Abstract
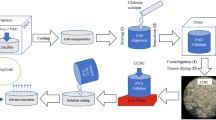
PbS nanoparticles were successfully synthesized in the presence of chitosan (CS) through an in situ method. This method is an effective, simple, and green synthetic approach to preparing nanomaterial films. The structure, morphology, and stability of the materials were examined via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and the characteristic peak of the NH2 group shifted from 1554 to 1598 cm-1 after PbS was formed in the film. The Pb–S bond exhibited a vibrational absorption peak at 605 cm-1, which further confirmed the generation of PbS nanoparticles. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) procedures were performed as well; well-defined nanoparticles were detected in the CS matrix by SEM. As per DSC findings, the thermal stabilities of the PbS/CS film were 50°C higher than those of pure CS. Moreover, the fluorescence emission of the films was sensitive to the presence of 2-isonaphthol. The effect of 2-isonaphthol concentration on the emission of films increases significantly with an increase in this concentration. The concentration-dependent fluorescence can be described by a correlation equation when 2-isonaphthol concentration ranges from 0 to 12.56 mg/L, and fluorescence results revealed that the PbS/CS nanoparticles were sensitive to 2-isonaphthol in the liquid phase. The proposed method may be applied to detect 2-isonaphthol in the environment and in the chemical industry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. F. Shen and X. P. Yan, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 46, 7659 (2007).
Y. R. Ma, L. M. Qi, J. M. Ma, and H. M. Cheng, Cryst. Growth Des. 4, 351 (2004).
A. M. Fernandes and M. H. Abdalhai, Biosens. Bioelectron. 63, 399 (2015).
C. **e, L. **ao, S. Peng, and X. Shi, New J. Chem. 38, 6095 (2014).
R. Jiang, J. Y. Zhu, Y. Fu, and Y. Guan, Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 3513 (2012).
P. D. Yang and C. M. Lieber, Science 273, 1836 (1996).
N. N. Zhao and L. M. Qi, Adv. Mater. 18, 359 (2006).
Y. H. Zhang, L. Guo, P. G. Yin, R. Zhang, Q. Zhang, and S. H. Yang, Chem. Eur. J. 13, 2903 (2007).
M. Kowshik, W. Vogel, J. Urban, S. K. Kulkarni, and K. M. Paknikar, Adv. Mater. 14, 815 (2002).
M. Orphanou, K. L. Tasoula, K. Frank, and C. Walter, Nano Lett. 3, 569 (2003).
Y. P. Zhang, Y. Chu, Y. Yang, L. H. Dong, F. Y. Yang, and J. G. Liu, Colloid Polym. Sci. 285, 1061 (2007).
P. T. Zhao, G. Chen, Y. Hu, X. L. He, K. Wu, Y. Cheng, and K. X. Huang, J. Cryst. Growth 303, 632 (2007).
S. L. **ong, B. J. **, D. C. Xu, C. G. Wang, X. M. Feng, H. Y. Zhou, and Y. T. Qian, J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 16761 (2007).
D. B. Kuang, A. W. Xu, Y. P. Fang, H. Q. Liu, C. Frommen, and P. Fenske, Adv. Mater. 20, 1747 (2003).
Y. H. Ni, H. J. Liu, F. Wang, Y. Y. Liang, J. M. Hong, X. Ma, and Z. Xu, Cryst. Growth Des. 4, 759 (2004).
M. Mohammadikish, F. Davar, E. Loghman, and R. Mohammad, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 2937 (2015).
W. X. Wang, Q. Li, M. Li, H. Lin, and L. J. Hong, J. Cryst. Growth 299, 17 (2007).
H. Tributsch and J. A. Rojas-Chapana, Electrochim. Acta 45, 4705 (2000).
Z. Li and Y. Du, Mater. Lett. 57, 2480 (2003).
S. Wang and M. Y. Zheng, J. Polym. Eng. 34 (4), 339 (2014).
S. Wang and D. M. Yu, Mater. Sci. Eng., B 176 (6), 873 (2011).
S. Wang and Y. H. Gao, Polym. Sci., Ser. B 57 (3), 252 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Yi, H. & Zheng, M. The green synthetic approach to prepare PbS/chitosan nanocomposites and its new optical sensing active properties for 2-isonaphthol. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 58, 474–478 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1560090416040084
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1560090416040084