Abstract
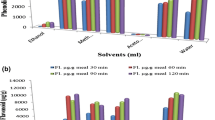
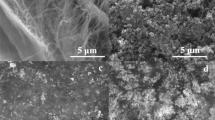
Silymarin (SM) from Silybum marianum (L.) is a sum of flavolignans (silibinin, silychristin, silydianin, and isosilibinin), exhibiting a wide spectrum of biological activity and having anti-inflammatory, antitumor, hepatoprotective, immunomodulatory effects. Using a modified emulsion method with solvent evaporation, lipid nanoparticles with silymarin (LNP-SM) were obtained, the size of which was 257 ± 6 nm, and the ζ potential was –20.8 ± 1.6 mV. The efficiency of SM inclusion in the LNP-SM was 89.8%, the loading degree was 5.4%. The release of CM from the composition of the resulting nanoparticles was prolonged; after 48 h, only 68.3 ± 5.4% of the active substance was released into the dialysis medium. The dynamics of the inclusion/release of SM in the composition of LNP into the films of bacterial cellulose (BC) produced by the Gluconacetobacter hansenii GH-1/2008 strain has been studied. It was shown, that after 24 h of incubation the maximum of BC film saturation with SM reached 0.745 ± 0.038 mg/cm2, and the maximum release was 0.520 ± 0.041 mg/cm2. It was demonstrated that both LNP-SM sols and samples of BC saturated with LNP-SM exhibited low hemolytic activity, which indicates the potential biosafety of these preparations. The preparation LNP-SM, in contrast to free SM, exhibited fungistatic action against the fungi of A. niger and C. albicans. Both free SM and LNP-SM suppressed the growth of gram-positive bacteria; however, the effect of LNP-SM was much more effective. The minimum inhibitory concentration of the LNP-SM preparation for B. subtilis and B. coagulans was 105 and 210 μg/mL, respectively. The possibility of develo** biocompatible coating materials based on BC saturated with LNP-SM is discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
R. Gazák, D. Walterová, and V. Kren, Curr. Med. Chem. 14, 315 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2174/092986707779941159
S. K. Manna, A. Mukhopadhyay, N. T. Van, and B. B. Aggarwal, J. Immunol. 163, 6800 (1999).
H. Basaga, G. Poli, C. Tekkaya, and I. Aras, Cell Biochem. Funct. 15, 27 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0844(199703)15:1<27::AID-CBF714>3.0.CO;2-W
N. Skottová and V. Krecman, Acta Univ. Palacki. Olomuc. Fac. Med. 141, 39 (1998).
C. H. Wu, S. M. Huang, and G. C. Yen, Antioxid. Redox Signal. 14, 353 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3134
Y. X. Wang, H. Cai, G. Jiang, et al., Asian Pacif. J. Cancer Prev. 15, 6791 (2014). https://doi.org/10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.16.6791
S. M. Woo, K. J. Min, S. Kim, et al., Chem.-Biol. Interact. 211, 36 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2014.01.004
M. B. Pirouzpanah, M. Sabzichi, S. Pirouzpanah, et al., Asian Pacif. J. Cancer Prev. 16, 2087 (2015). https://doi.org/10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.5.2087
A. Tyagi, C. Agarwal, G. Harrison, et al., Carcinogenesis 25, 1711 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgh180
J. Féher and G. Lengyel, Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 13, 210 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2174/138920112798868818
N. Vargas-Mendoza, E. Madrigal-Santillán, A. Morales-González, et al., World J. Hepatol. 6, 144 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i3.144
P. R. Rao and R. K. Viswanath, Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 12, 179 (2007).
A. Borah, R. Paul, S. Choudhury, et al., CNS Neurosci. Ther. 19, 847 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12175
M. Gharagozloo, M. Karimi, and Z. Amirghofran, Int. Immunopharmacol. 16, 243 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2013.04.016
N. Esmaeil, S. B. Anaraki, M. Gharagozloo, and B. Moayedi, Int. Immunopharmacol. 50, 194 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2017.06.030
D. G. Lee, H. K. Kim, Y. Park, et al., Arch. Pharm. Res. 26, 597 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976707
A. di Costanzo and R. Angelico, Molecules 24, 2155 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112155
M. S. El-Samaligy, N. N. Afifi, and E. A. Mahmoud, Int. J. Pharm. 308, 140 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.11.006
N. B. Feldman, T. I. Gromovykh, N. E. Sedyakina, et al., BioNanoSci. 8, 971 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-018-0556-x
N. Sun, X. Wei, B. Wu, et al., Powder Technol. 182, 72 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2007.05.029
S. Abrol, A. Trehan, and O. P. Katare, Drug Deliv. 11, 185 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1080/10717540490433958
Y. P. Wu, M. R. Huo, and J. P. Zhou, Yaoxue Xuebao 44, 651 (2009).
S. Bhatt, J. Sharma, M. Singh, and V. Saini, Acta Pharm. Sci. 56 (3), 27 (2018). https://doi.org/10.23893/1307-2080.APS.05616
M. Cengiz, H. M. Kutlu, D. D. Burukoglu, and A. Ayhancı, Food Chem. Toxicol. 77, 93 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.12.011
J. Q. Zhang, J. Liu, X. L. Li, and B. R. Jasti, Drug Deliv. 14, 381 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1080/10717540701203034
T. I. Gromovykh, V. S. Sadykova, S. V. Lutsenko, A. S. Dmitrenok, N. B. Feldman, T. N. Danilchuk, and V. V. Kashirin, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 53, 60 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683817010094
K. Liu, J. Sun, Y. Wang, et al., Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 34, 465 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/03639040701662230
X. Zhang, S. Lu, J. Han, et al., Pharmazie 66, 404 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1691/ph.2011.0350
M. Elmowafy, T. Viitala, H. M. Ibrahim, et al., Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 50, 161 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2013.06.012
M. Balouiri, M. Sadiki, and S. K. Ibnsouda, J. Pharm. Anal. 6, 71 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2015.11.005
R. L. Garcia and A. G. Rondero, J. Chem. Dermatol. Sci. Appl. 5, 62 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4236/jcdsa.2015.52008
P. Corchete, in Bioactive Nolecules and Nedicinal Plants, Ed. by K. Ramawat and J. Merillon (Springer, Berlin, 2008), p. 123. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74603-4_6
A. Q. Khan, R. Khan, M. Tahir, et al., Nutr. Cancer. 66, 249 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/01635581.2014.863365
M. L. Dupuis, F. Conti, A. Maselli, et al., Front. Immunol. 9, 1903 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01903
A. Valenzuela, T. Barría, R. Guerra, and A. Garrido, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 126, 712 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291x(85)90243-8
K. Amin and R. M. Dannenfelser, J. Pharm. Sci. 95, 1173 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.20627
D. R. de Oliveira, S. R. Tintino, M. F. Braga, et al., BioMed Res. Int., No. 292797 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/292797
D. G. Yun and D. G. Lee, IUBMB Life 69, 631 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1647
D. G. Lee, H. K. Kim, and Y. Park, Arch. Pharm. Res. 26, 597 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976707
Funding
This work was supported by a project to improve the competitiveness of leading Russian universities among the world's leading research and educational centers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahman, M.R., Feldman, N.B., Orekhov, S.N. et al. Saturation of Bacterial Cellulose with Silymarin Flavolignans in the Composition of Lipid Nanoparticles. Nanotechnol Russia 16, 239–245 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2635167621020038
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2635167621020038