Abstract
Background
The genetic variation underlying atorvastatin (ATV) pharmacokinetics was evaluated in a Mexican population. Aims of this study were: 1) to reveal the frequency of 87 polymorphisms in 36 genes related to drug metabolism in healthy Mexican volunteers, 2) to evaluate the impact of these polymorphisms on ATV pharmacokinetics, 3) to classify the ATV metabolic phenotypes of healthy volunteers, and 4) to investigate a possible association between genotypes and metabolizer phenotypes.
Methods
A pharmacokinetic study of ATV (single 80-mg dose) was conducted in 60 healthy male volunteers. ATV plasma concentrations were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated by the non-compartmental method. The polymorphisms were determined with the PHARMAchip® microarray and the TaqMan® probes genoty** assay.
Results
Three metabolic phenotypes were found in our population: slow, normal, and rapid. Six gene polymorphisms were found to have a significant effect on ATV pharmacokinetics: MTHFR (rs1801133), DRD3 (rs6280), GSTM3 (rs1799735), TNFα (rs1800629), MDR1 (rs1045642), and SLCO1B1 (rs4149056). The combination of MTHFR, DRD3 and MDR1 polymorphisms associated with a slow ATV metabolizer phenotype.
Conclusion
Further studies using a genetic preselection method and a larger population are needed to confirm these polymorphisms as predictive biomarkers for ATV slow metabolizers.
Trial registration
Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry: ACTRN12614000851662, date registered: August 8, 2014.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The drug atorvastatin (ATV) is widely prescribed to treat hypercholesterolemia, which is a predisposing factor for develo** atherosclerosis. ATV, like all statins, acts by inhibiting 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, an essential enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis. ATV reduces the risk of atherosclerosis by lowering the levels of low-density lipoprotein-bound cholesterol [1]. ATV is administered orally, as a calcium salt (acid form), at a dose that ranges between 10 and 80 mg/day. Once ATV is ingested, several enzymes participate in its metabolism. The enzymes encoded by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 are the most important ones [2]. These enzymes transform ATV first to its lactone form and subsequently into 2 pharmacologically active metabolites (2-hydroxy-ATV and 4-hydroxy-ATV) [3, 4]. Next, ATV and its secondary metabolites are glucuronidated by uridine diphosphoglucuronosyltransferases (encoded by UGT1A1 and UGT1A3) [5]. Apart from metabolic enzymes, carrier proteins are involved in ATV metabolism, such as: 1) P-glycoprotein, also known as multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1), product of ABCB1, 2) the organic anion-transporting polypeptides (OATP1B1 and OATP1B3) encoded by SCLO1B1 and SCLO1B3, respectively [6–8], and 3) the breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP2), product of ABCG2 [9, 10].
Drug performance is evaluated on two main areas: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. The former focuses primarily on the evaluation of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion processes (ADME) of a drug; consequently, the variation in genes responsible for this process contributes to interindividual variability [11]. On the other hand, pharmacodynamics evaluates biochemical and physiological effects, as well as the mechanisms of action of a drug, i.e. it focuses on the drug response [12]. The pharmacokinetics of ATV displays high interindividual variability of up to 30 % [13, 14]. This pharmacokinetic discrepancy reveals variations in the ADME processes as the drug passes through the human body [12]. Factors such as age, gender, ethnicity, and genetic variability are involved in such interindividual differences [15, 16]. Genetic factors are responsible for about 15 to 30 % of the interindividual variation in metabolism, and thus in the response of each patient to certain classes of drugs. However, for some drugs this percentage can increase to up to 95 % [17]. These genetic factors are mainly due to variations in short tandem repeats, copy number variations, insertions and deletions, and single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The latter is the most common source of variation [18–20]. The presence of these polymorphisms in genes involved in the metabolism of ATV may explain its pharmacokinetic variability [17], since the frequency and consequences also vary between different populations [21]. The aims of this study were: 1) to reveal the frequency of 87 polymorphisms in 36 genes related to drug metabolism in healthy volunteers, 2) to evaluate the impact of these polymorphisms on ATV pharmacokinetics, 3) to classify the metabolic phenotypes for ATV, and 4) to investigate a possible association between genotypes and phenotypes.
Methods
Design
A randomized pilot study was carried out in 60 healthy Mexican volunteers to determine ATV pharmacokinetic parameters. A single dose of 80 mg ATV was administered. The clinical study complied with Good Clinical Practice standards, the guidelines of the Declarations of Helsinki and Tokyo, and the Mexican regulations on Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies (NOM-177-SSA1-1998) [22]. Furthermore, the protocol was approved by the Research and Ethics Committee of the pharmacokinetic study center, Ipharma S.A. (Monterrey, Mexico). The clinical study has been registered at the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (registration number: ACTRN12614000851662).
Study population
Sixty four healthy male candidates from northeastern Mexico were recruited and a written informed consent was obtained. Inclusion criteria were: non-smoker, 18-to-45-year old, weight ≥ 50 kg, body mass index (BMI) of 20–26 kg/m2, availability for completing the study, being healthy. Since ATV is classified as a pregnancy category X drug, only males were considered for the study. Candidates were excluded for: any abnormal lab result, significant personal or family medical history of angioedema o allergies, the existence of concurrent disease, use of prescription or over-the-counter medication or alcohol before enrollment, history of smoking, alcohol or drug abuse, and incompliance or non-willingness to complete the study. Four candidates were excluded because of the consumption of alcohol and/or substances or an altered blood pressure. The health status of the volunteers was confirmed by a medical history, a physical examination, an electrocardiogram (ECG), laboratory tests (blood count, blood chemistry, liver function tests, and urinalysis), and seronegativity for human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis B and C viruses.
