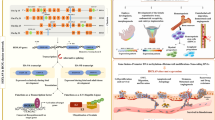
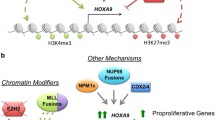
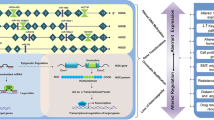
Abstract
HOXA9 functioning as a transcription factor is one of the members of HOX gene family, which governs multiple cellular activities by facilitating cellular signal transduction. In addition to be a driver in AML which has been widely studied, the role of HOXA9 in solid tumor progression has also received increasing attention in recent years, where the aberrant expression of HOXA9 is closely associated with the prognosis of patient. This review details the signaling pathways, binding partners, post-transcriptional regulation of HOXA9, and possible inhibitors of HOXA9 in solid tumors, which provides a reference basis for further study on the role of HOXA9 in solid tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Homeobox genes were firstly discovered when identifying the characterization of several functional genes in Drosophila development [1]. Members of the HOX family have a well-conserved DNA binding homeodomain which have indispensable roles in managing the expression of genes during early development [2]. At present, 39 HOX genes were identified and classified into four clusters including HOXA cluster, HOXB cluster, HOXC cluster, and HOXD cluster [ In addition to be regulated at transcriptional levels, many post-transcriptional events including microRNAs, long non-coding RNAs, and epigenetic modification could also determine HOXA9 protein level and function. These post-transcriptional events show alternative aspects of HOXA9 regulation and might offer novel therapeutic opportunities in cancer treatment. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a type of small and short RNAs which have critical roles in regulating the post-transcriptional of target genes. miRNAs are associated with the etiology mechanism of multiple diseases including asthma, allergic rhinitis, and tumor [77]. Retrieval of the published literature on HOXA9, we found that many documents involved the role of HOXA9 regulated by multiple microRNAs in various tumors (Table 2). In addition, we observed that study about HOXA9 as a target of these miRNAs in osteosarcoma is more than in other solid tumors, prompting that HOXA9 might implement a crucial role in osteosarcoma regulated by miRNAs. Research reported that HOXA9 was identified as a downstream target of miR-1294 in osteosarcoma [78]. Furthermore, HOXA9 as a direct target of miR-429 [54], miR-873 [79], miR-652 [165]. PD 0332991 (palbociclib), is a selectively and potently inhibitor of CDK4 and CDK6. The research performed by Yang et al. showed that PD 0332991 induced apoptosis of AML cells through inhibiting HOXA9 expression and reducing its target PIM1expression [166]. The role of PD 0332991 in solid tumors such as breast cancer [167], lung cancer [168], and glioma [169] has been widely studied. Multiple clinical trials about palbociclib treated in various tumors such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Besides, other CDK4/6 inhibitors such as Abemaciclib [170], Ribociclib [171], Lerociclib [172], Trilaciclib [173], Dinaciclib [174], and SHR6390 [175] are also being adopted in clinical testing. This review described the structures of HOXA9 and its expression and diverse roles in solid tumors. The signaling pathways, post-transcription of modification, potential inhibitors, and binding partners of HOXA9 were presented. Although HOXA9 is a promising therapeutic target for AML and solid tumors, some issues need to be addressed. HOXA9 functioning as an oncogene or suppressor gene mainly depends on the heterogeneity of tumors. It is a challenge for us to investigate the mechanism of HOXA9 in tumors, especially in using HOXA9 inhibitors. In addition, the inhibitors of HOXA9 play a crucial role in tumor therapy through indirectly regulation of HOXA9 expression, no directly small molecular inhibitors targeting HOXA9 are developed at present. Therefore, the development of HOXA9 inhibitors is a topic needed to be focused on. What’s more, researches about HOXA9 in tumors were mainly focused on the miRNA, lncRNA, and methylation, while the mechanism is not deep enough. Further detailed study on the mechanistic roles of HOXA9 in tumors are required in the near future.
Post-transcriptional regulation of HOXA9
HOXA9 regulated by microRNAs
Conclusions
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AML:
-
Acute myeloid leukemia
- miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- ncRNAs:
-
Non-coding RNAs
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma
- SC:
-
Stem cell
- CRC:
-
Colon cancer
- NPC:
-
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- cSCC:
-
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- HIF-1:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor
- pVHL:
-
Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene
- HNSCC:
-
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- JAK-STAT:
-
Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription
- ATAC-seq:
-
Transposase-accessible chromatin using sequencing
- PH:
-
Pleckstrin homology
- TSC1/2:
-
Tuberous sclerosis complex 1 and 2
- S6K1:
-
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase
- 4E-BP:
-
EIF4E binding protein 1
- KDM3:
-
Lysine demethylase 3
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- LSCs:
-
Leukemic stem cells
- TNBC:
-
Triple-negative breast cancer
- WDR5:
-
WD-40 repeat protein 5
- H3K9me2:
-
Lysine methyltransferase (KMT) di-methylates lysine 9 of histone H3
- BET:
-
Bromodomain and extra-terminal
References
McGinnis W, Levine MS, Hafen E, Kuroiwa A, Gehring WJ. A conserved DNA sequence in homoeotic genes of the Drosophila Antennapedia and bithorax complexes. Nature. 1984;308(5958):428–33.
Howard AGA, Nguyen AC, Tworig J, Ravisankar P, Singleton EW, Li C, Kotzur G, Waxman JS, Uribe RA. Elevated Hoxb5b expands vagal neural crest pool and blocks enteric neuronal development in zebrafish. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:803370.
Fang C, **n Y, Sun T, Monteiro A, Ye Z, Dai F, Lu C, Tong X. The Hox gene Antennapedia is essential for wing development in insects. Development. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.199841.
Al-Kershi S, Bhayadia R, Ng M, Verboon L, Emmrich S, Gack L, Schwarzer A, Strowig T, Heckl D, Klusmann JH. The stem cell-specific long noncoding RNA HOXA10-AS in the pathogenesis of KMT2A-rearranged leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019;3(24):4252–63.
**e HM, Bernt KM. HOXA amplification defines a genetically distinct subset of angiosarcomas. Biomolecules. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12081124.
