Abstract
Background
LncRNA ATP2B1-AS1 (ATP2B1-AS1) is involved in the occurrence and development of various diseases, while the relationship between lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and ATP2B1-AS1 is unclear. This study was to investigate the expression of ATP2B1-AS1 in LUAD and its influence on survival and prognosis of patients.
Methods
LUAD tissue samples from patients participating in this study were collected, and the expression levels of ATP2B1-AS1 and miR-141-3p in LUAD sampleswere detected by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The effect of ATP2B1-AS1 on the growth of A549 cells was investigated through cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) and transwell experiments. Besides, the prognostic value of ATP2B1-AS1 in LUAD was assessed via Kaplan-Meier curve and multivariate Cox regression.
Results
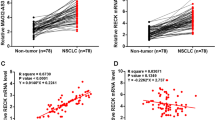
ATP2B1-AS1 was downregulated in LUAD tissues and cells, whereas miR-141-3p was upregulated. After pcDNA3.1-ATP2B1-AS1 was transfected into A549 cells, the proliferation ability of A549 cells was decreased, and the migration level and invasion of A549 cells were also inhibited. High expression of ATP2B1-AS1 sponge miR-141-3p exerted prognostic value.
Conclusions
ATP2B1-AS1 sponge miR-141-3p alleviated the progression of LUAD, and ATP2B1-AS1 may be deemed as a prognostic marker for LUAD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is a common subtype of non-small cell carcinoma, which is a classification of lung cancer [1]. According to data from 2020, lung cancer ranks second in incidence and first in mortality [20]. Nowadays, with the innovation and breakthroughs of bioinformatics, molecular biology, immunology and other technologies, promising methods such as molecular targeting and immunosuppression have been used in clinical practice, but the mortality rate of LUAD patients remains high [21, 22]. Therefore, it is also a new challenge to explore the specific prognostic markers of LUAD.
ATP2B1-AS1, also known as intergenic long non-protein-coding RNA 936 (LINC00936), is underexpressed in various diseases. Ren and colleagues assessed patients with diabetic retinopathy and learned that down-regulation of ATP2B1-AS1 expression could ameliorate cell permeability by targeting miR-4729, thereby alleviating retinopathy in patients [9]. Shu et al. stated that LINC00936 was downregulated in ovarian cancer tissues and that the combination of miR-221-3p with high expression of LINC00936 controlled the occurrence of ovarian cancer [23]. Similar results, ATP2B1-AS1 expression was decreased in LUAD tissues and cells. After constructing and overexpressing ATP2B1-AS1 in A549 cells, it was found that the proliferative capacity, migration performance, and invasion level of LUAD cells were inhibited. It is referenced that in LUAD-related literature, HCG11 expression was also reduced and the growth of LUAD cells was inhibited by IGF2BP2/LATS1 [24]. What’s more, highly expressed lncRNA ARAP1-AS1 promoted the progression of LUAD by mediating miR-8068/CEACAM5 [25].Subsequently, downstream target genes of ATP2B1-AS1 were predicted to show that there were binding sites between ATP2B1-AS1 and miR-141-3p, which might regulate LUAD through sponge miR-141-3p. Kang et al. confirmed that miR-141-3p was significantly elevated in Th17 cells and participated in differentiation, providing evidence for the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases [26]. Yang and colleagues revealed the upregulation mechanism of miR-141-3p in endometrial cancer and predicted the key role of miR-141-3poverexpression in carcinogenesis and prognosis [27]. In addition, miR-141-3p was confirmed to be differentially expressed as well in human diseases such as polycystic ovary syndrome [28], clear cell renal cell carcinoma [29], and colorectal cancer [30]. The above studies demonstrated the ability of ATP2B1-AS1 to affect the development of different types of tumors and the prognosis of patients through multiple mechanisms. The results of this study revealed that miR-141-3p was higher in LUAD tissues and cells than in the matched control group by PCR detection. The luciferase activity assay implied that ATP2B1-AS1 targets miR-141-3p to participate in the development of LUAD, and ATP2B1-AS1 negatively regulates miR-141-3p. Kaplan-Meier and multivariate analysis showed that high expression of ATP2B1-AS1 improved the survival time of patients. In dong’s study of breast cancer in vivo and in vitro, low expression of MEG3 sponge miR-141-3p affected cell proliferation performance and apoptosis, which was negatively correlated with high expression of miR-141-3p [31]. Meanwhile, circKEAP1 inhibited the progression of LUAD by targeting miR-141-3p and opened a new idea for the treatment of LUAD [32], which was consistent with our study. The previous analysis confirmed that ATP2B1-AS1 specifically binds to miR-141-3p to participate in the development of LUAD and play a regulatory role in the prognosis of patients from the aspects of cell function and biological mechanism.