Drug administration and sampling
After an overnight fast at the study center (Ipharma, S. A.), each subject was given a single dose of 80 mg of ATV-coated tablets (Pfizer Pharmaceuticals LLC, Caguas Site, Caguas, PR). The volunteers were under direct medical supervision at the study site. Venous blood (4 mL) was collected in K2EDTA-coated VacutainersTM (BD Diagnostics, Franklin Lakes, NJ, US), before ATV administration (time 0), and at the following time points after drug administration: 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 5, 6, 8, 12, 24, 36 and 48 h. Plasma was separated by centrifugation (15 min at 1600 g at 4 °C) and stored in cryovials at −80 °C until analysis, using a method validated by Ipharma S. A. [3, 23, 24].
Pharmacogenetic tests
Leukocytes were obtained from the buffy coat, and genomic DNA was extracted by the alkaline lysis method [25]. Seven multiplex polymerase chain reactions (PCRs) amplified the desired gene regions, following a validated protocol [26]. Screening for gene polymorphisms was performed using the PHARMAchip® microarray (Progenika, Derio, ES). This pharmacogenetic genoty** device detects, with a 99.9 % specificity and sensitivity, 85 gene polymorphisms in 34 genes involved in drug metabolism and response, including those encoding cytochrome P450 enzymes, phase II metabolism enzymes, receptors, and transporters. Amplified products were fractionated with DNAse according to a validated protocol [26], followed by fluorescent labeling and hybridization of the microarray, in an automated TECAN HS4800PRO platform (Ventana Medical Systems Inc., Tucson, AZ, US). The hybridization pattern was revealed using the Innoscan 710 scanner (Innopsys S.A., Carbonne, FR). Polymorphic variants were determined using PHARMAchip software V.3.2.9 [26]. Two additional polymorphisms not included in the PHARMAchip, rs2231142 (C__15854163_70) and rs4149056 (C__30633906_10), in ABCG2 and SLCO1B1 respectively, were included in the study and analyzed by Real-Time PCR system using validated Genoty** Assays (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, US) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Typed polymorphisms were only includedin subsequent association studies after having passed three quality control tests: the genotype call rate (>0.90 completeness to obtain 99.8 % accuracy), the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) test (P-value > 0.05), and the minor allele frequency (MAF) criterion (>0.01).
Determination of ATV calcium in plasma
Proteins were eliminated from the plasma samples by adding 4 volumes of acetonitrile to 100-μL samples, vortexing (70 rpm, 4 min.), and precipitating by centrifugation (9600 g, 10 min., 10 °C). Protein-free supernatant (300 μL) was recovered and 5-μL samples were injected into an Agilent 1100 high-performance liquid chromatographer (HPLC; equipped with an autosampler and a binary pump), which was connected to an Agilent 6410 tandem mass spectrometer (MS/MS) with a triple quadrupole detector (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, US) to measure ATV calcium levels. A C18 pre-column and a SynergiTM Fusion-RP column (4 μm, 80 Å, 50 × 2 mm; Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, US) formed the solid phase, whereas the mobile phase consisted of 0.03 % formic acid/70 % acetonitrile in analytical grade water. The column temperature was 40 °C, the flow rate 0.4 mL/min, and the auto-sampler temperature 20 °C. The detection system used an ESI MS/MS precursor ion (+) 559.3 m/z and a product ion (+) 440.3 m/z. Under these conditions, interday linearity was assessed by performing calibration curves from 0.5 to 100 ng/mL (0.5, 2.5, 5, 10, 25, 50 and 100); intraday quality control was evaluated by using eight ATV control samples of 1.7, 7.5, 35, and 75 ng/mL each.
Pharmacokinetic analysis
WinNonlin® professional software V.5.3 (Pharsight Corp., Mountain View, CA, US) was used for pharmacokinetic analysis. The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and the time to reach Cmax (Tmax) were calculated from the observed concentration-time data in plasma. Pharmacokinetic parameters were estimated with the non-compartmental method after oral administration of a single dose of ATV and were as follows: 1) the area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time 0 to the time of the last measurement (AUC0-t), calculated using the logarithmic-linear trapezoidal rule, 2) the area under the curve from time 0 to the time extrapolated to infinity (AUC0-∞), 3) the apparent clearance of the fraction dose absorbed (Cl/F), 4) the elimination rate constant in the terminal phase (Ke), and 5) the half-life in the terminal phase of the drug (T1/2).
Statistical analyses
For sample size calculation, it was assumed that the coefficient of variation (CV) was 45 % for the Cmax and AUC of ATV. Considering a significance level of 5 %, a minimum power of 80 %, an Ω of 0.25, and a confidence interval of 90 %, a sample size of 58 would suffice. The metabolizer phenotypes classification was made using a multivariate analysis of the combined pharmacokinetics parameters Cmax and AUC0-t. To minimize the effect of scale differences, before calculating the distance matrix, these variables were standardized. Next, the individual values of Cmax and AUC0-t were subjected to hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) using the Ward linkage method and the interindividual Manhattan distances were computed. The standardization, HCA, and the hierarchical clustering dendogram were made using Minitab 16 demo software (Minitab Inc., State College, PA, US) [27]. We identified the participants of each cluster and calculated the geometric means of all pharmacokinetic parameters of each cluster. According to the geometric means of the pharmacokinetic parameters of the clusters they were classified into metabolizer phenotypes. Next, one-way ANOVA and the Kruskal-Wallis H test were used to validate the classification model. The HWE was determined by comparing the genotype frequencies with the expected values using the maximum likelihood method [28]. To detect significant differences between 2 groups, Student’s t-test or the Mann Whitney U test were used for parametric and non-parametric distributions, respectively. Differences between more than 2 groups were assessed by one-way ANOVA or the Kruskal-Wallis H test for parametric and non-parametric distributions, respectively. Post hoc tests (LSD and Tamhane’s T2) were used for pairwise comparisons. To evaluate the contribution of genetic factors to the variability of the pharmacokinetic parameters linear regression analysis was done. Possible associations between genotypes or genotype combinations and phenotypes were assesed using contingency tables Χ2 statistics and Fisher’s exact tests. The linear regression analysis and association studies were performed under three different models (dominant, recessive, and additive). Odds ratios were estimated with 95 % confidence intervals. The model for prediction was confirmed using stepwise multiple linear regression analysis. Aforementioned analyses were performed with SPSS for Windows, V.20 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, US). All P-values were two-tailed. The corrected P (Pc) values were adjusted according to Bonferroni’s correction for multiple comparisons and the Benajmini-Hochberg procedure was applied to exclude spurious associations [29]. A P-value ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Study population
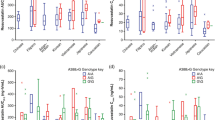
Sixty male subjects completed the study. Volunteers were of mestizo descent, most of them students (73 %) from the state of Nuevo Leon (83 %). Other demographic characteristics did not display significant variability (Table 1).
