Abstract
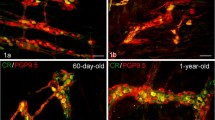
Calbindin 28 kDa (CB), calretinin (CR), and parvalbumin (PB) are calcium-binding proteins that are widely distributed in the nervous system and selectively expressed in certain population of neurons. These proteins are expressed not only in the central nervous system but also the autonomic ganglia. CB and PB are found in the sympathetic ganglia of rodents, and CB and CR are found in metasympathetic intramural ganglia. Their functions are poorly understood, but one can suggest that they have an important role in the regulation of Ca2+ levels in the cell. Calcium-binding proteins also play an important role in the age-related development of autonomic neurons. The percentage of CB- and CR-immunopositive neurons in the metasympathetic intramural ganglia of the small intestine in early postnatal development increases, whereas the percentage of CB decreases in sympathetic ganglia. It is possible that the functional meaning of such changes may be associated with the role of calcium currents in the development of neurons and the synaptic transmission.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gusev, N.B., Intracellular Ca-binding proteins. Part 1: Classification and structure, Soros. Obraz. Zh., 1998, no. 5, pp. 2–9.
Emanuilov, A.I., Moiseev, K.Yu., Filippov, I.V., and Maslyukov, P.M., Developmental characteristics of neurons in the intramural ganglia of the small intestine containing different types of calcium-binding proteins, Neurosci. Behav. Physiol., 2015, vol. 45, no. 9, pp. 986–990.
Maslyukov, P.M., Connections of the cat stellate ganglion with target organs during postnatal ontogenesis, Ross. Fiziol. Zh. im. I.M. Sechenova, 2000, vol. 86, no. 6, pp. 703–710.
Maslyukov, P.M., Korobkin, A.A., Konovalov, V.V., Porseva, V.V., and Emanuilov, A.I., Age-related development of calbindin-immunopositive neurons in rat sympathetic ganglia, Neurosci. Behav. Physiol., 2013, vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 153–156.
Maslyukov, P.M., Nozdrachev, A.D., and Timmermans, J.-P., Age-related characteristics of the neurotransmitter composition of neurons in the stellate ganglion, Neurosci. Behav. Physiol., 2007, vol. 37, no. 4, pp. 349–353.
Nozdrachev, A.D. and Maslyukov, P.M., Vozrastnoe razvitie neironov avtonomnykh gangliev (Age Development of Neurons in Autonomous Ganglia), St. Petersburg: Inform-Navigator, 2014.
Permyakov, E.A., Kal’tsii-svyazyvayushchie belki (Calcium- Binding Proteins), Moscow: Nauka, 1993.
Permyakov, E.A., Metall-svyazyvayushchie belki: struktura, svoistva, funktsii (Metal-Binding Proteins: Structure, Properties, and Functions), Moscow: Nauchnyi Mir, 2012.
Porseva, V.V., Shilkin, V.V., Strelkov, A.A., and Maslyukov, P.M., Calbindin-containing neurons in the ventral horn of the gray matter of the spinal cord in mice, Neurosci. Behav. Physiol., 2015, vol. 45, no. 6, pp. 710–714.
Abrahám, H., Veszprémi, B., Kravják, A., et al., Ontogeny of calbindin immunoreactivity in the human hippocampal formation with a special emphasis on granule cells of the dentate gyrus, Int. J. Dev. Neurosci., 2009, vol. 27, pp. 115–127.
Amenta, F., Cavalotta, D., Del Valle, M.E., et al., Calbindin D-28k immunoreactivity in the rat cerebellar cortex: age-related changes, Neurosci. Lett., 1994, vol. 178, pp. 131–134.
Andressen, C., Blumcke, I., and Celio, M.R., Calcium-binding proteins: selective markers of nerve cells, Cell Tissue Res., 1993, vol. 271, pp. 181–208.
Arciszewski, M.B., Calka, J., Wasowicz, K., and Majewski, M., Distribution and chemical coding of calretinin- and calbindin-expressing enteric neurons in the duodenum of the sheep, Pol. J. Vet. Sci., 2009, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 423–431.
Baimbridge, K.G., Celio, M.R., and Rogers, J.H., Calcium-binding proteins in the nervous system, Trends Neurosci., 1992, vol. 15, pp. 303–308.
Bastianelli, E., Distribution of calcium-binding proteins in the cerebellum, Cerebellum, 2003, vol. 2, pp. 242–262.