Brinkmeier ML, Geister KA, Jones M, Waqas M, Maillard I, Camper SA. The histone methyltransferase gene absent, small, or homeotic Discs-1 like is required for normal hox gene expression and fertility in mice. Biol Reprod. 2015;93(5):121.
Pan M, Sun Q, Li C, Tai R, Shi X, Sun C. Hoxa5 inhibits adipocyte proliferation through transcriptional regulation of Ccne1 and blocking JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in mice. Biochem Cell Biol. 2022;100(4):325–37.
Luo B, Feng S, Li T, Wang J, Qi Z, Zhao Y, Hu B. Transcription factor HOXB2 upregulates NUSAP1 to promote the proliferation, invasion and migration of nephroblastoma cells via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2022.12721.
Yoshino S, Yokoyama T, Sunami Y, Takahara T, Nakamura A, Yamazaki Y, Tsutsumi S, Aburatani H, Nakamura T. Trib1 promotes acute myeloid leukemia progression by modulating the transcriptional programs of Hoxa9. Blood. 2021;137(1):75–88.
Li DP, Li ZY, Sang W, Cheng H, Pan XY, Xu KL. HOXA9 gene expression in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;67(3):935–8.
Faaborg L, Jakobsen A, Waldstrom M, Petersen CB, Andersen RF, Steffensen KD. HOXA9-methylated DNA as a diagnostic biomarker of ovarian malignancy. Biomark Med. 2021;15(15):1309–17.
Sun M, Song CX, Huang H, Frankenberger CA, Sankarasharma D, Gomes S, Chen P, Chen J, Chada KK, He C, et al. HMGA2/TET1/HOXA9 signaling pathway regulates breast cancer growth and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(24):9920–5.
LaRonde-LeBlanc NA, Wolberger C. Structure of HoxA9 and Pbx1 bound to DNA: Hox hexapeptide and DNA recognition anterior to posterior. Genes Dev. 2003;17(16):2060–72.
Popovic R, Erfurth F, Zeleznik-Le N. Transcriptional complexity of the HOXA9 locus. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008;40(2):156–9.
Schnabel CA, Jacobs Y, Cleary ML. HoxA9-mediated immortalization of myeloid progenitors requires functional interactions with TALE cofactors Pbx and Meis. Oncogene. 2000;19(5):608–16.
Erfurth FE, Popovic R, Grembecka J, Cierpicki T, Theisler C, **a ZB, Stuart T, Diaz MO, Bushweller JH, Zeleznik-Le NJ. MLL protects CpG clusters from methylation within the Hoxa9 gene, maintaining transcript expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(21):7517–22.
** Y, Kim HK, Lee J, Soh EY, Kim JH, Song I, Chung YS, Choi YJ. Transcription factor HOXA9 is linked to the calcification and invasion of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):6773.
Steger J, Fuller E, Garcia-Cuellar MP, Hetzner K, Slany RK. Insulin-like growth factor 1 is a direct HOXA9 target important for hematopoietic transformation. Leukemia. 2015;29(4):901–8.
Bei L, Lu Y, Eklund EA. HOXA9 activates transcription of the gene encoding gp91Phox during myeloid differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(13):12359–70.
Bei L, Shah C, Wang H, Huang W, Platanias LC, Eklund EA. Regulation of CDX4 gene transcription by HoxA9, HoxA10, the Mll-Ell oncogene and Shp2 during leukemogenesis. Oncogenesis. 2014;3: e135.
Miyamoto R, Kanai A, Okuda H, Komata Y, Takahashi S, Matsui H, Inaba T, Yokoyama A. HOXA9 promotes MYC-mediated leukemogenesis by maintaining gene expression for multiple anti-apoptotic pathways. Elife. 2021. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.64148.
Bandyopadhyay S, Ashraf MZ, Daher P, Howe PH, DiCorleto PE. HOXA9 participates in the transcriptional activation of E-selectin in endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27(12):4207–16.
Zhu Q, Hu S, He Y, Qiu C, Chen T, He Y, Wu Z, Tian L, Shang T, **ang Y, et al. Nuclear factor kappa-B/homeobox A9-mediated modulation of leucine-rich repeat flightless-interacting protein 1 is involved in advanced glycation end product-induced endothelial dysfunction. J Vasc Res. 2021;58(5):311–20.
Gwin K, Frank E, Bossou A, Medina KL. Hoxa9 regulates Flt3 in lymphohematopoietic progenitors. J Immunol. 2010;185(11):6572–83.
Goncalves CS, Xavier-Magalhaes A, Martins EP, Pinto AA, Pires MM, Pinheiro C, Reis RM, Sousa N, Costa BM. A novel molecular link between HOXA9 and WNT6 in glioblastoma identifies a subgroup of patients with particular poor prognosis. Mol Oncol. 2020;14(6):1224–41.
Hu YL, Passegue E, Fong S, Largman C, Lawrence HJ. Evidence that the Pim1 kinase gene is a direct target of HOXA9. Blood. 2007;109(11):4732–8.
Gilbert PM, Mouw JK, Unger MA, Lakins JN, Gbegnon MK, Clemmer VB, Benezra M, Licht JD, Boudreau NJ, Tsai KK, et al. HOXA9 regulates BRCA1 expression to modulate human breast tumor phenotype. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(5):1535–50.
Ohno Y, Yasunaga S, Janmohamed S, Ohtsubo M, Saeki K, Kurogi T, Mihara K, Iscove NN, Takihara Y. Hoxa9 transduction induces hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell activity through direct down-regulation of geminin protein. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(1): e53161.
Zhou B, Liu C, Xu Z, Zhu G. Structural basis for homeodomain recognition by the cell-cycle regulator Geminin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109(23):8931–6.
Costa BM, Smith JS, Chen Y, Chen J, Phillips HS, Aldape KD, Zardo G, Nigro J, James CD, Fridlyand J, et al. Reversing HOXA9 oncogene activation by PI3K inhibition: epigenetic mechanism and prognostic significance in human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2010;70(2):453–62.
Osmond B, Facey COB, Zhang C, Boman BM. HOXA9 overexpression contributes to stem cell overpopulation that drives development and growth of colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126799.