ATV pharmacokinetics
Despite controlling physiological and environmental conditions the pharmacokinetic parameters were highly variable (Table 2). The geometric mean ± SD for the pharmacokinetic parameters obtained were: Cmax = 41.44 ± 23.35 ng/mL, AUC0-t = 141.88 ± 86.78 ng/mL*h, AUC0-∞ = 157.12 ± 87.24 ng/mL*hr, Cl/F = 509.20 ± 265.57 L/h, T1/2 = 9.81 ± 6.58 h, and the Ke = 0.071 ± 0.035.
Classification of metabolizer phenotypes
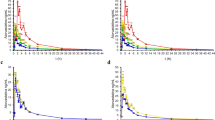
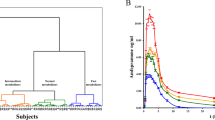
Cmax and AUC0-t were used for HCA classification of pharmacokinetic profiles, because Cmax tends to best reveal differences in pharmacokinetic profiles and AUC0-t is considered to be the best parameter to evaluate a drug’s interindividual pharmacokinetic variation [30]. The HCA, based on centroid distance, revealed three main clusters. Which we identified as slow metabolizers (30.00 %), normal metabolizers (41.66 %), and rapid metabolizers (28.33 %), as shown in Fig. 1. The geometric means of the pharmacokinetics parameters were significantly different among the three clusters (P ≤ 0.016), except for T1/2 (Table 2). The mean concentration-time profile and the geometric mean pharmacokinetic parameters of ATV obtained for each metabolizer phenotype are shown in Fig. 2a and Table 2, respectively. We observed a > 9-fold difference in ATV pharmacokinetic paratmeters between the fastest metabolizer indivual (Cmax = 10.94 ng/mL and AUC0-t = 55.23 ng/mL*h) and the slowest metabolizer individual (Cmax = 101.85 ng/mL and AUC0-t = 454.41 ng/mL*h). The distribution of phenotypes regarding Cmax-AUC0-t values, are presented in Fig. 2b.
Distinctive pharmacokinetic profiles of rapid, normal and slow metabolizers. a Mean peak plasma ATV concentration-time curves after a single 80-mg dose of ATV of the three metabolizer phenotypes. Data shown are mean ± standard error (SE) concentrations. b Distributions of metabolizer phenotypes with regard to Cmax-AUC0>-t values. For both a xand b: rapid metabolizers in red, normal in green, and slow ones in blue
Pharmacogenetic tests
The allele and genotype frequencies of the gene polymorphisms with a potential impact on drug metabolism are presented in Additional file 1. The HWE applied to most of the gene polymorphisms, with the exception of the gene deletions of GSTM1 and GSTT1, because the heterozygous variants were not detected [31]. The polymorphism rs1800896 in the IL10 was not in HWE equilibrium. The polymorphisms in CYP2D6, NAT2, TPMT, and TYMS were below the call rate threshold of 0.9. The SNPs in DPYD, rs1799807 in BCHE, and rs28399504 and rs41291556 in CYP2C19 had a MAF < 0.01. The aforementioned polymorphisms were excluded from subsequent analyses; a total of 30 SNPs remained for statistical analysis.
