Abstract
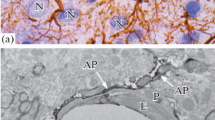
Despite a growing interest in gap junctions (GJs) of mammalian brain, their distribution and role in cell ensembles of thalamus remains unknown. The aim of this work was ultrastructural and immunoelectron study of glial GJs in ventral posteromedial (VPM) and posteromedial (POM) thalamic nuclei and thalamic reticular nucleus (RTN) of rats. GJs were identified by standard techniques of transmission electron microscopy and by pre-embedding immunohistochemistry protocol using anti-connexin-43 antibodies with Dako EnVision System + Peroxidase (DAB) detecting system. It was found that glial cells surround thalamocortical axons and axo-spiny synapses and form numerous elongated gap junction plaques located near chemical synapses. A single axon-spiny chemical synapse can be surrounded by several (up to 4) gap junctions that seem to form peculiar networks of glial cells united by GJs. Closely adjacent gap junctions disposed at an angle from 30° to 140° to each other were revealed. Immunoelectron labeling demonstrated that gap junction plaques located around chemical synapses have an astroglial origin. Despite the accumulation of osmiophilic material in the contact zone, ultrastructural signs of GJs were clearly identified. Due to the formation of intercellular glia-glial GJs astroglia may acquire a function of spatial buffer to regulate extracellular concentration of potassium and other ions, providing intracellular and extracellular ion homeostasis. We believe that astroglial processes joined into a network by GJs play a key role in the circulation of information and can modulate subcortical neuronal ensembles. We suggest that a close spatial location of astroglial GJs and asymmetrical chemical synapses is reflected in the functional organization of specific and nonspecific thalamic nuclei, which are the main centers of the afferent and efferent inputs of the cerebral cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kotini M., Mayor R. 2015. Connexins in migration during development and cancer. Develop. Biology. 401, 143–151.
Krutkovskikh V.A. 2005. The role of the gap-junctionmediated cell-to-cell interactions in cancerogenesis. Doct. Sci. (Med.) Dissertation, St.-Petersburg, Petrov Oncological Research Institute, 2005.
Tonkin R.S., Mao Y., O’Carroll S.J., Nicholson L.F., Green C.R., Gorrie C.A., Moalem-Taylor G. 2015. Gap junction proteins and their role in spinal cord injury. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 7 (102), doi 10.3389/ fnmol.2014.00102
Evans W.H. 2015. Cell communication across gap junctions: A historical perspective and current developments. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 43 (3), 450–459.
**e H., Cui Y., Deng F., Feng J. 2015. Connexin: A potential novel target for protecting the central nervous system? Neural Regen. Res. 10 (4), 659–666.
Belousov A.B., Fontes J.D. 2013. Neuronal gap junctions: Making and breaking connections during development and injury. Trends Neurosci. 36 (4), 227–236.
Wu X.L., Tang Y.C., Lu Q.Y., **ao X.L., Song T.B., Tang F.R. 2015. Astrocytic Cx 43 and Cx 40 in the mouse hippocampus during and after pilocarpine induced status epilepticus. Exp. Brain Res. 233 (5), 1529–1539.
Yamamoto T., Ochalski A., Hertzberg E.L., Nagy J.I. 1990. On the organization of astrocytic gap junctions in rat brain as suggested by LM and EM immunohistochemistry of connexin43 expression. J. Comp. Neurol. 302 (4), 853–883.
Houades V., Rouach N., Ezan P., Kirchhoff F., Koulakoff A., Giaume C. 2006. Shapes of astrocyte networks in the juvenile brain. Neuron Glia Biol. 2 (1), 3–14.
Takeuchi H., Suzumura A. 2014. Gap junctions and hemichannels composed of connexins: Potential therapeutic targets for neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 8 (189). doi 10.3389/fncel.2014.0018
Chever O., Pannasch U., Ezan P., Rouach N. 2014. Astroglial connexin 43 sustains glutamatergic synaptic efficacy. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 369. doi 10.1098/rstb.2013.0596
Blanc E.M., Bruce-Keller A.J., Mattson M.P. 1998. Astrocytic gap junctional communication decreases neuronal vulnerability to oxidative stress-induced disruption of Ca2+ homeostasis and cell death. J. Neurochem. 70 (3), 958–970.
Eugenin E.A., Basilio D., Sáez J.C., Orellana J.A., Raine C.S., Bukauskas F., Bennett M.V., Berman J.W. 2012. The role of gap junction channels during physiologic and pathologic conditions of the human central nervous system. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 7 (3), 499–518.
Pannasch U., Rouach N. 2013. Emerging role for astroglial networks in information processing: From synapse to behavior. Trends Neurosci. 36, 405–417.