Liu T, Ji C, Sun Y, Bai W. HOXA9 expression is associated with advanced tumour stage and prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 2021;13:4147–54.
Zhou L, Wang Y, Zhou M, Zhang Y, Wang P, Li X, Yang J, Wang H, Ding Z. HOXA9 inhibits HIF-1alpha-mediated glycolysis through interacting with CRIP2 to repress cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma development. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1480.
Yu H, Lin L, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Hu H. Targeting NF-kappaB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):209.
Liu D, Zhong Z, Karin M. NF-kappaB: a double-edged sword controlling inflammation. Biomedicines. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061250.
Yu M, Qi B, **aoxiang W, Xu J, Liu X. Baicalein increases cisplatin sensitivity of A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells via PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;90:677–85.
Hou J, Zhuo H, Chen X, Cheng J, Zheng W, Zhong M, Cai J. MiR-139-5p negatively regulates PMP22 to repress cell proliferation by targeting the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in gastric cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(7):1218–29.
Zhu B, Chen JJ, Feng Y, Yang JL, Huang H, Chung WY, Hu YL, Xue WJ. DNMT1-induced miR-378a-3p silencing promotes angiogenesis via the NF-kappaB signaling pathway by targeting TRAF1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40(1):352.
Han S, Li X, Liang X, Zhou L. HOXA9 transcriptionally promotes apoptosis and represses autophagy by targeting NF-kappaB in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Cells. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111360.
Trivedi CM, Patel RC, Patel CV. Differential regulation of HOXA9 expression by nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) and HOXA9. Gene. 2008;408(1–2):187–95.
Yu SL, Lee DC, Sohn HA, Lee SY, Jeon HS, Lee JH, Park CG, Lee HY, Yeom YI, Son JW, et al. Homeobox A9 directly targeted by miR-196b regulates aggressiveness through nuclear Factor-kappa B activity in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 2016;55(12):1915–26.
Zeng J, Yi D, Sun W, Liu Y, Chang J, Zhu L, Zhang Y, Pan X, Dong Y, Zhou Y, et al. Overexpression of HOXA9 upregulates NF-kappaB signaling to promote human hematopoiesis and alter the hematopoietic differentiation potentials. Cell Regen. 2021;10(1):9.
Lee JW, Bae SH, Jeong JW, Kim SH, Kim KW. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)alpha: its protein stability and biological functions. Exp Mol Med. 2004;36(1):1–12.
Luo Z, Tian M, Yang G, Tan Q, Chen Y, Li G, Zhang Q, Li Y, Wan P, Wu J. Hypoxia signaling in human health and diseases: implications and prospects for therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):218.
Sun Q, Zhang SY, Zhao JF, Han XG, Wang HB, Sun ML. Erratum: HIF-1alpha or HOTTIP/CTCF promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression and drug resistance by targeting HOXA9. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022;28:32–4.
**a Z, Yang C, Yang X, Wu S, Feng Z, Qu L, Chen X, Liu L, Ma Y. miR-652 promotes proliferation and migration of uveal melanoma cells by targeting HOXA9. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:8722–32.
Hu X, Li J, Fu M, Zhao X, Wang W. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway: from bench to clinic. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):402.
Zhu N, Zhang J, Du Y, Qin X, Miao R, Nan J, Chen X, Sun J, Zhao R, Zhang X, et al. Loss of ZIP facilitates JAK2-STAT3 activation in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117(26):15047–54.
Huang W, Li Y, Zhang C, Zha H, Zhou X, Fu B, Guo J, Wang G. IGF2BP3 facilitates cell proliferation and tumorigenesis via modulation of JAK/STAT signalling pathway in human bladder cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(23):13949–60.
de Bock CE, Demeyer S, Degryse S, Verbeke D, Sweron B, Gielen O, Vandepoel R, Vicente C, Vanden Bempt M, Dagklis A, et al. HOXA9 cooperates with activated JAK/STAT signaling to drive leukemia development. Cancer Discov. 2018;8(5):616–31.
de Bock CE, Cools J. JAK3 mutations and HOXA9 expression are important cooperating events in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol Cell Oncol. 2018;5(3): e1458014.
Schworer S, Becker F, Feller C, Baig AH, Kober U, Henze H, Kraus JM, **n B, Lechel A, Lipka DB, et al. Author correction: epigenetic stress responses induce muscle stem-cell ageing by Hoxa9 developmental signals. Nature. 2019;572(7769):E11–5.
Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell. 2017;169(6):985–99.
Sun L, Wang L, Luan S, Jiang Y, Wang Q. miR-429 inhibits osteosarcoma progression by targeting HOXA9 through suppressing Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 2020;20(3):2447–55.
Xu Q, Zhang Q, Dong M, Yu Y. MicroRNA-638 inhibits the progression of breast cancer through targeting HOXA9 and suppressing Wnt/beta-cadherin pathway. World J Surg Oncol. 2021;19(1):247.
**a P, Xu XY. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in cancer stem cells: from basic research to clinical application. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5(5):1602–9.
Guerrero-Zotano A, Mayer IA, Arteaga CL. PI3K/AKT/mTOR: role in breast cancer progression, drug resistance, and treatment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016;35(4):515–24.
Yang C, Chen Y, **ong W, Xu K. miR-652 inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by targeting HOXA9 and regulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Oncol. 2022;2022:4809312.
Li Z, Zhang Z, Li Y, Arnovitz S, Chen P, Huang H, Jiang X, Hong GM, Kunjamma RB, Ren H, et al. PBX3 is an important cofactor of HOXA9 in leukemogenesis. Blood. 2013;121(8):1422–31.
Morgan R, Plowright L, Harrington KJ, Michael A, Pandha HS. Targeting HOX and PBX transcription factors in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:89.
Morgan R, Boxall A, Harrington KJ, Simpson GR, Gillett C, Michael A, Pandha HS. Targeting the HOX/PBX dimer in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;136(2):389–98.
Ando H, Natsume A, Senga T, Watanabe R, Ito I, Ohno M, Iwami K, Ohka F, Motomura K, Kinjo S, et al. Peptide-based inhibition of the HOXA9/PBX interaction retards the growth of human meningioma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014;73(1):53–60.