Association between gene polymorphisms and ATV pharmacokinetics
The various pharmacokinetic parameters were affected differentially by the different genetic loci;i.e. a certain polymorphism had an effect on Cmax but not on AUC0-t or the other way round, while there were also polymorphisms that affected both and/or other parameters (Table 3). The effect of MTHFR-rs1801133 on Cmax was statistically significant. Heterozygous variant (C/T) carriers and homozygous variant (T/T) carriers had lower Cmax values compared to homozygous wild-type (C/C) carriers (P = 0.018 and 0.004, respectively). Carriers of the variant genotype (C/T or T/T) showed significant lower values of Cmax (P = 0.006), AUC0-t (P = 0.050) and AUC0-∞ (P = 0.044) but statistically significant higher values of Cl/F (P = 0.044) as compared to homozygous wild-type subjects (C/C). The genotypes resulting from the DRD3-rs6280 (Ser9Gly) polymorphism had a significant impact on ATV pharmacokinetics. First, the homozygous wild-type (C/C) carriers had lower T1/2 values (P = 0.003) and higher Ke values (P = 0.008) as compared to homozygous variant (T/T) carriers. Second, when comparing T/T with (C/T) genotypes, there were significant differences for AUC0-t, AUC0-∞, Cl/F, T1/2 and Ke values (P were 0.027, 0.024, 0.024, 0.027, and 0.041, respectively). Third, the presence of the wild-type allele, combination (C/C + C/T), had a significant influence on all pharmacokinetics parameters (P values: Cmax = 0.050, AUC0-t = 0.026, AUC0-∞ = 0.016, Cl/F = 0.016, T1/2 = 0.004, and Ke = 0.007). GSTM3- rs1799735 had a significant effect on AUC0-∞ and Cl/F when *A/*A and *A/*B were compared (P = 0.041 for both parameters). Regarding TNF-rs1800629, the A allele carriers had significantly higher AUC0-t, AUC0-∞, and T1/2 values (P = 0.035, 0.030, and 0.025, respectively) and lower Cl/F and Ke values (P = 0.030 and 0.025). The homozygous variant (A/A) carrier was not found. MDR1 (ABCB1) and OATP1B1 (SLCO1B1) were the only ATV transport-related genes with an effect on ATV pharmacokinetics. The variant allele (T) of MDR1-rs1045642 produced a significant increase of Cmax (P = 0.037) when the combination of the heterozygous and homozygous variant (C/T + T/T) is compared with the homozygous wild-type (C/C). The C allele of the SLCO1B1-rs4149056 polymorphism significantly affected AUC0-t, AUC0-∞, and Cl/F values (P = 0.004 for all three parameters) in homozygous wild-type allele and heterozygous (C/C + C/T) carriers. None of the other 24 polymorphisms tested had a significant impact on ATV pharmacokinetics. The influences of polymorphisms on the ATV pharmacokinetics are shown in Table 3.
Association between genotypes and metabolizer phenotypes
No individual genotype correlated with any metabolizer phenotype after Bonferroni’s correction for multiple testing. However, MDR1-rs1045642 behavior was remarkable in this aspect, as no homozygous wild-type (C/C) was a slow metabolizer.
Of the six polymorphisms with an effect on ATV pharmacokinetics, three polymorphisms associated with the slow metabolizer phenotype considering genetic models. The C/T or T/T genotype of MTHFR-rs1801133, the T/T genotype of DRD3-rs6280, and the C/T or T/T genotype of MDR1-rs1045642 were significantly associated with slow metabolizer phenotype using dominant, recessive, and dominant models, respectively. This association remained statistically significant after adjusting for multiple testing using Bonferroni’s correction (P < 0.05; Table 4).
Linear regression analysis using aforementioned genetic models confirmed that these five polymorphisms affected the variability of pharmacokinetic parameters of ATV, except for the TNF-rs1800629 polymorphism (Additional file 2).
Next, we analyzed genotype combinations of the six polymorphisms that individually had a significant effect on ATV pharmacokinetic parameters (Table 3 and Additional file 3): cluster A (subjects with genotypes related to normal metabolism), cluster B (subjects with only 1 genotype related to decreased metabolism), and cluster C (subjects with 2 or more genotypes related to decreased metabolism). As the MTHFR, MDR1, and DRD3 genotypes effected pharmacokinetics most, clusters that only considered these genes were formed: Cluster D (subjects with MTHFR, MDR1 and DRD3 genotypes related to normal metabolism), cluster E (subjects in which either MTHFR, MDR1 or DRD3 gentoype related to decreased metabolism), and cluster F (subjects in which all MTHFR, MDR1 and DRD3 genotypes were related to decreased metabolism). The analysis of genotype combinations revealed that cluster C, i.e. subjects with 2 or more genotypes related to decreased metabolism, had a significant higher Cmax (P ≤ 0.016), AUC0-t (P ≤ 0.011) and AUC0-∞ (P = 0.011), but significantly lower Cl/F values (P = 0.011) when compared with cluster A and B. The genotype combination analysis limited to MTHFR, MDR1 and DRD3 showed that cluster F was significantly different from clusters D and E; a higher Cmax (P = 5.3 × 10−5), AUC0-t (P = 3.61 × 10−4), and AUC0-∞ = (4.22 × 10−4), but lower Cl/F (P = 1.35 × 10−4). The influences of the clusters on ATV pharmacokinetics are shown in Table 3.
The association analysis between clusters and phenotypes displayed a mutual dependency and association (P ≤ 0.05). The C and F cluster were associated with slow metabolizers as shown in Table 5. The stepwise multiple regression analysis showed that the combination of MTHFR, DRD3 and MDR1 polymorphisms are related to ATV slow metabolizers. The combination of these three polymorphisms contributed to the pharmacokinetic variability prediction with an R2 = 0.295, and adjusted R2 = 0.257 with a P = 2.26 × 10−4.
Adverse effects
ATV was well tolerated by all subjects, since no volunteer showed any adverse effects during and at the end of the pharmacokinetic study. No clinically significant changes from baseline were observed in the physical examination or the ECG during the study, and no clinically significant mean changes from baseline were observed for any laboratory parameters.
Discussion
Numerous studies have been performed to better characterize the high variability in ATV pharmacokinetic parameters. In this study, the maximum and minimum Cmax and AUC0-t values differed by approximately 10-folds in 60 healthy volunteers. Other studies even observed 15-folds for the Cmax and 12-folds for AUC, after a single dosis of ATV [42]. Allele frequencies found for rs1799735 are similar to those reported by Jain et al. [42]. Nevertheless, the homozygous variant (*B/*B) carrier was absent in our sample.
Heterozygous A allele carriers of TNF-rs1800629 had pharmacokinetic parameters that were consistent with a diminished clearance of ATV. Nevertheless, their influence on ATV pharmacokinetic variability was not confirmed by linear regression analysis. The rs1800629 (G/A) polymorphism is located in the promoter region of TNF. TNF encodes the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha. The variant A allele increases protein expression; therefore the wild-type G allele has a protective effect by reducing the risk of thrombosis in patients with hemodialysis [43]. It is unknown how TNF is involved in ATV metabolism, but there is evidence that ATV may attenuate TNF expression [44], which results in a reduction of the inflammatory process. The allele and genotype frequencies in our study group are similar to those of a Turkish population [43].
