Abstract
Background
microRNAs (miRNAs) play both oncogenic and oncostatic roles in leukemia. However, the molecular details underlying miRNA-mediated regulation of their target genes in pediatric B- and T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias (ALLs) remain unclear. The present study investigated the relationship between miR-2909 and Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4), and its functional relevance to cell cycle progression and immortalization in patients with pediatric ALL.
Methods
Elevated levels of miR-2909 targeted the tumor suppressor gene KLF4 in pediatric B-cell, but not pediatric T-cell ALL, as detected by pMIR-GFP reporter assay. Expression levels of genes including apoptosis-antagonizing transcription factor (AATF), MYC, B-cell lymphoma (BCL3), P21CIP, CCND1 and SP1 in B- and T-cells from patients with pediatric ALL were compared with control levels using real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, western blotting, and reporter assays.
Results
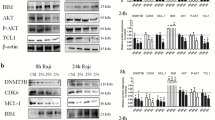
We identified two novel mutations in KLF4 in pediatric T-ALL. A mutation in the 3′ untranslated region of the KLF4 gene resulted in loss of miR-2909-mediated regulation, while mutation in its first or third zinc-finger motif (Zf1/Zf3) rendered KLF4 transcriptionally inactive. This mutation was a frameshift mutation resulting in alteration of the Zf3 motif sequence in the mutant KLF4 protein in all pediatric T-ALL samples. Homology models, docking studies and promoter activity of its target gene P21CIP confirmed the lack of function of the mutant KLF4 protein in pediatric T-ALL. Moreover, the inability of miR-2909 to regulate KLF4 and its downstream genes controlling cell cycle and apoptosis in T-cell but not in B-ALL was verified by antagomiR-2909 transfection. Comprehensive sequence analysis of KLF4 identified the predominance of isoform 1 (~55 kDa) in most patients with pediatric B-ALL, while those with pediatric T-ALL expressed isoform 2 (~51 kDa).
Conclusions
This study identified a novel miR-2909-KLF4 molecular axis able to differentiate between the pathogeneses of pediatric B- and T-cell ALLs, and which may represent a new diagnostic/prognostic marker.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is widely recognized as the most prevalent pediatric leukemia [1]; however, the genomic mechanisms responsible for the uncontrolled cell proliferation coupled with cell immortalization remain unknown [2]. In this context, the genes for apoptosis-antagonizing transcription factor (AATF) and Kruppel like factor 4 (KLF4) have assumed importance. AATF provides a critical link between cell cycle progression, check-point control, and apoptosis [3], and also encodes the novel microRNA (miRNA) miR-2909, which regulates genes involved in inflammation, cell cycle, and immune response [4–6]. KLF4, a member of the SP1/KLF transcription factor family, is characterized by three highly conserved C2H2-type zinc-finger motifs at its carboxyl terminus, which are crucial for its interaction with its target DNA [7]. The KLF4 gene acts as both an oncogene and a tumor suppressor, depending on its genetic and cellular contexts [8]. The tumor-suppressive role of KLF4 and its involvement in regulating apoptosis, proliferation, and differentiation in B-cell malignancies suggest that KLF4 may play a critical role in leukemogenesis [34]. B- and T-cells were purified using MiniMACS™ Separator Kit.
RNA Extraction, cDNA synthesis and qRT-PCR
Total RNA including the small RNA was extracted from patient samples using miRNeasy mini kit in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The quality and quantity of extracted RNAs were analyzed using electrophoresis and optical density measurement at 260 nm; cDNA synthesis was performed via miScript Reverse transcription kit as per suppliers’s instructions. For assaying gene expression, miScript SYBR Green Mix and the Real-time PCR (Stratagene, San Diego, CA, USA) were used. The qRT-PCR reaction was performed with a starting temperature of 95°C for 10 min, followed by 35 cycles of 45 s at 94°C, 30 s at 56°C, and 45 s at 72°C. The small non-coding nuclear RNA U6 and β-actin were used as an invariant controls for normalizing the expression of miR-2909 and other genes respectively. The 2-ΔΔCT method was used to calculate the relative expression of target genes.