Errico MC, Felicetti F, Bottero L, Mattia G, Boe A, Felli N, Petrini M, Bellenghi M, Pandha HS, Calvaruso M, et al. The abrogation of the HOXB7/PBX2 complex induces apoptosis in melanoma through the miR-221&222-c-FOS pathway. Int J Cancer. 2013;133(4):879–92.
Mohr S, Doebele C, Comoglio F, Berg T, Beck J, Bohnenberger H, Alexe G, Corso J, Strobel P, Wachter A, et al. Hoxa9 and Meis1 cooperatively induce addiction to Syk signaling by suppressing miR-146a in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2017;31(4):549-562 e511.
Lawrence HJ, Rozenfeld S, Cruz C, Matsukuma K, Kwong A, Komuves L, Buchberg AM, Largman C. Frequent co-expression of the HOXA9 and MEIS1 homeobox genes in human myeloid leukemias. Leukemia. 1999;13(12):1993–9.
Zhou X, Lu R. HOXA9/MEIS1 targets in leukemia: reinforced signaling networks and therapeutic opportunities. Haematologica. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2022.281779.
Li Z, Chen P, Su R, Hu C, Li Y, Elkahloun AG, Zuo Z, Gurbuxani S, Arnovitz S, Weng H, et al. PBX3 and MEIS1 cooperate in hematopoietic cells to drive acute myeloid leukemias characterized by a core transcriptome of the MLL-rearranged disease. Cancer Res. 2016;76(3):619–29.
Zhu N, Chen M, Eng R, DeJong J, Sinha AU, Rahnamay NF, Koche R, Al-Shahrour F, Minehart JC, Chen CW, et al. MLL-AF9- and HOXA9-mediated acute myeloid leukemia stem cell self-renewal requires JMJD1C. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(3):997–1011.
Lynch JR, Salik B, Connerty P, Vick B, Leung H, Pijning A, Jeremias I, Spiekermann K, Trahair T, Liu T, et al. JMJD1C-mediated metabolic dysregulation contributes to HOXA9-dependent leukemogenesis. Leukemia. 2019;33(6):1400–10.
Kim H, Ronai ZA. PRMT5 function and targeting in cancer. Cell Stress. 2020;4(8):199–215.
Bandyopadhyay S, Harris DP, Adams GN, Lause GE, McHugh A, Tillmaand EG, Money A, Willard B, Fox PL, Dicorleto PE. HOXA9 methylation by PRMT5 is essential for endothelial cell expression of leukocyte adhesion molecules. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32(7):1202–13.
Quere R, Karlsson G, Hertwig F, Rissler M, Lindqvist B, Fioretos T, Vandenberghe P, Slovak ML, Cammenga J, Karlsson S. Smad4 binds Hoxa9 in the cytoplasm and protects primitive hematopoietic cells against nuclear activation by Hoxa9 and leukemia transformation. Blood. 2011;117(22):5918–30.
Lehnertz B, Pabst C, Su L, Miller M, Liu F, Yi L, Zhang R, Krosl J, Yung E, Kirschner J, et al. The methyltransferase G9a regulates HoxA9-dependent transcription in AML. Genes Dev. 2014;28(4):317–27.
Garcia-Dominguez DJ, Hajji N, Lopez-Alemany R, Sanchez-Molina S, Figuerola-Bou E, Moron Civanto FJ, Rello-Varona S, Andres-Leon E, Benito A, Keun HC, et al. Selective histone methyltransferase G9a inhibition reduces metastatic development of Ewing sarcoma through the epigenetic regulation of NEU1. Oncogene. 2022;41(18):2638–50.
Topisirovic I, Kentsis A, Perez JM, Guzman ML, Jordan CT, Borden KL. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E activity is modulated by HOXA9 at multiple levels. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(3):1100–12.
Huang Y, Sitwala K, Bronstein J, Sanders D, Dandekar M, Collins C, Robertson G, MacDonald J, Cezard T, Bilenky M, et al. Identification and characterization of Hoxa9 binding sites in hematopoietic cells. Blood. 2012;119(2):388–98.
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR, Soleymani Fard S, Ghaffari SH. An overview of microRNAs: biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5451–65.
Zhang ZF, Li GR, Cao CN, Xu Q, Wang GD, Jiang XF. MicroRNA-1294 targets HOXA9 and has a tumor suppressive role in osteosarcoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(24):8582–8.
Liu Y, Wang Y, Yang H, Zhao L, Song R, Tan H, Wang L. MicroRNA873 targets HOXA9 to inhibit the aggressive phenotype of osteosarcoma by deactivating the Wnt/betacatenin pathway. Int J Oncol. 2019;54(5):1809–20.
Zhang ZF, Wang YJ, Fan SH, Du SX, Li XD, Wu DM, Lu J, Zheng YL. MicroRNA-182 downregulates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, inhibits proliferation, and promotes apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells by targeting HOXA9. Oncotarget. 2017;8(60):101345–61.
Zhang N, Meng X, Mei L, Zhao C, Chen W. LncRNA DLX6-AS1 promotes tumor proliferation and metastasis in osteosarcoma through modulating miR-641/HOXA9 signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28426.
Zhang S, Chen R. LINC01140 regulates osteosarcoma proliferation and invasion by targeting the miR-139-5p/HOXA9 axis. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022;31: 101301.
Zheng DH, Wang X, Lu LN, Chen DL, Chen JM, Lin FM, Xu XB. MiR-638 serves as a tumor suppressor by targeting HOXA9 in glioma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(22):7798–806.
Qin K, Tian G, Chen G, Zhou D, Tang K. miR-647 inhibits glioma cell proliferation, colony formation and invasion by regulating HOXA9. J Gene Med. 2020;22(3): e3153.
Gao L, Yan SB, Yang J, Kong JL, Shi K, Ma FC, Huang LZ, Luo J, Yin SY, He RQ, et al. MiR-182-5p and its target HOXA9 in non-small cell lung cancer: a clinical and in-silico exploration with the combination of RT-qPCR, miRNA-seq and miRNA-chip. BMC Med Genomics. 2020;13(1):3.