Bellido, T., Huening, M., Raval-Pandya, M., et al., Calbindin-D28k is expressed in osteoblastic cells and suppresses their apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-3 activity, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, vol. 275, pp. 26328–26332.
Brandt, M., Jessberger, S., Steiner, B., et al., Transient calretinin expression defines early post-mitotic step of neuronal differentiation in adult hippocampal neurogenesis, Mol. Cell Neurosci., 2003, vol. 24, pp. 603–613.
Brookes, S.J.H., Steele, P.A., and Costa, M., Calretinin immunoreactivity in cholinergic motor neurones, interneurones and vasomotor neurons in the guinea-pig small intestine, Cell Tissue Res., 1991, vol. 263, pp. 471–481.
Broughton, B.R., Reutens, D.C., and Sobey, C.G., Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia, Stroke, 2009, vol. 40, no. 5, pp. e331–e339.
Caillard, O., Moreno, H., Schwaller, B., et al., Role of the calcium-binding protein parvalbumin in short-term synaptic plasticity, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2000, vol. 97, no. 24, pp. 13372–13377.
Camandola, S. and Mattson, M.P., Aberrant subcellular neuronal calcium regulation in aging and Alzheimer’s disease, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2011, vol. 1813, no. 5, pp. 965–973.
Camp, A.J. and Wijesinghe, R., Calretinin: modulator of neuronal excitability, Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 2009, vol. 41, no. 11, pp. 2118–2121.
Chard, P.S., Bleakman, D., Christakos, S., et al., Calcium buffering properties of calbindin-D28k and parvalbumin in rat sensory neurons, J. Physiol., 1993, vol. 472, pp. 341–357.
Cheron, G., Schurmans, S., Lohof, A., et al., Electro physiological behavior of Purkinje cells and motor coordination in calretinin knock-out mice, Prog. Brain Res., 2000, vol. 124, pp. 299–308.
Cheron, G., Servais, L., and Dan, B., Cerebellar network plasticity: from genes to fast oscillation, Neuroscience, 2008, vol. 153, no. 1, pp. 1–19.
Corns, R.A., Boolaky, U.V., and Santer, R.M., Decreased calbindin-D28k immunoreactivity in aged rat sympathetic pelvic ganglionic neurons, Neurosci. Lett., 2000, vol. 292, no. 2, pp. 91–94.
Demarque, M. and Spitzer, N.C., Activity-dependent expression of Lmx1b regulates specification of serotonergic neurons modulating swimming behavior, Neuron, 2010, vol. 67, pp. 321–334.
Endo, T. and Onaya, T., Immunohistochemical localization of parvalbumin in rat and monkey autonomic ganglia, J. Neurocytol., 1988, vol. 17, pp. 73–77.
Furness, J.B., Kunze, W.A., Bertrand, P.P., et al., Intrinsic primary afferent neurons of the intestine, Prog. Neurobiol., 1998, no. 54, pp. 1–18.
Girard, F., Venail, J., Schwaller, B., and Celio, M.R., The EF-hand Ca(2+)-binding protein super-family: a genome-wide analysis of gene expression patterns in the adult mouse brain, Neuroscience, 2015, vol. 294, pp. 116–155.
Gonzalez-Gomes, M. and Meyer, G., Dynamic expression of calretinin in embryonic and early fetal human cortex, Front. Neuroanat., 2014, vol. 8, p. 41.
Grkovic, I. and Anderson, C.R., Calbindin D28Kimmunoreactivity identifies distinct subpopulations of sympathetic pre- and postganglionic neurons in the rat, J. Comp. Neurol., 1997, vol. 386, pp. 245–259.
Grkovic, I. and Anderson, C.R., Calretinin-containing preganglionic nerve terminals in the rat superior cervical ganglion surround neurons projecting to the submandibular salivary gland, Brain Res., 1995, vol. 684, no. 2, pp. 127–135.
Hao, M.M., Bornstein, J.C., Vanden Berghe, P., et al., The emergence of neural activity and its role in the development of the enteric nervous system, Dev. Biol., 2013, vol. 382, no. 1, pp. 365–374.
Hao, M.M., Moore, R.E., Roberts, R.R., et al., The role of neural activity in the migration and differentiation of enteric neuron precursors, Neurogastroenterol. Motil., 2010, vol. 22, no. 5, pp. e127–e137.
Hao, M.M. and Young, H.M., Development of enteric neuron diversity, J. Cell Mol. Med., 2009, vol. 13, no. 7, pp. 1193–1210.
Heiman, M.G. and Shaham, S., Twigs into branches: how a filopodium becomes a dendrite, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 2010, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 86–91.
