Abstract
Background
Angiopoietin-like protein 2 (ANGPTL2) mediates chronic inflammation. Tumor cell-derived ANGPTL2 promotes tumor invasion and angiogenesis. Overexpression of ANGPTL2 in tumor cells is associated with tumor progression and has been recognized in lung, breast, colon, and gastric cancer. However, to our knowledge the functional and clinical significance of ANGPTL2 expression has not been investigated in patients with esophageal cancer (EC).
Methods
First, in vitro assays were performed for functional analysis of ANGPTL2 using small interfering RNA. Next, ANGPTL2 expression in EC tissues (n = 71) was evaluated by immunohistochemistry (IHC in patients with EC (n = 71). Finally, serum ANGPLT2 levels from patients with EC (n = 71) and healthy controls (n = 35) were evaluated using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results
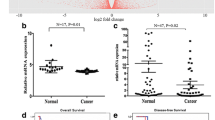
Knockdown of ANGPTL2 expression decreased the proliferative, invasive, and migration capacity in EC cell lines. ANGPTL2 expression in EC tissues was significantly elevated in patients with a high T stage, squamous cell carcinoma, and high TNM stage. Patients with high ANGPTL2 expression had significantly poorer overall and disease-free survival than those with low expression. Furthermore, high ANGPTL2 expression in EC tissues was an independent predictive marker for a poor prognosis. On the other hand, the serum ANGPTL2 level in patients with EC was significantly higher than that in healthy controls, and allowed for highly accurate discrimination between patients with and without EC. However, no significant association between serum ANGPTL2 levels and clinicopathological findings was observed in patients with EC.
Conclusions
We have demonstrated novel evidence for the clinical significance of ANGPTL2 as a biomarker in patients with EC.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANGPTL2:
-
angiopoietin-like protein 2
- EC:
-
esophageal cancer
- siRNA:
-
small interfering RNA
- ESCC:
-
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- EAD:
-
esophageal adenocarcinoma
- IHC:
-
immunohistochemistry
- GC:
-
gastric cancer
- CRC:
-
colorectal cancer
- cDNA:
-
complementary DNA
- qRT-PCR:
-
quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- ELISA:
-
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- OS:
-
overall survival
- DFS:
-
disease-free survival
- ROC:
-
receiver operating characteristic
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69-90.
Lin Y, Totsuka Y, He Y, et al. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer in Japan and China. J Epidemiol. 2013;23:233-42.
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2241-52.
Mariette C, Balon JM, Piessen G, Fabre S, Van Seuningen I, Triboulet JP. Pattern of recurrence following complete resection of esophageal carcinoma and factors predictive of recurrent disease. Cancer. 2003;97:1616-23.
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 2010;140:883-99.
Radojicic J, Zaravinos A, Spandidos DA. HPV, KRAS mutations, alcohol consumption and tobacco smoking effects on esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma carcinogenesis. Int J Biol Markers. 2012;27:1-12.
Toh Y, Oki E, Ohgaki K, et al. Alcohol drinking, cigarette smoking, and the development of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: molecular mechanisms of carcinogenesis. Int J Clin Oncol. 2010;15:135-44.
Gilbert EW, Luna RA, Harrison VL, Hunter JG. Barrett’s esophagus: a review of the literature. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011;15:708-18.
Oike Y, Yasunaga K, Suda T. Angiopoietin-related/angiopoietin-like proteins regulate angiogenesis. Int J Hematol. 2004;80:21-8.
Tabata M, Kadomatsu T, Fukuhara S, et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 2 promotes chronic adipose tissue inflammation and obesity-related systemic insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2009;10:178-88.
Okada T, Tsukano H, Endo M, et al. Synoviocyte-derived angiopoietin-like protein 2 contributes to synovial chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Pathol. 2010;176:2309-19.
Ogata A, Endo M, Aoi J, et al. The role of angiopoietin-like protein 2 in pathogenesis of dermatomyositis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;418:494-9.