Li ZL, Li D, Yin GQ. MiR-19b-3p promotes tumor progression of non-small cell lung cancer via downregulating HOXA9 and predicts poor prognosis in patients. Histol Histopathol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-18-448.
Liu J, Qian J, Mo Q, Tang L, Xu Q. Long non-coding RNA PCED1B-AS1 promotes the proliferation of colorectal adenocarcinoma through regulating the miR-633/HOXA9 axis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):5407–20.
Zhang Y, Li K, Wang W, Han J. miR-381-3p attenuates doxorubicin resistance in human anaplastic thyroid carcinoma via targeting homeobox A9. Int J Exp Pathol. 2021;102(4–5):209–17.
Wang X, Bu J, Liu X, Wang W, Mai W, Lv B, Zou J, Mo X, Li X, Wang J, et al. miR-133b suppresses metastasis by targeting HOXA9 in human colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(38):63935–48.
Wang K, ** J, Ma T, Zhai H. MiR-139-5p inhibits the tumorigenesis and progression of oral squamous carcinoma cells by targeting HOXA9. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(12):3730–40.
Quinn JJ, Chang HY. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17(1):47–62.
Sanchez Calle A, Kawamura Y, Yamamoto Y, Takeshita F, Ochiya T. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA in cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018;109(7):2093–100.
Xavier-Magalhaes A, Goncalves CS, Fogli A, Lourenco T, Pojo M, Pereira B, Rocha M, Lopes MC, Crespo I, Rebelo O, et al. The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is transcriptionally activated by HOXA9 and is an independent prognostic marker in patients with malignant glioma. Oncotarget. 2018;9(21):15740–56.
Cheng Y, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Corton JC, Safe S. The long non-coding RNA HOTTIP enhances pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, survival and migration. Oncotarget. 2015;6(13):10840–52.
Fu Z, Chen C, Zhou Q, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Zhao X, Li W, Zheng S, Ye H, Wang L, et al. LncRNA HOTTIP modulates cancer stem cell properties in human pancreatic cancer by regulating HOXA9. Cancer Lett. 2017;410:68–81.
Malek R, Gajula RP, Williams RD, Nghiem B, Simons BW, Nugent K, Wang H, Taparra K, Lemtiri-Chlieh G, Yoon AR, et al. TWIST1-WDR5-hottip regulates Hoxa9 chromatin to facilitate prostate cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2017;77(12):3181–93.
Wang SM, Pang J, Zhang KJ, Zhou ZY, Chen FY. lncRNA MIR503HG inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in TNBC cells via the miR-224-5p/HOXA9 axis. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021;21:62–73.
Li Z, Zhang C, Zong X, Wang Z, Ren R, Wang L, Sun P, Zhu C, Guo M, Guo G, et al. ST8SIA6-AS1 promotes the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis of pituitary adenoma. J Oncol. 2022;2022:7960261.
Li Y, Yan B, Wang X, Li Q, Kan X, Wang J, Sun Y, Wang P, Tian L, Liu M. ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification of lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 triggers the development of LSCC via upregulation of HOXA9. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(2):385–98.
Wen ZQ, Li SH, Shui X, Tang LL, Zheng JR, Chen L. LncRNA PEG10 aggravates cardiac hypertrophy through regulating HOXA9. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(3 Suppl):281–6.
Zhou G, Li C, Feng J, Zhang J, Fang Y. lncRNA UCA1 Is a novel regulator in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through targeting the miR-184/HOXA9 Axis. Cardiorenal Med. 2018;8(2):130–9.
Horvath S, Raj K. DNA methylation-based biomarkers and the epigenetic clock theory of ageing. Nat Rev Genet. 2018;19(6):371–84.
Kuo CC, Lin CY, Shih YL, Hsieh CB, Lin PY, Guan SB, Hsieh MS, Lai HC, Chen CJ, Lin YW. Frequent methylation of HOXA9 gene in tumor tissues and plasma samples from human hepatocellular carcinomas. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2014;52(8):1235–45.
Hwang SH, Kim KU, Kim JE, Kim HH, Lee MK, Lee CH, Lee SY, Oh T, An S. Detection of HOXA9 gene methylation in tumor tissues and induced sputum samples from primary lung cancer patients. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011;49(4):699–704.
Singh A, Gupta S, Badarukhiya JA, Sachan M. Detection of aberrant methylation of HOXA9 and HIC1 through multiplex MethyLight assay in serum DNA for the early detection of epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer. 2020;147(6):1740–52.
Cai H, Ke ZB, Dong RN, Chen H, Lin F, Zheng WC, Chen SH, Zhu JM, Chen SM, Zheng QS, et al. The prognostic value of homeobox A9 (HOXA9) methylation in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl Cancer Res. 2021;10(10):4347–54.
Lambert M, Alioui M, Jambon S, Depauw S, Van Seuningen I, David-Cordonnier MH. Direct and indirect targeting of HOXA9 transcription factor in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancers. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060837.
Neeli PK, Sahoo S, Karnewar S, Singuru G, Pulipaka S, Annamaneni S, Kotamraju S. DOT1L regulates MTDH-mediated angiogenesis in triple-negative breast cancer: intermediacy of NF-kappaB-HIF1alpha axis. FEBS J. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.16605.
Daigle SR, Olhava EJ, Therkelsen CA, Majer CR, Sneeringer CJ, Song J, Johnston LD, Scott MP, Smith JJ, **ao Y, et al. Selective killing of mixed lineage leukemia cells by a potent small-molecule DOT1L inhibitor. Cancer Cell. 2011;20(1):53–65.
Yu W, Chory EJ, Wernimont AK, Tempel W, Scopton A, Federation A, Marineau JJ, Qi J, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Yi J, et al. Catalytic site remodelling of the DOT1L methyltransferase by selective inhibitors. Nat Commun. 2012;3:1288.
Daigle SR, Olhava EJ, Therkelsen CA, Basavapathruni A, ** L, Boriack-Sjodin PA, Allain CJ, Klaus CR, Raimondi A, Scott MP, et al. Potent inhibition of DOT1L as treatment of MLL-fusion leukemia. Blood. 2013;122(6):1017–25.
Waters NJ. Preclinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pinometostat (EPZ-5676), a first-in-class, small molecule S-adenosyl methionine competitive inhibitor of DOT1L. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2017;42(6):891–901.