Previous studies have reported that the MDR1-rs1045642 polymorphism affects the response to ATV treatment. However, different studies disagree with respect to which homozygous genotype results in a better response to therapy [45–47]. MDR1 encodes a P-glycoprotein transporter, that functions as an ATP-dependent efflux pump and thus protects against harmful substances. MDR1 is widely expressed, for example in the small intestine, the blood–brain barrier, hepatocytes, and kidney proximal tubules [48, 49]. The MDR1-rs1045642 (C3435T) polymorphism is located in exon 26 of the MDR1/ABCB1 at a wobble position that does not produce an amino acid change. However, Hoffmeyer et al. [48] have reported that subjects homozygous for the variant (T/T) not only had reduced expression of MDR1 but also higher drug plasma levels as compared to subjects homozygous for the wild-type (C/C) [48]. In our study, carriers of the variant T allele, either homozygous or heterozygous, had a higher Cmax. Similar results were found by Zhou et al. [50] and Gonzalez-Vacarezza et al. [51] on fluvastatin and quetiapine pharmacokinetics, respectively. The T allele and genotype frequencies found in our study group were similar to those reported in the Lahu population (0.54) [52], the Dutch population (0.52) [53], and in Caucasians (0.53) [54]; however, they differ from those found in the Chilean population (0.34) [16], the African population (0.17), and in African-Americans (0.39) [55].
Similar to MDR1 polymorphisms, there are conflicting reports about the response and adverse drug reactions to statins in subjects with the SLCO1B1-rs4149056 (SLCO1B1*5) polymorphism [47, 56]. SLCO1B1, which is highly expressed in the liver, encodes an organic anion influx pump for numerous compounds. The SLCO1B1-rs4149056 (c.T521C) polymorphism results in the substitution of alanine for valine at amino acid residue 174, which reduces transport activity and leads to higher circulating statin concentrations that could be responsible for the reported adverse effects [57]. Our results support that rs4149056 affects ATV pharmacokinetics. However, the polymorphism did not associate with metabolic phenotypes. This could be due to the low frequency of C allele carriers in our sample. The variant T allele is the most frequent in Mexican population.
In summary, in our study we found six polymorphisms in different genes that have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of ATV. GSTM3 is a phase II metabolizing enzyme, which explains its impact on clearing parameters (Cl/F), and as a consequence AUC. MDR1 and SLCO1B1 are transporters, and this function may explain their impacton ATV pharmacokinetic parameters (Cmax, AUC, and Cl/F). However, the significant impact of the DRD3, MTHFR, and TNF polymorphisms on ATV Cmax, AUC’s, Cl/F T1/2, and Ke is achieved by so far unknown mechanisms.
The value of a pharmacokinetic parameter is the end result of a complex ADME process that involves many proteins. Polymorphisms in the different encoding genes may neutralize each other, which makes it highly unlikely that a single polymorphism determines a metabolizer phenotype. However, a slow metabolizer phenotype may be the result of various polymorphisms that reinforce a certain impact. Indeed the accumulation of polymorphisms of the six genes (MTHFR, GSTM3, DRD3, TNF, MDR1, and SLCO1B1) coincided with a shift from rapid metabolizers (no genotypes related to decreased metabolism in cluster A) to slow metabolizers (cluster C, up to six polymorphisms). MTHFR, MDR1 and DRD3 polymorphisms seem to have a leading impact on metabolizer phenotype, and were sufficient to identify slow metabolizers in our study group. For example, cluster D, comprised of MTHFR, MDR1 and DRD3 wild-type genotypes, were rapid metabolizers; cluster E is a mixture of the rapid and normal metabolizers, whereas the accumulation of these three polymorphisms (cluster F) is sufficient to identify slow metabolizers. These results were confirmed by association tests with different models, and stepwise multiple regression analysis. The interference of other genes in the A and B clusters may explain the lack of association with the rapid metabolizer phenotype. This can be explained by the complexity of the process that underlies the pharmacokinetic parameters, which involves many genes and other environmental factors. Thus, if a gene variant has a relatively small impact it will not be detected. The distribution plot (Fig. 2b) illustrates that slow metabolizer phenotype accumulates the widest variability of polymorphisms. Although we found six polymorphism with effect on the ATV pharmacokinetics, we know that the variability is not limited to the presence of these six markers, since other polymorphisms with little or moderate influence and not analyzed in this study, could contribute to the observed variability in each metabolic phenotype.
To our knowledge, this is the first report on the use of a massive genoty** tool (microarrays) to associate gene polymorphisms with pharmacokinetic variability of a drug commonly used by the Mexican population. The pharmacokinetic variability of ATV depends on several factors, including genetic factors. We identified six polymorphisms on six different genes that, individually, had an impact on some or all pharmacokinetic parameters. Absence of all polymorphism corresponded to rapid metabolizers, whereas the accumulation of polymorphisms caused a shift to slow metabolizers. However, some shortcomings existed in our study. First, there were insufficient data to correlate the metabolic phenotypes with the ATV response. Second, the number of participants was not large enough to validate our findings. Hence, our findings need to be validated in a larger population with genotype preselection. In order to identify (a set of) candidate predictors for ATV metabolizer phenotype, confirmative studies should be performed that focuse on the identified six polymorphisms. Our results may also be considered for future meta-analysis. The ultimate aim is that a pharmacogenetic analysis of a set of genes can be used to guide a personalized dosage that ensures drug response and prevents adverse drug effects.