Obviously, the deficiency lies in that the downstream target of miR-141-3p has not been further studied, and the samples need to be expanded for follow-up exploration, so as to more clearly understand the regulatory pathway and prognostic value of ATP2B1- AS1 on LUAD. In addition, we also need to design animal assays in subsequent studies to grasp more clinical information and increase the reliability of research results.
Conclusions
In conclusion, ATP2B1-AS1 was markedly underexpressed in LUAD and elucidated poor prognosis of LUAD, which may serve as a valuable prognostic biomarker. In addition, overexpression of ATP2B1-AS1 suppressed the proliferation capacity, migration level and invasion of A549 cells.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ATCC:
-
American Type Culture Collection
- ATP2B1-AS1:
-
LncRNA ATP2B1-AS1
- CCK-8:
-
cell counting kit-8
- LINC00936:
-
long non-protein-coding RNA 936
- LUAD:
-
lung adenocarcinoma
- miRNAs:
-
microRNAs
- RT-qPCR:
-
real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction
References
Wang L, Shang M, Dai Q, He PA. Prediction of lncRNA-disease association based on a Laplace normalized random walk with restart algorithm on heterogeneous networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022;23(1):5.
Leng Y, Dang S, Yin F, Gao T, **ao X, Zhang Y, et al. GDPLichi: a DNA damage repair-related Gene Classifier for Predicting Lung Adenocarcinoma Immune checkpoint inhibitors response. Front Oncol. 2021;11:733533.
**ao J, Chen X, Lu X, **e M, He B, He S, et al. Progesterone/Org inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell growth via membrane progesterone receptor alpha. Thorac Cancer. 2020;11(8):2209–23.
Baraibar I, Roman M, Rodríguez-Remírez M, López I, Vilalta A, Guruceaga E et al. Id1 and PD-1 combined blockade impairs Tumor Growth and Survival of KRAS-mutant Lung Cancer by stimulating PD-L1 expression and Tumor infiltrating CD8(+) T cells. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(11).
Liu X, Jia Y, Shi C, Kong D, Wu Y, Zhang T, et al. CYP4B1 is a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target in lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(2):e0247020.
Liu HY, Lu SR, Guo ZH, Zhang ZS, Ye X, Du Q, et al. lncRNA SLC16A1-AS1 as a novel prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. J Investig Med. 2020;68(1):52–9.
Zhang R, Ma L, Li W, Zhou S, Xu S. Diagnostic value of multiple tumor-associated autoantibodies in lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:457–69.
Wang L, Tan Y, Zhu Z, Chen J, Sun Q, Ai Z, et al. ATP2B1-AS1 promotes cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through regulating the miR-330-5p/TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:720468.
Ren Z, Wang X. Long non-coding ribonucleic acid ATP2B1-AS1 modulates endothelial permeability through regulating the mir-4729-IQGAP2 axis in diabetic retinopathy. J Diabetes Investig. 2022;13(3):443–52.
Chen Y, Zhang X, Li J, Zhou M. Immune-related eight-lncRNA signature for improving prognosis prediction of lung adenocarcinoma. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021;35(11):e24018.
Xu Y, Lin L, Lv D, Yan S, He S, Ge H. LncRNA-LINC01089 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis via sponging miR-543. Tissue Cell. 2021;72:101535.
Wu L, Wen Z, Song Y, Wang L. A novel autophagy-related lncRNA survival model for lung adenocarcinoma. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(12):5681–90.
Yao J, Chen X, Liu X, Li R, Zhou X, Qu Y. Characterization of a ferroptosis and iron-metabolism related lncRNA signature in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):340.
Wu ZH, Zhou J, Hu GH, Liu J, Li WC, Lai XH, et al. LncRNA CASC2 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma progression through forming feedback loop with miR-21/p53 axis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2021;37(8):675–85.
Chodary Khameneh S, Razi S, Shamdani S, Uzan G, Naserian S. Weighted correlation network analysis revealed novel long non-coding RNAs for colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):2990.