Immunoblotting
Total cellular protein was extracted using Laemmli’s buffer [35] and the protein levels of KLF4, p21CIP, SP1, MYC and CCND1 was determined through western blotting using appropriate antibodies as described previously [36]. β-actin antibody was used as an internal control. Scion Image Analysis software was used for densitometry analysis and the results were expressed as intensity ratio of target protein to β-actin protein taken as arbitrary unit.
DNA sequencing
Primer sets were designed to amplify the full coding region and 3′untranslated region of KLF4 in ALL samples using Pfu polymerase. The resultant PCR products were purified using Qiaquick PCR purification kit and sequenced to detect the presence of any genetic aberration(s) in KLF4 in samples from pediatric patients with ALL. The sequence data was analysed using Cluster X 2.0.12 Software (http://www.clustal.org/clustal2) [37].
Plasmid constructs and reporter assays
Full length 3′UTR of KLF4 in B-ALL was cloned into miRNASelect™ pMIR GFP reporter vector; designated as pGFP-KLF4-3′UTR-B which carried no substitution of nucleotides within miR-2909 target site in KLF4 3′UTR. Mutant 3′UTR of KLF4 present in T-ALL was named as pGFP-KLF4-3′UTR-T with substitution of nucleotides within core binding site in KLF4 3′UTR. The plasmid constructs were transfected in HEK-293 cells. After 48 h, fluoresence microscopy and FACS analysis was performed to quantitate the number of cells expressing GFP. For p21CIP promoter analysis, promoter sequence of p21CIP with putative KLF4 binding site was cloned into pBlue TOPO reporter vector with subsequent transfection of β-gal construct into control and T- lymphoblasts. For analysis of SP1 transcriptional activity, B- and T-lymphoblasts with reporter plasmids containing SP1 response elements were transfected. β galactosidase activity was measured 72 h after transfection. To knockdown miR-2909 expression, leukemia cells were transfected with miRCURY LNA™ miR-2909 power inhibitor. To increase miR-2909 expression, HeLa cells were transfected with the PMIRH-2909 expression vector. All the transfections were performed with Lipofectamine 2000 transfection reagent according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Cell cycle analysis and apoptosis assays by Flow cytometry
Cell cycle analysis and apoptotic assays was done on leukemia cells transfected with antagomiR-2909 (50 nM) and scrambled RNA (50 nM) for 48 h in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin under 5% CO2 at 37°C. For cell cycle experiments, cells were fixed in 70% ethanol and stained with PI. Cells percentage at different phases were analysed with FACSCalibur cytometer and Cell Quest Pro software (Becton Dickinson, NJ, USA). For apoptosis assays, cells were stained with FITC Annexin V coupled with propidium iodide and apoptosis was measured using BD FACS Diva Software (Becton Dickinson, FACS Canto II).
KLF4 structural model & docking with target DNA
The structural models of zinc finger motifs of wild-type and mutant KLF4 were modeled with template PDB ID: 2WBUA. The Homology models were built using MODELLER (9.9) [38]. Model validation was performed using Verify-3D (http://nihserver.mbi.ucla.edu/Verify_3D/) [39] and PROCHECK [40]. The quality of the final models was evaluated from Ramachandran plot (Additional file 3: Figure S3B). Molecular visualization and structural alignment was done using CHIMERA http://bioinformatics.org/wiki/Chimera[41] and PYMOL http://www.pymol.org/[42]. Target DNA sequence (5′-cgggcggggc-3′) in p21CIP promoter was modeled into B-FORM using DNA analysis servers [43]. Docking studies were performed using High Ambiguity-Driven bimolecular Docking (HADDOCK) under solvated conditions [44, 45]. Cation-π interactions were analysed with CAPTURE http://capture.caltech.edu/[46].
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed by SPSS Windows version 19. Data was expressed as mean ± S.D of the experiments performed in triplicate. Student’s t test or Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon test was performed to determine the significance of difference between two groups. Differences were considered significant at p < 0.01 and p < 0.05.
Abbreviations
- ALL:
-
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- miR:
-
microRNA
- B-ALL:
-
B-cell lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- T-ALL:
-
T-cell lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- AATF:
-
Anti-apoptotic transcription factor
- KLF4:
-
Kruppel like factor transcription factor 4
- BCL3:
-
B-cell lymphoma 3-encoded protein
- CCND1:
-
Cyclin D1
- Zf1:
-
First zinc finger motif
- Zf2:
-
Second zinc finger motif
- Zf3:
-
Third zinc finger motif
- SP1 :
-
Specificity protein transcription factor-1
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- CD:
-
Cluster of differentiation
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- β-gal:
-
β-galactosidase.