Conclusions
In summary, this pilot study offers a novel, comprehensive approach to understand the genetic contribution to the variability of ATV metabolism in a Mexican population. It enabled the identification of candidate predictive biomarkers for slow ATV metabolizers. The future confirmation of the predictive potential of these candidate genetic biomarkers and their incorporation in routine genoty** tests may optimize ATV efficacy in the clinical practice.
Abbreviations
- ATV:
-
Atorvastatin
- ADME:
-
Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion processes
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- HWE:
-
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
- MAF:
-
Minor allele frequency
- Cmax:
-
Maximum plasma concentration
- AUC0-t:
-
Area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time 0 to the time of the last measurement
- AUC0-∞:
-
Area under the curve from time 0 to the time extrapolated to infinity
- Cl/F:
-
Apparent clearance of the fraction dose absorbed
- Ke:
-
Elimination rate constant in the terminal phase
- T1/2:
-
Half-life in the terminal phase of the drug
- HCA:
-
Hierarchical cluster analysis
References
Lennernas H. Clinical pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2003;42(13):1141–60. doi:10.2165/00003088-200342130-00005.
Kivisto KT, Niemi M, Schaeffeler E, Pitkala K, Tilvis R, Fromm MF, et al. Lipid-lowering response to statins is affected by CYP3A5 polymorphism. Pharmacogenetics. 2004;14(8):523–5. doi:00008571-200408000-00005.
Ahmed T, Kollipara S, Gautam A, Gigras R, Kothari M, Saha N, et al. Bioavailability and Interaction Potential of Atorvastatin and Losartan on Coadministration in Healthy Human Subjects. J Bioequivalence Bioavailability. 2009;1(1):018–27. doi:10.4172/jbb.1000004.
Jacobsen W, Kuhn B, Soldner A, Kirchner G, Sewing KF, Kollman PA, et al. Lactonization is the critical first step in the disposition of the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor atorvastatin. Drug Metab Dispos. 2000;28(11):1369–78.
Riedmaier S, Klein K, Hofmann U, Keskitalo JE, Neuvonen PJ, Schwab M, et al. UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) polymorphisms affect atorvastatin lactonization in vitro and in vivo. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010;87(1):65–73. doi:10.1038/clpt.2009.181.
Chen C, Mireles RJ, Campbell SD, Lin J, Mills JB, Xu JJ, et al. Differential interaction of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coa reductase inhibitors with ABCB1, ABCC2, and OATP1B1. Drug Metab Dispos. 2005;33(4):537–46. doi:10.1124/dmd.104.002477.
Romaine SP, Bailey KM, Hall AS, Balmforth AJ. The influence of SLCO1B1 (OATP1B1) gene polymorphisms on response to statin therapy. Pharmacogenomics J. 2010;10(1):1–11. doi:10.1038/tpj.2009.54tpj200954.
Schwarz UI. Meyer zu Schwabedissen HE, Tirona RG, Suzuki A, Leake BF, Mokrab Y et al. Identification of novel functional organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1B3 polymorphisms and assessment of substrate specificity. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2011;21(3):103–14. doi:10.1097/FPC.0b013e328342f5b1.
Keskitalo JE, Zolk O, Fromm MF, Kurkinen KJ, Neuvonen PJ, Niemi M. ABCG2 polymorphism markedly affects the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009;86(2):197–203. doi:10.1038/clpt.2009.79.
Mangravite LM, Thorn CF, Krauss RM. Clinical implications of pharmacogenomics of statin treatment. Pharmacogenomics J. 2006;6(6):360–74. doi:10.1038/sj.tpj.6500384.6500384.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry Clinical Pharmacogenomics: Premarket Evaluation in Early-Phase Clinical Studies and Recommendations for Labeling.Silver Spring: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; 2013.
Leon-Cachon RB, Ascacio-Martinez JA, Barrera-Saldana HA. Individual response to drug therapy: bases and study approaches. Rev Invest Clin. 2012;64(4):364–76.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Draft Guidance on Atorvastatin Calcium and Ezetimibe. Silver Spring: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; 2014.
Gandelman K, Malhotra B, LaBadle R, Crownover P, Bergstrom T. Analytes of Interest and Choice of Dose: Two Important Considerations in the Design of Bioequivalence Studies with Atorvastatin. J Bioequiv Availab. 2011;3(4):062–8. doi:10.4172/jbb.1000060.
Cavallari L, Lam Y. Pharmacogenetics. In: DiPiro J, Talbert R, Yee G, Matzke G, Wells B, Posey L, eds. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach. 9a ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2014. p. 2559.
Rosales A, Alvear M, Cuevas A, Saavedra N, Zambrano T, Salazar LA. Identification of pharmacogenetic predictors of lipid-lowering response to atorvastatin in Chilean subjects with hypercholesterolemia. Clin Chim Acta Intl J Clin Chem. 2012;413(3–4):495–501. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2011.11.003.
Eichelbaum M, Ingelman-Sundberg M, Evans WE. Pharmacogenomics and individualized drug therapy. Annu Rev Med. 2006;57:119–37. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.56.082103.104724.
Abecasis GR, Altshuler D, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Gibbs RA, et al. A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature. 2010;467(7319):1061–73. doi:10.1038/nature09534. nature09534.
Madsen BE, Villesen P, Wiuf C. Short tandem repeats and genetic variation. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;628:297–306. doi:10.1007/978-1-60327-367-1_16.
Pang AW, MacDonald JR, Pinto D, Wei J, Rafiq MA, Conrad DF, et al. Towards a comprehensive structural variation map of an individual human genome. Genome Biol. 2010;11(5):R52. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-r52.gb-2010-11-5-r52.
Hirschhorn JN, Daly MJ. Genome-wide association studies for common diseases and complex traits. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6(2):95–108. doi:10.1038/nrg1521. nrg1521.