Sarno F, Nebbioso A, Altucci L. DOT1L: a key target in normal chromatin remodelling and in mixed-lineage leukaemia treatment. Epigenetics. 2020;15(5):439–53.
Zhang W, Zhao C, Zhao J, Zhu Y, Weng X, Chen Q, Sun H, Mi JQ, Li J, Zhu J, et al. Inactivation of PBX3 and HOXA9 by down-regulating H3K79 methylation represses NPM1-mutated leukemic cell survival. Theranostics. 2018;8(16):4359–71.
Liu W, Deng L, Song Y, Redell M. DOT1L inhibition sensitizes MLL-rearranged AML to chemotherapy. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(5): e98270.
Fang Y, Liao G, Yu B. Targeting histone lysine demethylase LSD1/KDM1A as a new avenue for cancer therapy. Curr Top Med Chem. 2019;19(11):889–91.
Sprussel A, Schulte JH, Weber S, Necke M, Handschke K, Thor T, Pajtler KW, Schramm A, Konig K, Diehl L, et al. Lysine-specific demethylase 1 restricts hematopoietic progenitor proliferation and is essential for terminal differentiation. Leukemia. 2012;26(9):2039–51.
Lv YX, Tian S, Zhang ZD, Feng T, Li HQ. LSD1 inhibitors for anticancer therapy: a patent review (2017–present). Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2022;32(9):1027–42.
Wass M, Gollner S, Besenbeck B, Schlenk RF, Mundmann P, Gothert JR, Noppeney R, Schliemann C, Mikesch JH, Lenz G, et al. A proof of concept phase I/II pilot trial of LSD1 inhibition by tranylcypromine combined with ATRA in refractory/relapsed AML patients not eligible for intensive therapy. Leukemia. 2021;35(3):701–11.
Maes T, Mascaro C, Tirapu I, Estiarte A, Ciceri F, Lunardi S, Guibourt N, Perdones A, Lufino MMP, Somervaille TCP, et al. ORY-1001, a potent and selective covalent KDM1A inhibitor, for the treatment of acute leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2018;33(3):495-511 e412.
Lillico R, Lawrence CK, Lakowski TM. Selective DOT1L, LSD1, and HDAC class I inhibitors reduce HOXA9 expression in MLL-AF9 rearranged leukemia cells, but dysregulate the expression of many histone-modifying enzymes. J Proteome Res. 2018;17(8):2657–67.
Fiskus W, Sharma S, Shah B, Portier BP, Devaraj SG, Liu K, Iyer SP, Bearss D, Bhalla KN. Highly effective combination of LSD1 (KDM1A) antagonist and pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor against human AML cells. Leukemia. 2014;28(11):2155–64.
Sugino N, Kawahara M, Tatsumi G, Kanai A, Matsui H, Yamamoto R, Nagai Y, Fujii S, Shimazu Y, Hishizawa M, et al. A novel LSD1 inhibitor NCD38 ameliorates MDS-related leukemia with complex karyotype by attenuating leukemia programs via activating super-enhancers. Leukemia. 2017;31(11):2303–14.
Liu S, Lu W, Li S, Li S, Liu J, **ng Y, Zhang S, Zhou JZ, **ng H, Xu Y, et al. Identification of JL1037 as a novel, specific, reversible lysine-specific demethylase 1 inhibitor that induce apoptosis and autophagy of AML cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8(19):31901–14.
Yang C, Fang Y, Luo X, Teng D, Liu Z, Zhou Y, Liao G. Discovery of natural product-like spirooxindole derivatives as highly potent and selective LSD1/KDM1A inhibitors for AML treatment. Bioorg Chem. 2022;120: 105596.
Fang Y, Yang C, Teng D, Su S, Luo X, Liu Z, Liao G. Discovery of higenamine as a potent, selective and cellular active natural LSD1 inhibitor for MLL-rearranged leukemia therapy. Bioorg Chem. 2021;109: 104723.
Barth J, Abou-El-Ardat K, Dalic D, Kurrle N, Maier AM, Mohr S, Schutte J, Vassen L, Greve G, Schulz-Fincke J, et al. LSD1 inhibition by tranylcypromine derivatives interferes with GFI1-mediated repression of PU.1 target genes and induces differentiation in AML. Leukemia. 2019;33(6):1411–26.
Lu X, Liang B, Li S, Chen Z, Chang W. Modulation of HOXA9 after skeletal muscle denervation and reinnervation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020;318(6):C1154–65.
Karatas H, Townsend EC, Cao F, Chen Y, Bernard D, Liu L, Lei M, Dou Y, Wang S. High-affinity, small-molecule peptidomimetic inhibitors of MLL1/WDR5 protein-protein interaction. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135(2):669–82.
Karatas H, Li Y, Liu L, Ji J, Lee S, Chen Y, Yang J, Huang L, Bernard D, Xu J, et al. Discovery of a highly potent, cell-permeable macrocyclic peptidomimetic (MM-589) targeting the WD repeat domain 5 protein (WDR5)-mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) protein–protein interaction. J Med Chem. 2017;60(12):4818–39.
Li DD, Chen WL, Wang ZH, **e YY, Xu XL, Jiang ZY, Zhang XJ, You QD, Guo XK. High-affinity small molecular blockers of mixed lineage leukemia 1 (MLL1)-WDR5 interaction inhibit MLL1 complex H3K4 methyltransferase activity. Eur J Med Chem. 2016;124:480–9.
Zhang J, Zhou Q, **e K, Cheng L, Peng S, **e R, Liu L, Zhang Y, Dong W, Han J, et al. Targeting WD repeat domain 5 enhances chemosensitivity and inhibits proliferation and programmed death-ligand 1 expression in bladder cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40(1):203.
Haebe JR, Bergin CJ, Sandouka T, Benoit YD. Emerging role of G9a in cancer stemness and promises as a therapeutic target. Oncogenesis. 2021;10(11):76.
Kondengaden SM, Luo LF, Huang K, Zhu M, Zang L, Bataba E, Wang R, Luo C, Wang B, Li KK, et al. Discovery of novel small molecule inhibitors of lysine methyltransferase G9a and their mechanism in leukemia cell lines. Eur J Med Chem. 2016;122:382–93.