Liu X, Wei H, Liao S, Ye J, Zhu L, Xu Z. MicroRNA transcriptome analysis of porcine vital organ responses to immunosuppressive porcine cytomegalovirus infection. Virol J. 2018;15(1):16.
Matboli M, Shafei AE, Ali MA, El-Din Ahmed TS, Naser M, Abdel-Rahman T, et al. Role of extracellular LncRNA-SNHG14/miRNA-3940-5p/NAP12 mRNA in colorectal cancer. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2021;127(6):479–85.
Liu J, Feng Y, Zeng X, He M, Gong Y, Liu Y. LncRNA VPS9D1-AS1 promotes malignant progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma by Targeting miRNA-30a-5p/KIF11 Axis. Front Genet. 2021;12:807628.
Li Y, Lin M, Wang S, Cao B, Li C, Li G. Novel angiogenic regulators and anti-angiogenesis drugs targeting Angiogenesis Signaling pathways: perspectives for Targeting Angiogenesis in Lung Cancer. Front Oncol. 2022;12:842960.
Wang Y, Tan H, Yu T, Chen X, **g F, Shi H. Potential Immune Biomarker candidates and Immune subtypes of Lung Adenocarcinoma for develo** mRNA vaccines. Front Immunol. 2021;12:755401.
Yuan Y, Jiang X, Tang L, Wang J, Liu Q, Zou X, et al. SNX20AR/MiRNA-301a-3p/SNX20 Axis Associated with Cell Proliferation and Immune Infiltration in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:744363.
Yin J, Che G, Jiang K, Zhou Z, Wu L, Xu M, et al. Ciclopirox Olamine exerts tumor-suppressor effects via Topoisomerase II alpha in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 2022;12:791916.
Shu C, Wang W, Wu L, Qi C, Yan W, Lu W, et al. LINC00936/microRNA-221-3p regulates tumor progression in ovarian cancer by interacting with LAMA3. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov; 2022.
Mao J, Qiu H, Guo L. LncRNA HCG11 mediated by METTL14 inhibits the growth of lung adenocarcinoma via IGF2BP2/LATS1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;580:74–80.
Wu Z, Zeng X, Wang H, Wang X. LncRNA ARAP1-AS1 contributes to lung adenocarcinoma development by targeting miR-8068 to upregulate CEACAM5. Cancer Biomark. 2023;38(2):177–89.
Bahmani L, Baghi M, Peymani M, Javeri A, Ghaedi K. MiR-141-3p and miR-200a-3p are involved in Th17 cell differentiation by negatively regulating RARB expression. Hum Cell. 2021;34(5):1375–87.
Yang LJ, Gao L, Guo YN, Liang ZQ, Li DM, Tang YL, et al. Upregulation of microRNA mir-141-3p and its prospective targets in endometrial carcinoma: a comprehensive study. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):2941–56.
Fan L, Wang C, Zhan P, Liu Y. Mir-141-3p is poorly expressed in polycystic ovary syndrome and correlates with glucose and lipid metabolism. Int J Endocrinol. 2021;2021:2022938.
Liu Y, Fu W, Yin F, **a L, Zhang Y, Wang B, et al. Mir-141-3p suppresses development of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by regulating NEK6. Anticancer Drugs. 2022;33(1):e125–e33.
Tong SJ, Zhang XY, Guo HF, Yang J, Qi YP, Lu S. Study on effects of mir-141-3p in proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of colon cancer cells by inhibiting Bcl2. Clin Transl Oncol. 2021;23(12):2526–35.
Dong S, Ma M, Li M, Guo Y, Zuo X, Gu X, et al. LncRNA MEG3 regulates breast cancer proliferation and apoptosis through miR-141-3p/RBMS3 axis. Genomics. 2021;113(4):1689–704.
Wang Y, Ren F, Sun D, Liu J, Liu B, He Y, et al. CircKEAP1 suppresses the progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma via the miR-141-3p/KEAP1/NRF2 Axis. Front Oncol. 2021;11:672586.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors designed this study. SY C, C H and E J conducted the experiment and analyzed the data. SY C and C H wrote the manuscript. E J revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was conducted under the guidance of the hospital Ethics Committee and with the consent of the patients.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Huang, C. & **, E. Regulation of overexpression lncRNA ATP2B1-AS1 on lung adenocarcinoma progression. J Cardiothorac Surg 19, 88 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13019-024-02507-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13019-024-02507-2