Solorzano-Flores LI. NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-177-SSA1-1998, Que establece las pruebas y procedimientos para demostrar que un medicamento es intercambiable. Requisitos a que deben sujetarse los terceros autorizados que realicen las pruebas. Secretaría de Salud, México, DF. 1999. http://www.salud.gob.mx/unidades/cdi/nom/177ssa18.html. 2010.
Ma L, Dong J, Chen X, Wang G. Development and validation of atorvastatin by LC–ESI–MS and application in bioequivalence research in healthy Chinese volunteers. Chromatographia. 2007;65(11):737–41. doi:10.1365/s10337-007-0236-4.
Stanisz B, Kania L. Validation of HPLC method for determination of atorvastatin in tablets and for monitoring stability in solid phase. Acta Pol Pharm. 2006;63(6):471–6.
Sambrook J. Russell D W. Preparation and Analysis of Eukaryotic Genomic DNA. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Third ed. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2001.
Tejedor D, Castillo S, Mozas P, Jimenez E, Lopez M, Tejedor MT, et al. Reliable low-density DNA array based on allele-specific probes for detection of 118 mutations causing familial hypercholesterolemia. Clin Chem. 2005;51(7):1137–44. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2004.045203.
Miyaji K, Nagao K, Bannai M, Asakawa H, Kohyama K, Ohtsu D, et al. Characteristic metabolism of free amino acids in cetacean plasma: cluster analysis and comparison with mice. PLoS One. 2010;5(11):e13808. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013808.
Reed TE, Schull WJ. A general maximum likelihood estimation program. Am J Hum Genet. 1968;20(6):579–80.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol. 1995;57(1):289–300.
Endrenyi L, Fritsch S, Yan W. Cmax/AUC is a clearer measure than Cmax for absorption rates in investigations of bioequivalence. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1991;29(10):394–9.
Burim RV, Canalle R, Martinelli Ade L, Takahashi CS. Polymorphisms in glutathione S-transferases GSTM1, GSTT1 and GSTP1 and cytochromes P450 CYP2E1 and CYP1A1 and susceptibility to cirrhosis or pancreatitis in alcoholics. Mutagenesis. 2004;19(4):291–8.
Huang Q, Aa J, Jia H, **n X, Tao C, Liu L et al. A Pharmacometabonomic Approach to Predicting Metabolic Phenotypes and Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Atorvastatin in Healthy Volunteers. Journal of proteome research. 2015. doi:10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00440.
Maitland-van der Zee A-H, Lynch A, Boerwinkle E, Arnett DK, Davis BR, Leiendecker-Foster C, et al. Interactions between the SNPs in the homocysteine pathway (MTHFR 677C > T, MTHFR 1298 A > C and CBSins) and the efficacy of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in preventing cardiovascular disease in high-risk hypertensives: The GenHAT Study. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2008;18(8):651–6. doi:10.1097/FPC.0b013e3282fe1759.
Izmirli M, Bacaksiz A, Alptekin D, Uysal O, Kilic U. Statin and MTHFR C677T Polymorphism in Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases. Bezmialem Sci. 2014;2014(1):38–41.
Savitz J, Hodgkinson CA, Martin-Soelch C, Shen PH, Szczepanik J, Nugent A, et al. The functional DRD3 Ser9Gly polymorphism (rs6280) is pleiotropic, affecting reward as well as movement. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54108. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054108.
Kang SG, Lee BH, Lee JS, Chai YG, Ko KP, Lee HJ, et al. DRD3 gene rs6280 polymorphism may be associated with alcohol dependence overall and with Lesch type I alcohol dependence in Koreans. Neuropsychobiology. 2014;69(3):140–6. doi:10.1159/000358062.
Kuo SC, Yeh YW, Chen CY, Huang CC, Chang HA, Yen CH, et al. DRD3 variation associates with early-onset heroin dependence, but not specific personality traits. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014;51:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.12.018.
Jimenez-Jimenez FJ, Alonso-Navarro H, Martinez C, Zurdo M, Turpin-Fenoll L, Millan J, et al. Dopamine receptor D3 (DRD3) gene rs6280 variant and risk for restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2013;14(4):382–4. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2012.11.009.
Lopez Aspiroz E, Cabrera Figueroa SE, Porras Hurtado GL, Cruz Guerrero R, Dominguez-Gil Hurle A, Carracedo A, et al. Pharmacogenetic analysis of SNPs in genes involved in the pharmacokinetics and response to lopinavir/ritonavir therapy. Curr Drug Metab. 2013;14(7):729–37.
Xu Y, Wang J, Dong W. GSTM3 A/B polymorphism and risk for head and neck cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e83851. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0083851.
Salinas-Souza C, Petrilli AS, de Toledo SR. Glutathione S-transferase polymorphisms in osteosarcoma patients. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2010;20(8):507–15. doi:10.1097/FPC.0b013e32833caa45.
Jain M, Kumar S, Lal P, Tiwari A, Ghoshal UC, Mittal B. Role of GSTM3 polymorphism in the risk of develo** esophageal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16(1):178–81. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-0542.
Sener EF, Taheri S, Korkmaz K, Zararsiz G, Serhatlioglu F, Unal A, et al. Association of TNF-alpha −308 G > A and ACE I/D gene polymorphisms in hemodialysis patients with arteriovenous fistula thrombosis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2014;46(7):1419–25. doi:10.1007/s11255-013-0580-2.
Sun YM, Tian Y, Li X, Liu YY, Wang LF, Li J, et al. Effect of atorvastatin on expression of IL-10 and TNF-alpha mRNA in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;382(2):336–40. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.03.019.