Kim JH, Kim J, Im SS, Lee JH, Hwang S, Chang EJ, Shin DM, Rho JK, Son J. BIX01294 inhibits EGFR signaling in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma cells through a BCKDHA-mediated reduction in the EGFR level. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(12):1877–87.
Liu XR, Zhou LH, Hu JX, Liu LM, Wan HP, Zhang XQ. UNC0638, a G9a inhibitor, suppresses epithelialmesenchymal transitionmediated cellular migration and invasion in triple negative breast cancer. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(2):2239–44.
Cao YP, Sun JY, Li MQ, Dong Y, Zhang YH, Yan J, Huang RM, Yan X. Inhibition of G9a by a small molecule inhibitor, UNC0642, induces apoptosis of human bladder cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019;40(8):1076–84.
Cao H, Li L, Yang D, Zeng L, Yewei X, Yu B, Liao G, Chen J. Recent progress in histone methyltransferase (G9a) inhibitors as anticancer agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2019;179:537–46.
Sharifulina S, Dzreyan V, Guzenko V, Demyanenko S. Histone methyltransferases SUV39H1 and G9a and DNA methyltransferase DNMT1 in penumbra neurons and astrocytes after photothrombotic stroke. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212483.
San Jose-Eneriz E, Agirre X, Rabal O, Vilas-Zornoza A, Sanchez-Arias JA, Miranda E, Ugarte A, Roa S, Paiva B, de Mendoza AE-M, et al. Discovery of first-in-class reversible dual small molecule inhibitors against G9a and DNMTs in hematological malignancies. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15424.
Segovia C, San Jose-Eneriz E, Munera-Maravilla E, Martinez-Fernandez M, Garate L, Miranda E, Vilas-Zornoza A, Lodewijk I, Rubio C, Segrelles C, et al. Inhibition of a G9a/DNMT network triggers immune-mediated bladder cancer regression. Nat Med. 2019;25(7):1073–81.
Issa GC, Ravandi F, DiNardo CD, Jabbour E, Kantarjian HM, Andreeff M. Therapeutic implications of menin inhibition in acute leukemias. Leukemia. 2021;35(9):2482–95.
Wu Y, Doepner M, Hojnacki T, Feng Z, Katona BW, He X, Ma J, Cao Y, Busino L, Zhou F, et al. Disruption of the menin-MLL interaction triggers menin protein degradation via ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 2019;9(8):1682–94.
Fiskus W, Boettcher S, Daver N, Mill CP, Sasaki K, Birdwell CE, Davis JA, Takahashi K, Kadia TM, DiNardo CD, et al. Effective menin inhibitor-based combinations against AML with MLL rearrangement or NPM1 mutation (NPM1c). Blood Cancer J. 2022;12(1):5.
Fiskus W, Daver N, Boettcher S, Mill CP, Sasaki K, Birdwell CE, Davis JA, Das K, Takahashi K, Kadia TM, et al. Activity of menin inhibitor ziftomenib (KO-539) as monotherapy or in combinations against AML cells with MLL1 rearrangement or mutant NPM1. Leukemia. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-022-01707-w.
Zhang M, Aguilar A, Xu S, Huang L, Chinnaswamy K, Sleger T, Wang B, Gross S, Nicolay BN, Ronseaux S, et al. Discovery of M-1121 as an orally active covalent inhibitor of menin-MLL interaction capable of achieving complete and long-lasting tumor regression. J Med Chem. 2021;64(14):10333–49.
Kulikowski E, Rakai BD, Wong NCW. Inhibitors of bromodomain and extra-terminal proteins for treating multiple human diseases. Med Res Rev. 2021;41(1):223–45.
Groves A, Clymer J, Filbin MG. Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Protein Inhibitors: Biologic Insights and Therapeutic Potential in Pediatric Brain Tumors. Pharmaceuticals. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060665.
Zha J, Lai Q, Deng M, Shi P, Zhao H, Chen Q, Wu H, Xu B. Disruption of CTCF boundary at HOXA locus promote BET inhibitors’ therapeutic sensitivity in acute myeloid leukemia. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020;16(6):1280–91.
Bardini M, Trentin L, Rizzo F, Vieri M, Savino AM, Garrido Castro P, Fazio G, Van Roon EHJ, Kerstjens M, Smithers N, et al. Antileukemic efficacy of BET inhibitor in a Preclinical mouse model of MLL-AF4(+) infant ALL. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018;17(8):1705–16.
Lin CH, Kuo JC, Li D, Koenig AB, Pan A, Yan P, Bai XF, Lee RJ, Ghoshal K. AZD5153, a bivalent BRD4 inhibitor, suppresses hepatocarcinogenesis by altering BRD4 chromosomal landscape and modulating the transcriptome of HCC cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10: 853652.
Hilton J, Cristea M, Postel-Vinay S, Baldini C, Voskoboynik M, Edenfield W, Shapiro GI, Cheng ML, Vuky J, Corr B, et al. BMS-986158, a small molecule inhibitor of the bromodomain and extraterminal domain proteins, in patients with selected advanced solid tumors: results from a phase 1/2a Trial. Cancers. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174079.
Tontsch-Grunt U, Traexler PE, Baum A, Musa H, Marzin K, Wang S, Trapani F, Engelhardt H, Solca F. Therapeutic impact of BET inhibitor BI 894999 treatment: backtranslation from the clinic. Br J Cancer. 2022;127(3):577–86.
Aggarwal R, Starodub AN, Koh BD, **ng G, Armstrong AJ, Carducci MA. Phase Ib study of the BET inhibitor GS-5829 as monotherapy and combined with enzalutamide in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28(18):3979–89.
Ohnesorge PV, Berchtold S, Beil J, Haas SA, Smirnow I, Schenk A, French CA, Luong NM, Huang Y, Fehrenbacher B, et al. Efficacy of oncolytic herpes simplex virus T-VEC combined with BET inhibitors as an innovative therapy approach for NUT carcinoma. Cancers. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14112761.
Cui QH, Li WB, Wang ZY, Xu KY, Wang S, Shi JT, Zhang LW, Chen SW. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of coumarin derivatives as potential BRD4 inhibitors. Bioorg Chem. 2022;128: 106117.