Heizmann, C.W., Calcium signaling in the brain, Acta Neurobiol. Exp. (Warsaw), 1993, vol. 53, no. 1, pp. 15–23.
Heizmann, C.W. and Braun, K., Changes in Ca(2+)- binding proteins in human neurodegenerative disorders, Trends Neurosci., 1992, vol. 15, pp. 259–264.
Huerta, J.J., Nori, S., Llamosas, M.M., et al., Calretinin immunoreactivity in human sympathetic ganglia, Anat. Embryol. (Berlin), 1996, vol. 194, no. 4, pp. 373–378.
Iacopino, A.M. and Christakos, S., Specific reduction of calcium binding protein (28-kilodalton calbindin-D) gene expression in aging and neurodegenerative diseases, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1990, vol. 87, pp. 4078–4082.
Isaacs, K.R., Winsky, L., Strauss, K.I., and Jacobowitz, D.M., Quadruple co-localization of calretinin,calcitonin gene-related peptide,vasoactive intestinal peptide,and substance P in fibers within the villi of the rat intestine, Cell Tissue Res., 1995, vol. 280, pp. 639–651.
Lee, D., Obukhov, A.G., Shen, Q., et al., Calbindin-D28k decreases L-type calcium channel activity and modulates intracellular calcium homeostasis in response to K+ depolarization in a rat beta cell line RINr1046–38, Cell Calcium, 2006, vol. 39, pp. 475–485.
Lutz, W., Frank, E.M., Craig, T.A., et al., Calbindin D28K interacts with Ran-binding protein M: identification of interacting domains by NMR spectroscopy, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm., 2003, vol. 303, no. 4, pp. 1186–1192.
Mann, P.T., Southwell, B.R., Ding, Y.Q., et al., Localization of neurokinin 3 (NK3) receptor immunoreactivity in the rat gastrointestinal tract, Cell Tissue Res., 1997, vol. 289, pp. 1–9.
Masliukov, P.M., Emanuilov, A.I., Moiseev, K., et al., Development of non-catecholaminergic sympathetic neurons in para- and prevertebral ganglia of cats, Int. J. Dev. Neurosci., 2015, vol. 40, pp. 76–84.
Masliukov, P.M., Konovalov, V.V., Emanuilov, A.I., and Nozdrachev, A.D., Development of neuropeptide Y-containing neurons in sympathetic ganglia of rats, Neuropeptides, 2012, vol. 46, no. 6, pp. 345–352.
Masliukov, P.M., Korobkin, A.A., Nozdrachev, A.D., and Timmermans, J.P., Calbindin-D28k immunoreactivity in sympathetic ganglionic neurons during development, Auton. Neurosci., 2012, vol. 167, nos. 1–2, pp. 27–33.
Massouh, M., Wallman, M.J., Pourcher, E., and Parent, A., The fate of the large striatal interneurons expressing calretinin in Huntington’s disease, Neurosci. Res., 2008, vol. 62, no. 4, pp. 216–224.
Mattson, M.P., Calcium and neurodegeneration, Aging Cell, 2007, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 337–350.
Misawa, R., Girotti, P.A., Mizuno, M.S., et al., Effects of protein deprivation and re-feeding on P2X2 receptors in enteric neurons, World J. Gastroenterol., 2010, vol. 16, no. 29, pp. 3651–3663.
Mitsui, R., Immunohistochemical analysis of substance P-containing neurons in rat small intestine, Cell Tissue Res., 2011, vol. 343, no. 2, pp. 331–341.
Moyer, J.R., Furtak, S.C., McGann, J.P., and Brown, T.H., Aging-related changes in calcium-binding proteins in rat perirhinal cortex, Neurobiol. Aging, 2011, vol. 32, no. 9, pp. 1693–1706.
Obermair, G.J., Szabo, Z., Bourinet, E., and Flucher, B.E., Differential targeting of the L-type Ca2+ channel a1C (CaV1.2) to synaptic and extrasynaptic compartments in hippocampal neurons, Eur. J. Neurosci., 2004, vol. 19, pp. 2109–2122.
Orduz, D., Bischop, D.P., Schwaller, B., et al., Parvalbumin tunes spike-timing and efferent short-term plasticity in striatal fast spiking interneurons, J. Physiol., 2013, vol. 591, part 13, pp. 3215–3232.
Qu, Z.D., Thacker, M., Castelucci, P., et al., Immunohistochemical analysis of neuron types in the mouse small intestine, Cell Tissue Res., 2008, vol. 334, no. 2, pp. 147–161.