Ka**ami K, Brousseau ME, Ordovas JM, Schaefer EJ. Polymorphisms in the multidrug resistance-1 (MDR1) gene influence the response to atorvastatin treatment in a gender-specific manner. Am J Cardiol. 2004;93(8):1046–50. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.01.014.
Hoenig MR, Walker PJ, Gurnsey C, Beadle K, Johnson L. The C3435T polymorphism in ABCB1 influences atorvastatin efficacy and muscle symptoms in a high-risk vascular cohort. J Clin Lipidol. 2011;5(2):91–6. doi:10.1016/j.jacl.2011.01.001.
Shabana MF, Mishriki AA, Issac MS, Bakhoum SW. Do MDR1 and SLCO1B1 polymorphisms influence the therapeutic response to atorvastatin? A study on a cohort of Egyptian patients with hypercholesterolemia. Mol Diagn Ther. 2013;17(5):299–309. doi:10.1007/s40291-013-0038-3.
Hoffmeyer S, Burk O, von Richter O, Arnold HP, Brockmoller J, Johne A, et al. Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(7):3473–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.050585397.
Wessler JD, Grip LT, Mendell J, Giugliano RP. The P-glycoprotein transport system and cardiovascular drugs. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61(25):2495–502. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.02.058.
Zhou Q, Ruan ZR, Yuan H, Zeng S. CYP2C9*3(1075A > C), MDR1 G2677T/A and MDR1 C3435T are determinants of inter-subject variability in fluvastatin pharmacokinetics in healthy Chinese volunteers. Arzneimittelforschung. 2012;62(11):519–24. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1323696.
Gonzalez-Vacarezza N, Dorado P, Penas-Lledo EM, Farinas H, Estevez-Carrizo FE, Llerena A. MDR-1 genotypes and quetiapine pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers. Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 2013;28(3):163–6. doi:10.1515/dmdi-2013-0008.
Dong Q, Xu B, Tan Y, Liu Z, Tian L, Zhang B, et al. The genetic variability of MDR1 C3435T polymorphisms in four Southern Chinese populations. Biomed Pharmacother. 2009;63(9):658–62. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2008.09.003.
Becker ML, Visser LE, van Schaik RH, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG, Stricker BH. Influence of genetic variation in CYP3A4 and ABCB1 on dose decrease or switching during simvastatin and atorvastatin therapy. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2010;19(1):75–81. doi:10.1002/pds.1866.
Henningsson A, Marsh S, Loos WJ, Karlsson MO, Garsa A, Mross K, et al. Association of CYP2C8, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and ABCB1 polymorphisms with the pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(22):8097–104. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1152.
Schaeffeler E, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U, Penger A, Asante-Poku S, Zanger UM, et al. Frequency of C3435T polymorphism of MDR1 gene in African people. Lancet. 2001;358(9279):383–4. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05579-9.
Santos PC, Gagliardi AC, Miname MH, Chacra AP, Santos RD, Krieger JE, et al. SLCO1B1 haplotypes are not associated with atorvastatin-induced myalgia in Brazilian patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;68(3):273–9. doi:10.1007/s00228-011-1125-1.
Pasanen MK, Fredrikson H, Neuvonen PJ, Niemi M. Different effects of SLCO1B1 polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;82(6):726–33. doi:10.1038/sj.clpt.6100220.
Acknowledgements
Research was mainly supported by Ipharma S.A., Monterrey, Mexico. We thank the technical staff of Ipharma, S.A. and Vitagenesis, S.A. for facilities, advice and technical support. We also thank Lourdes Garza-Rodríguez and Herminia G. Martínez-Rodríguez for valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and the financial support for this work has not influenced its outcome.
Authors’ contributions
Designed research and conception: RBRLC, HABRS, JAAM, MGS, and EPG; Performed research: RBRLC, JAAM, MGS, and EPG; Pharmacokinetic analysis data: MEGP; Analyzed data: RBRLC, MEGP, RMCF, and HLGB; Data interpretation: RBRLC, RMCF, IM, and HLGB; Wrote manuscript: RBRLC, IM, and HABRS; Edited manuscript: RBRLC, IM, and HABS. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional files
Additional file 1:
Allele and genotype frequencies of polymorphism in genes involved in drug metabolism and response. HWE = Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, P = gene present, A = gene absent, ǂ = genotypes with frequency < 0.01, ¥ = not calculated. (DOCX 33 kb)
Additional file 2:
The P-values of results of linear regression for polymorphisms on ATV pharmacokinetic parameters using different genetic models. a = Dominant (C/C vs. C/T + T/T), b = Recessive (C/C + C/T vs. T/T), c = Additive (*A/*A vs. *A/*B), d = Additive (G/G vs. G/A), e = Additive (G/G vs. G/A), f = Recessive (C/C + C/T vs. T/T), Pc = P-values adjusted by using Bonferroni’s correction for multiple comparisons, − = Not significant, * = Significant. (DOC 36 kb)
Additional file 3:
Genotype clusters. Genotype combinations are classified as follows: altered genotypes are in red and other genotypes are in green; Cluster A:subjects with genotypes related to normal metabolism, cluster B: subjects with only 1 genotype related to decreased metabolism, cluster C: subjects with 2 or more genotypes related to decreased metabolism, cluster D: subjects with MDR1 and DRD3 genotypes related to normal metabolism, cluster E: subjects in which either MDR1 or DRD3 was altered, and cluster F: subjects in which both MDR1 and DRD3 were altered. (TIFF 3555 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
León-Cachón, R.B.R., Ascacio-Martínez, J.A., Gamino-Peña, M.E. et al. A pharmacogenetic pilot study reveals MTHFR, DRD3, and MDR1 polymorphisms as biomarker candidates for slow atorvastatin metabolizers. BMC Cancer 16, 74 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-016-2062-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-016-2062-2