References
Pieters R, Carroll WL: Biology and treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2008, 55: 1-20. 10.1016/j.pcl.2007.11.002
Armstrong SA, Look AT: Molecular genetics of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2005, 23: 6306-6315. 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.047
Passananti C, Floridi A, Fanciulli M: Che-1/AATF, a multivalent adaptor connecting transcriptional regulation, checkpoint control, and apoptosis. Biochem Cell Biol. 2007, 85: 477-483. 10.1139/O07-062
Kaul D, Hussain A: Cellular AATF gene encodes a novel miRNA that can contribute to HIV-1 latency. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2009, 46: 237-240.
Kaul D, Sasikala M, Raina A: Regulatory role of miR-2909 in cell-mediated immune response. Cell Biochem Funct. 2012, 30: 500-504. 10.1002/cbf.2828
Sharma M, Sharma S, Arora M, Kaul D: Regulation of cellular CCND1 gene by arsenic is mediated through miR-2909. Gene. 2013, 522: 60-64. 10.1016/j.gene.2013.03.058
McConnell BB, Yang WV: Mammalian Kruppel-like factors in Health and Diseases. Physiol Rev. 2010, 90: 1337-1381. 10.1152/physrev.00058.2009
Rowland BD, Peeper DS: KLF4, p21 and context-dependent opposing forces in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006, 6: 11-23. 10.1038/nrc1780
Guan H, **e L, Leithäuser F, Flossbach L, Möller P, Wirth T, Ushmorov A: KLF4 is a tumor suppressor in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma and in classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2010, 116: 1469-1478. 10.1182/blood-2009-12-256446
Lutherborrow M, Bryant A, Jayaswal V, Agapiou D, Palma C, Yang YH, Ma DDF: Expression profiling of cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia identifies MicroRNAs that target genes involved in monocytic differentiation. Am J Hematol. 2011, 86: 2-11. 10.1002/ajh.21864
Schotte D, Pieters R, Den Boer ML: MicroRNAs in acute leukemia: from biological players to clinical contributors. Leukemia. 2012, 26: 1-12. 10.1038/leu.2011.151
Ambros V: The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004, 431: 350-355. 10.1038/nature02871
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, Rassenti L, Kipps T, Negrini M, Bullrich F, Croce CM: Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002, 99: 15524-15529. 10.1073/pnas.242606799
Garzon R, Volinia S, Liu CG, Fernandez-Cymering C, Palumbo T, Pichiorri F, Fabbri M, Coombes K, Alder H, Nakamura T, Flomenberg N, Marcucci G, Calin GA, Kornblau SM, Kantarjian H, Bloomfield CD, Andreeff M, Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures associated with cytogenetics and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2008, 111: 3183-3189. 10.1182/blood-2007-07-098749
de Oliveira JC, Scrideli CA, Brassesco MS, Morales AG, Pezuk JA, Queiroz RP, Yunes JA, Brandalise SR, Tone LG: Differential miRNA expression in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and association with clinical and biological features. Leuk Res. 2012, 36: 293-298. 10.1016/j.leukres.2011.10.005
Rehmsmeier M, Steffen P, Hochsmann M, Giegerich R: Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target duplexes. RNA. 2004, 10: 1507-1517. 10.1261/rna.5248604
, : The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt). Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37: D169-D174.