Siu KT, Ramachandran J, Yee AJ, Eda H, Santo L, Panaroni C, Mertz JA, Sims Iii RJ, Cooper MR, Raje N. Preclinical activity of CPI-0610, a novel small-molecule bromodomain and extra-terminal protein inhibitor in the therapy of multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2017;31(8):1760–9.
Leal AS, Liu P, Krieger-Burke T, Ruggeri B, Liby KT. The bromodomain inhibitor, INCB057643, targets both cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment in two preclinical models of pancreatic cancer. Cancers. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13010096.
Lu Q, Ding X, Huang T, Zhang S, Li Y, Xu L, Chen G, Ying Y, Wang Y, Feng Z, et al. BRD4 degrader ARV-825 produces long-lasting loss of BRD4 protein and exhibits potent efficacy against cholangiocarcinoma cells. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(9):5728–39.
Lee L, Hizukuri Y, Severson P, Powell B, Zhang C, Ma Y, Narahara M, Sumi H, Hernandez D, Rajkhowa T, et al. A novel combination regimen of BET and FLT3 inhibition for FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2021;106(4):1022–33.
Ramsey HE, Greenwood D, Zhang S, Childress M, Arrate MP, Gorska AE, Fuller L, Zhao Y, Stengel K, Fischer MA, et al. BET inhibition enhances the antileukemic activity of low-dose venetoclax in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(2):598–607.
Sun Y, Han J, Wang Z, Li X, Sun Y, Hu Z. Safety and efficacy of bromodomain and extra-terminal inhibitors for the treatment of hematological malignancies and solid tumors: a systematic study of clinical trials. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11: 621093.
Moreno V, Sepulveda JM, Vieito M, Hernandez-Guerrero T, Doger B, Saavedra O, Ferrero O, Sarmiento R, Arias M, De Alvaro J, et al. Phase I study of CC-90010, a reversible, oral BET inhibitor in patients with advanced solid tumors and relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2020;31(6):780–8.
Ameratunga M, Brana I, Bono P, Postel-Vinay S, Plummer R, Aspegren J, Korjamo T, Snapir A, de Bono JS. First-in-human Phase 1 open label study of the BET inhibitor ODM-207 in patients with selected solid tumours. Br J Cancer. 2020;123(12):1730–6.
Spring LM, Wander SA, Andre F, Moy B, Turner NC, Bardia A. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: past, present, and future. Lancet. 2020;395(10226):817–27.
Yang C, Boyson CA, Di Liberto M, Huang X, Hannah J, Dorn DC, Moore MA, Chen-Kiang S, Zhou P. CDK4/6 inhibitor PD 0332991 sensitizes acute myeloid leukemia to cytarabine-mediated cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 2015;75(9):1838–45.
Haley B, Batra K, Sahoo S, Froehlich T, Klemow D, Unni N, Ahn C, Rodriguez M, Hullings M, Frankel AE. A phase I/Ib trial of PD 0332991 (palbociclib) and T-DM1 in HER2-positive advanced breast cancer after trastuzumab and taxane therapy. Clin Breast Cancer. 2021;21(5):417–24.
Liu M, Cui L, Li X, **a C, Li Y, Wang R, Ren F, Liu H, Chen J. PD-0332991 combined with cisplatin inhibits nonsmall cell lung cancer and reversal of cisplatin resistance. Thorac Cancer. 2021;12(6):924–31.
Barton KL, Misuraca K, Cordero F, Dobrikova E, Min HD, Gromeier M, Kirsch DG, Becher OJ. PD-0332991, a CDK4/6 inhibitor, significantly prolongs survival in a genetically engineered mouse model of brainstem glioma. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(10): e77639.
Konstantinopoulos PA, Lee EK, **ong N, Krasner C, Campos S, Kolin DL, Liu JF, Horowitz N, Wright AA, Bouberhan S, et al. A phase II, two-stage study of letrozole and abemaciclib in estrogen receptor-positive recurrent endometrial cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.22.00628.
Coffman LG, Orellana TJ, Liu T, Frisbie LG, Normolle D, Griffith K, Uppal S, McLean K, Berger J, Boisen M, et al. Phase I trial of ribociclib with platinum chemotherapy in ovarian cancer. JCI Insight. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.160573.
Andreano KJ, Wardell SE, Baker JG, Desautels TK, Baldi R, Chao CA, Heetderks KA, Bae Y, **ong R, Tonetti DA, et al. G1T48, an oral selective estrogen receptor degrader, and the CDK4/6 inhibitor lerociclib inhibit tumor growth in animal models of endocrine-resistant breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020;180(3):635–46.
Tan AR, Wright GS, Thummala AR, Danso MA, Popovic L, Pluard TJ, Han HS, Vojnovic Z, Vasev N, Ma L, et al. Trilaciclib prior to chemotherapy in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: final efficacy and subgroup analysis from a randomized phase II study. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28(4):629–36.
Gregory GP, Kumar S, Wang D, Mahadevan D, Walker P, Wagner-Johnston N, Escobar C, Bannerji R, Bhutani D, Chang J, et al. Pembrolizumab plus dinaciclib in patients with hematologic malignancies: the phase 1b KEYNOTE-155 study. Blood Adv. 2022;6(4):1232–42.
Zhang P, Xu B, Gui L, Wang W, **u M, Zhang X, Sun G, Zhu X, Zou J. A phase 1 study of dalpiciclib, a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor in Chinese patients with advanced breast cancer. Biomark Res. 2021;9(1):24.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82173201, 82272758), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (No. 2021JJ30422), Hunan Cancer Hospital Climb Plan (2020NSFC-A001, 20210405-1001), and Scientific Research Project of Hunan Provincial Health Commission (A202302088151, B202304127661). The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: HW and PC. Compilation of literature: LP, CT and HL. Article writing and editing: LT. Supervision: HW and CP. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
These authors declared no competing interests in this research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, L., Peng, L., Tan, C. et al. Role of HOXA9 in solid tumors: mechanistic insights and therapeutic potential. Cancer Cell Int 22, 349 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-022-02767-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-022-02767-9