Resibois, A., Vienne, G., and Pochet, R., Calbindin-D28K and the peptidergic neuroendocrine system in rat gut: an immunohistochemical study, Biol. Cell, 1988, vol. 63, pp. 67–75.
Richardson, R.J., Grkovic, I., Allen, A.M., and Anderson, C.R., Separate neurochemical classes of sympathetic postganglionic neurons project to the left ventricle of the rat heart, Cell Tissue Res., 2006, vol. 324, pp. 9–16.
Rosenberg, S.S. and Spitzer, N.C., Calcium signaling in neuronal development, Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol., 2011, vol. 3, no. 10. doi 10.1101/cshperspect.a004259
Sang, Q. and Young, H.M., Chemical coding of neurons in the myenteric plexus and external muscle of the small and large intestine of the mouse, Cell Tissue Res., 1996, vol. 284, no. 1, pp. 39–53.
Satake, S. and Imoto, K., Cav2.1 channels control multivesicular release by relying on their distance from exocytotic Ca2+ sensors at rat cerebellar granule cells, J. Neurosci., 2014, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 1462–1474.
Sayegh, A.I. and Ritter, R.C., Morphology and distribution of nitric oxide synthase-,neurokinin-1 receptor-,calretinin-,calbindin-,and neurofilament-Mimmunoreactive neurons in the myenteric and submucosal plexuses of the rat small intestine, Anat. Rec., Part A, 2003, vol. 271, no. 1, pp. 209–216.
Schmidt, H., Three functional facets of calbindin D-28k, Front. Mol. Neurosci., 2012, vol. 5, p. 25.
Schwaller, B., Calretinin: from a “simple” Ca2+ buffer to a multifunctional protein implicated in many biological processes, Front. Neuroanat., 2014, vol. 5, no. 8, p. 3.
Schwaller, B., Cytosolic Ca2+ buffers, Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol., 2010, vol. 11. doi 10.1101/cshperspect. a004051
Schwaller, B., The continuing disappearance of “pure” Ca2+ buffers, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 2009, vol. 66, pp. 275–300.
Schwaller, B., Meyer, M., and Schiffmann, S., “New” functions for “old” proteins: the role of the calciumbinding proteins calbindin D-28k, calretinin and parvalbumin, in cerebellar physiology. Studies with knockout mice, Cerebellum, 2002, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 241–258.
Shetty, A.K. and Turner, D.A., Hippocampal interneurons expressing glutamic acid decarboxylase and calcium-binding proteins decrease with aging in Fischer 344 rats, J. Comp. Neurol., 1998, vol. 394, pp. 252–269.
Siechen, S., Yang, S., Chiba, A., and Saif, T., Mechanical tension contributes to clustering of neurotransmitter vesicles at presynaptic terminals, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2009, vol. 106, pp. 12611–12616.
Simons, M.J. and Pellionisz, A.J., Genomics, morphogenesis and biophysics: triangulation of Purkinje cell development, Cerebellum, 2006, vol. 5, pp. 27–35.
Song, Z.M., Brookes, S.J., and Costa, M., All calbindin- immunoreactive myenteric neurons project to the mucosa of the guineapig small intestine, Neurosci. Lett., 1994, vol. 180, pp. 219–222.
Villa, A., Podini, P., Panzeri, M.C., et al., Cytosolic Ca2+ binding proteins during rat brain ageing: loss of calbindin and calretinin in the hippocampus, with no change in the cerebellum, Eur. J. Neurosci., 1994, vol. 6, pp. 1491–1499.
Wilhelm, M., Lawrence, J.J., and Gábriel, R., Enteric plexuses of two choline-acetyltransferase transgenic mouse lines: chemical neuroanatomy of the fluorescent protein-expressing nerve cells, Brain Res. Bull., 2015, vol. 111, pp. 76–83.
Yano, S., Tokumitsu, H., and Soderling, T.R., Calcium promotes cell survival through CaM-K kinase activation of the proteinkinase-B pathway, Nature, 1998, vol. 396, pp. 584–587.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
iginal Russian Text © P.M. Masliukov, A.D. Nozdrachev, A.I. Emanuilov, 2016, published in Uspekhi Gerontologii, 2016, Vol. 29, No. 2, pp. 247–253.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masliukov, P.M., Nozdrachev, A.D. & Emanuilov, A.I. Age-related features in expression of calcium-binding proteins in autonomic ganglionic neurons. Adv Gerontol 6, 298–303 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S207905701604010X
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S207905701604010X