Shields JM, Yang VW: Identification of the DNA sequence that interacts with the gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26: 796-802. 10.1093/nar/26.3.796
Zhang W, Geiman DE, Shields JM, Dang DT, Mahatan CS, Kaestner KH, Biggs JR, Kraft AS, Yang VW: The gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor (Krüppel-like factor 4) mediates the transactivating effect of p53 on the p21WAF1/Cip1 promoter. J Biol Chem. 2000, 275: 18391-18398. 10.1074/jbc.C000062200
Rowland BD, Bernards R, Peeper DS: The KLF4 tumour suppressor is a transcriptional repressor of p53 that acts as a context-dependent oncogene. Nat Cell Biol. 2005, 7: 1074-1082. 10.1038/ncb1314
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM: CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1 phase progression. Genes Dev. 1999, 13: 1501-1512. 10.1101/gad.13.12.1501
Kanai M, Wei D, Li Q, Jia Z, Ajani J, Le X, Yao J, **e K: Loss of Kruppel-like factor expression contributes to SP1 over expression and human gastric cancer development and progression. Clin Cancer Res. 2006, 12: 6395-6402. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1034
Kaul D, Mehrotra A: Functional characterization of AATF transcriptome in human leukemic cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007, 297: 215-220. 10.1007/s11010-006-9317-1
Yasunaga J, Taniguchi Y, Nosaka K, Yoshida M, Satou Y, Sakai T, Mitsuya H, Matsuoka M: Identification of aberrantly methylated genes in association with adult T-cell leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004, 64: 6002-6009. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1422
Kluiver J, Poppema S, de Jong D, Blokzijl T, Harms G, Jacobs S, Kroesen BJ, van den Berg A: BIC and miR-155 are highly expressed in Hodgkin, primary mediastinal and diffuse large B cell lymphomas. J Pathol. 2005, 207: 243-249. 10.1002/path.1825
Eis PS, Tam W, Sun L, Chadburn A, Li Z, Gomez MF, Lund E, Dahlberg JE: Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005, 102: 3627-3632. 10.1073/pnas.0500613102
Mattiske S, Suetani RJ, Neilsen PM, Callen DF: The oncogenic role of miR-155 in breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2012, 21: 1236-1243. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-12-0173
Xu N, Papagiannakopoulos T, Pan G, Thomson JA, Kosik KS: MicroRNA-145 regulates OCT4, SOX2 and KLF4 and represses pluripotencyin human embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2009, 137: 647-658. 10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.038
Tian Y, Luo A, Cai Y, Su Q, Ding F, Chen H, Liu Z: MicroRNA-10b promotes migration and invasion through KLF4 in human esophageal cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem. 2010, 285: 7986-7994. 10.1074/jbc.M109.062877
Schuetz A, Nana D, Rose C, Zocher G, Milanovic M, Koeniqsmann J, Blasig R, Heinemann U, Carstanjen D: The structure of the KLF4 DNA-binding domain links to self-renewal and macrophage differentiation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011, 68: 3121-3131. 10.1007/s00018-010-0618-x
Zhao W, Hisamuddin IM, Nandan MO, Babbin BA, Lamb NE, Yang VW: Identification of Krüppel-like factor 4 as a potential tumor suppressor gene in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2004, 15: 395-402.
Kharas MG, Yusuf I, Scarfone VM, Yang VW, Segre JA, Huettner CS, Fruman DA: KLF4 suppresses transformation of pre-B cells by ABL oncogenes. Blood. 2007, 109: 747-755. 10.1182/blood-2006-03-011106
Yang WT, Zheng PS: Krüppel-like factor 4 functions as a tumor suppressor in cervical carcinoma. Cancer. 2012, 118: 3691-3702. 10.1002/cncr.26698
Boyum A: Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968, 21: 77-89. 10.3109/00365516809076979. 10.3109/00365516809076979
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970, 227: 680-685. 10.1038/227680a0
Raina A, Kaul D: LXR-α genomics programmes neuronal death observed in Alzheimer’s disease. Apoptosis. 2010, 15: 1461-1469. 10.1007/s10495-010-0541-5
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG: Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics. 2007, 23: 2947-2948. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Sali A, Blundell TL: Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol Biol. 1993, 234: 779-815. 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1626
Bowie JU, Lüthy R, Eisenberg D: A method to identify protein sequences that fold into a known three-dimensional structure. Science. 1991, 253: 164-170. 10.1126/science.1853201
Laskowski RA, Moss DS, Thornton JM: Main-chain bond lengths and bond angles in protein structures. J Mol Biol. 1993, 231: 1049-1067. 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1351
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE: UCSF Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem. 2004, 25: 1605-1612. 10.1002/jcc.20084