Griemsmann S., Hoft S.P., Bedner P., Zhang J., Staden E., Beinhauer A., Degen J., Dublin P., Cope D.W., Richter N., Crunelli V., Jabs R., Willecke K., Theis M., Seifert G., Kettenmann H., Steinhä user C. 2014). Characterization of panglial gap junction networks in the thalamus, neocortex, and hippocampus reveals a unique population of glial cells. Cerebral Cortex. doi 10.1093/cercor/bhu157
Steriade M. 2006. Grou** of brain rhythms in corticothalamic systems. Neuroscience. 137 (4), 1087–1106.
Crunelli V., Hughes S.W. 2010. The slow (<1 Hz) rhythm of non-REM sleep: A dialogue between three cardinal oscillators. Nat. Neurosci. 13 (1), 9–17.
Bureau I., von Saint Paul F., Svoboda K. 2006. Interdigitated paralemniscal and lemniscal pathways in the mouse barrel cortex. PloS Biol. 4 (12). doi 10.1371/journalpbio.0040382
Liao C.C., Chen R.F., Lai W.S., Lin R.C., Yen C.T. 2010. Distribution of large terminal inputs from the primary and secondary somatosensory cortices to the dorsal thalamus in the rodent. J. Comp. Neurol. 518 (13), 2592–2611.
Lam Y.W., Sherman S.M. 2015. Functional topographic organization of the motor reticulothalamic pathway. J. Neurophysiol. 113 (9), 3090–3097.
Paxinos G., Watson C. 1998. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 4th ed. San Diego: Acad. Press.
Bozzola J.J., Russell L.D. 1992). Quantitative electron microscopy. In: Electron microscopy: Principles and techniques for biologists. Boston: Jones and Bartlett Publ., p. 287–303.
Genoud C., Houades V., Kraftsik R., Welker E., Giaume C. 2015. Proximity of excitatory synapses and astroglial gap junctions in layer IV of the mouse barrel cortex. Neuroscience. 291, 241–249.
Laird D.W. 2006. Life cycle of connexins in health and disease. Biochem. J. 394, 527–543.
Theis M., Giaume C. 2012. Connexin-based intercellular communication and astrocyte heterogeneity. Brain Res. 1487, 88–98.
Hoogland P.V., Wouterlood F.G., Welker E., Van der Loos H. 1991. Ultrastructure of giant and small thalamic terminals of cortical origin: A study of the projections from the barrel cortex in mice using Phaseolus vulgaris leuco-agglutinin (PHA-L). Exp. Brain Res. 87, 159–172.
Kirichenko E.Yu., Sukhov A.G., Logvinov A.K., Povilaitite P.E. 2013. Analysis of the spatial distribution of gap junctions relative to chemical synapses on serial ultrathin sections of the rat barrel cortex. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 43 (3), 336–340.
Giaume C., Tabernero A., Medina J.M. 1997. Metabolic trafficking through astrocytic gap junctions. Glia. 21 (1), 114–123.
Pellerin L., Magistretti P.J. 2012. Sweet sixteen for ANLS. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 32 (7), 1152–1166.
Blomstrand F., Giaume C. 2006. Kinetics of endothelin- induced inhibition and glucose permeability of astrocyte gap junctions. J. Neurosci. Res. 83 (6), 996–1003.
Rouach N., Koulakoff A., Abudara V., Willecke K., Giaume C. 2008. Astroglial metabolic networks sustain hippocampal synaptic transmission. Science. 322 (5907), 1551–1555.
Lam Y.W., Sherman S.M. 2015. Functional topographic organization of the motor reticulothalamic pathway. J. Neurophysiol. 113 (9), 3090–3097.
Shigeri Y., Seal R. P., Shimamoto K. 2004. Molecular pharmacology of glutamate transporters, EAATs and VGLUTs. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 45, 250–265.
Tress O., Maglione M., May D., Pivneva T., Richter N., Seyfarth J., Binder S., Zlomuzica A., Seifert G., Theis M., Dere E., Kettenmann H., Willecke K. 2012. Panglial gap junctional communication is essential for maintenance of myelin in the CNS. J. Neurosci. 32 (22), 7499–7518.
Nualart-Marti A., Solsona C., Fields R.D. 2012. Gap junction communication in myelinating glia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1828 (2013), 69–78.
Dunn K.M., Nelson M.T. 2010. Potassium channels and neurovascular coupling. Circ. J. 74 (4), 608–616.
Dere E., Zlomuzica A. 2012. The role of gap junctions in the brain in health and disease. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 36, 206–217.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.Yu. Kirichenko, G.A. Churyumova, A.K. Logvinov, 2016, published in Biologicheskie Membrany, 2016, Vol. 33, No. 3, pp. 194–206.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirichenko, E.Y., Churyumova, G.A. & Logvinov, A.K. Ultrastructural study of glial gap junctions in the thalamic nuclei of rat. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 10, 207–217 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747816020070
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747816020070