Aoi J, Endo M, Kadomatsu T, et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 2 is an important facilitator of inflammatory carcinogenesis and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011;71:7502-12.
Endo M, Nakano M, Kadomatsu T, et al. Tumor cell-derived angiopoietin-like protein ANGPTL2 is a critical driver of metastasis. Cancer Res. 2012;72:1784-94.
Toiyama Y, Takahito Kitajima, Tadanobu Shimura, et al. (2014) Angiopoietin-like protein 2 is a novel serum biomarker of diagnosis and prognosis in patients with gastrointestinal cancer. Gastroenterology.;146(5 Suppl 1):s-30–s-1.
Toiyama Y, Tanaka K, Kitajima T, et al. Elevated serum angiopoietin-like protein 2 correlates with the metastatic properties of colorectal cancer: a serum biomarker for early diagnosis and recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:6175–86.
Strong VE, D’Amico TA, Kleinberg L, Ajani J. Impact of the 7th Edition AJCC staging classification on the NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology for gastric and esophageal cancers. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2013;11:60-6.
Ando N, Ozawa S, Kitagawa Y, Shinozawa Y, Kitajima M. Improvement in the results of surgical treatment of advanced squamous esophageal carcinoma during 15 consecutive years. Ann Surg. 2000;232:225-32.
Ando N, Iizuka T, Ide H, et al. Surgery plus chemotherapy compared with surgery alone for localized squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus: a Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study–JCOG9204. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:4592-6.
Ando N, Kato H, Igaki H, et al. A randomized trial comparing postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil versus preoperative chemotherapy for localized advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus (JCOG9907). Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:68-74.
Endo M, Yamamoto Y, Nakano M, et al. Serum ANGPTL2 levels reflect clinical features of breast cancer patients: implications for the pathogenesis of breast cancer metastasis. Int J Biol Markers. 2014;29:e239–45.
Disclosure
Shozo Ide, Yuji Toiyama, Tadanobu Shimura, Mikio Kawamura, Hiromi Yasuda, Susumu Saigusa, Masaki Ohi, Koji Tanaka, Yasuhiko Mohri, and Masato Kusunoki have nothig to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10434_2014_4315_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Extent of ANGPTL2 IHC staining.Representative photomicrographs obtained from immunohistochemicalstaining to analyze ANGPTL2 expression in primary esophageal cancer (EC) tissue specimens (original magnification, ×100). Scores for extent of ANGPTL2 staining in EC: 0%: 0, (a) 1–25%: 1, (b) 26–50%: 2, (c) 51–75%: 3, and (d) 76–100%: 4 (TIFF 3916 kb)
10434_2014_4315_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Intensity of ANGPTL2IHC staining.Representative photomicrographs obtained from immunohistochemicalstaining to analyze ANGPTL2 expression in primary esophageal cancer (EC) tissue specimens (original magnification, ×100). Scores for intensity of ANGPTL2 staining in EC: (a) no staining: 0, (b) weak staining: 1, (c) moderate staining: 2, and (d) strong staining: 3 (TIFF 3912 kb)
10434_2014_4315_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Expression and knockdown of ANGPTL2 in EC cell lines.(a)Relative quantification of ANGPTL2 mRNA expression in six esophageal cancer (EC) cell lines based on the 2-⊿Ct method. (b, c) Expression of ANGPTL2 in TE1 and TE2 after siRNA transfection (2-⊿Ct method). (d, e) ANGPTL2 expression in TE1 and TE3 at 48 hours after siRNA transfection as evaluated by ELISA. Control: negative-control siRNA-treated cells, si: ANGPTL2 siRNA-treated cells (TIFF 238 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ide, S., Toiyama, Y., Shimura, T. et al. Angiopoietin-Like Protein 2 Acts as a Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis and Prognosis in Patients with Esophageal Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 22, 2585–2592 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-4315-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-4315-0