DeLano WL: The PyMOL molecular graphics system. 2010, San Carlos, CA, USA: DeLano Scientific,
Vlahovicek K, Kajan L, Pongor S: DNA analysis servers: plot.it, bend.it, model.it and IS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31: 3686-3687. 10.1093/nar/gkg559
De Vries SJ, van Dijk M, Bonvin AM: The HADDOCK web server for data-driven biomolecular docking. Nat Protoc. 2010, 5: 883-897. 10.1038/nprot.2010.32
De Vries SJ, Bonvin AMJJ: CPORT: a consensus interface predictor and its performance in prediction-driven docking with HADDOCK. PLoS One. 2011, 6: e17695- 10.1371/journal.pone.0017695
Gallivan JP, Dougherty DA: Cation-pi Interactions in Structural Biology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999, 96: 9459-9464. 10.1073/pnas.96.17.9459
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Dr. Neelam Varma for her support in the diagnosis of leukemic samples through Immunophenoty**. We thank Dr. Nitin Patel for his invaluable inputs and critical reading of the manuscript. The study was supported by the funds provided by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi (India). http://www.icmr.nic.in/ and this funding agency had no role in designing the experiment, sample collections and analysis done or preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
The work was conceived by DK and executed by DM and NC. Patients were supplied by RK. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12943_2013_1375_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Additional file 1: Figure S1: Sequence analysis of KLF4 coding region in pediatric T-ALL samples. (A-F) Representative DNA sequence alignment of KLF4 coding region (corresponding to the three zinc finger motifs in exon 5) in T-ALL samples. NCBI sequence is shown for comparison. Sequence analyses indicate insertion (A), deletion (B-F) of nucleotides in the first or third zinc finger motif (Zf1, Zf3) of KLF4 in T-ALL samples. These genetic aberration(s) changed the entire reading frame, altering the sequence of KLF4 third zinc finger motif and potentially destroying its DNA-binding affinity (G) Protein sequence alignment of these same 6 T-ALL samples with respect to NCBI. Identical Zf1 and Zf2 motif in pediatric T-ALL samples is highlighted. (PDF 308 KB)
12943_2013_1375_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Additional file 2: Figure S2: Sequence analysis of KLF4 coding region in pediatric B-ALL samples. (A,B) Representative DNA (A) and protein sequence alignment (B) of KLF4 coding region (corresponding to the three zinc finger motifs; Zf1, Zf2, Zf3 in exon 5) in all B-ALL samples in the present study. NCBI sequence is shown for comparison. Sequence analysis revealed no genetic aberrations in any of the three zinc-fingers regions of KLF4 in samples from pediatric patients with B-ALL, suggesting that the conformation of KLF4 was unaffected in these patients (sample size 10). (PDF 237 KB)
12943_2013_1375_MOESM3_ESM.pdf
Additional file 3: Figure S3: Structural models and docking studies of wild-type and mutant KLF4 (A) Predicted residues in the active site of KLF4 were Arg449, Arg467, Lys453, Gly456, His457, Arg458, Ser470, Arg471 and His474 as given by CASTP server. Most of the active residues reside in the second and third zinc finger motifs; Zf2 and Zf3 as indicated by green dots. (B) Ramachandran plot of wild-type and mutant KLF4 which was built using PROCHECK; wild- type KLF4 has 82.7% of residues in favoured region and the remaining 16.0% in additionally allowed regions; mutant KLF4 has 81.4% residues in the most favoured region and remaining 17.1% in additionally allowed regions. (C-D) Representative table exhibited the formation of hydrogen bonds between Ser 470 and guanine (at position 11) in wild-type (C) and between Arg458 and guanine (at position 3) in mutant (D) KLF4 (E-F) Representative table showed non-covalent interactions, primarily electrostatic hydrophobic and Van der waals forces between protein residues and bases (guanine and cytidine) in wild-type (E) and mutant KLF4 (F). DNA bases within the parentheses interact simultaneously with its corresponding protein residue. All the active site residues in wild-type KLF4 displayed hydrophobic and Van der waal interactions, in contrast only few active site residues in mutant KLF4 were involved in these interactions. (PDF 212 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Malik, D., Kaul, D., Chauhan, N. et al. miR-2909-mediated regulation of KLF4: a novel molecular mechanism for differentiating between B-cell and T-cell pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Mol Cancer 13, 175 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-13-175
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-13-175