vinci **-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy: first clinical report. Breast J. 2018;24(3):373–6.
Mittal AK, Dubey M, Arora M, Bhagat S, Bhargava AK. Anaesthetic consideration for robotic nipple sparing mastectomy. Indian J Anaesth. 2017;61(6):519–21.
Lai HW, Lin SL, Chen ST, Chen SL, Lin YL, Chen DR, Kuo SJ. Robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction with gel implant. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2018;6:e1828.
Lai HW, Wang CC, Lai YC, Chen CJ, Lin SL, Chen ST, Lin YJ, Chen DR, Kuo SJ. The learning curve of robotic nipple sparing mastectomy for breast cancer: an analysis of consecutive 39 procedures with cumulative sum plot. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019;45(2):125–33.
Lai HW, Lin HY, Chen SL, Chen ST, Chen DR, Kuo SJ. Endoscopy-assisted surgery for the management of benign breast tumors: technique, learning curve, and patient-reported outcome from preliminary 323 procedures. World J Surg Oncol. 2017;15(1):19.
Sarfati B, Struk S, Leymarie N, Honart JF, Alkhashnam H, Kolb F, Rimareix F. Robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy with immediate prosthetic breast reconstruction: surgical technique. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;142(3):624–7.
Lai HW, Lin SL, Chen ST, Lin YL, Chen DR, Pai SS, Kuo SJ. Robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction with robotic latissimus dorsi flap harvest: technique and preliminary results. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018;71(10):e59–61.
Lai HW, Chen ST, Lin SL, Lin YL, Wu HK, Pai SH, Chen DR, Kuo SJ. Technique for single axillary incision robotic assisted quadrantectomy and immediate partial breast reconstruction with robotic latissimus dorsi flap harvest for breast cancer: a case report. Medicine. 2018;97(27):e11373.
Moran MS, Schnitt SJ, Giuliano AE, et al. Society of Surgical Oncology-American Society for Radiation Oncology consensus guideline on margins for breast-conserving surgery with whole-breast irradiation in stages I and II invasive breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21(3):704–16.
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology-Breast Cancer. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/breast.pdf. Accessed Mar 2017.
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ, Panel M. Strategies for subtypes–dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 2011;22(8):1736–47.
Curigliano G, Burstein HJ, E PW, Gnant M, Dubsky P, Loibl S, Colleoni M, Regan MM, Piccart-Gebhart M, Senn HJ, et al. De-escalating and escalating treatments for early-stage breast cancer: the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus Conference on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2017. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(8):1700–12.
Piper M, Peled AW, Foster RD, Moore DH, Esserman LJ. Total skin-sparing mastectomy: a systematic review of oncologic outcomes and postoperative complications. Ann Plast Surg. 2013;70(4):435–7.
Carlson GW, Chu CK, Moyer HR, Duggal C, Losken A. Predictors of nipple ischemia after nipple sparing mastectomy. Breast J. 2014;20(1):69–73.
Wohl H. The cusum plot: its utility in the analysis of clinical data. N Engl J Med. 1977;296(18):1044–5.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ya-Ling Lin, Yun-Ting Chang, Shu-Hsin Pai, Yi-Ru Ke, and Shun-Ing Tsai for assistance with this study.
Funding
This study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan, and the number of this funding was: MOST-108-2314-B-371-006-. This study was also sponsored by research funding provided by the Changhua Christian Hospital, and the numbers of the funding were: 106-CCH-IRP-015, 106-CCH-IRP-201, 106-CCH-IRP-202, 107-CCH-HCR-035, and 108-CCH-IRP-122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None of the authors have conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 52647 kb)
Supplementary material 2 (MP4 32848 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, HW., Chen, ST., Tai, CM. et al. Robotic- Versus Endoscopic-Assisted Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate Prosthesis Breast Reconstruction in the Management of Breast Cancer: A Case–Control Comparison Study with Analysis of Clinical Outcomes, Learning Curve, Patient-Reported Aesthetic Results, and Medical Cost. Ann Surg Oncol 27, 2255–2268 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-08223-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-08223-0