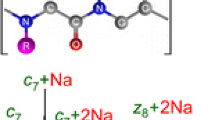
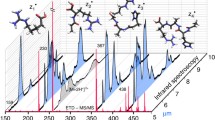
Abstract—
A scheme for analyzing the mass spectra of fragmented peptides, including chemical modification of the N-terminal amino group of the peptide by 5-(N,N-dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonyl chloride followed by ionization of the dansylated peptide by electrospray and its fragmentation at the low vacuum zone of the sample solution input unit into the mass spectrometer (ESI-o-TOF scheme), has been proposed. It is shown that the resulting ions are fragmented with the predominant formation of b-ions bearing a Dns-group. In this way, it is possible to obtain high-intensity b-ions (peak/noise intensity ratio of 10/1 to 100/1), including b1 and b2 ions that are especially valuable for determining the structure. In combination with the previously proposed method of obtaining informative y-ions, this approach allows one to reliably determine the complete amino acid sequence of peptides containing up to 10 amino acid residues, without using computer programs for analyzing the fragment composition of peptides.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Fragments of the internal splitting that do not contain Dns-groups are marked on the mass spectra as y#.
REFERENCES
Nazimov, I.V. and Bublyaev, R.A., Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem., 2018, vol. 44, pp. 481–491.
Lebedev, A.T., Artemenko, K.A., and Samgina, T.Yu., in Osnovy mass-spektrometrii belkov i peptidov (Basics of Mass Spectrometry of Proteins and Peptides), Moscow: Tekhnosfera, 2012, p. 49.
Summerfield, S.G., Bolgar, M.S., and Gaskell, S.J., Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Processes, 1997, vol. 32, pp. 225–231.
Baldwin, M.A., Methods in Enzymology, San Diego, California: Academic, 2005, vol. 402, pp. 33–48.
Bieman, K., Methods in Enzymology, San Diego, California: Academic, 1990, vol. 193, pp. 455–479.
Verenchikov, A.N., Nauchnoe Priborostroenie, 2004, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 4–23.
Harrison, A.G., J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom., 2008, vol. 19, pp. 1776–1780.
Lebedev, A.T., Artemenko, K.A., and Samgina, T.Yu., Osnovy mass-spektrometrii belkov i peptidov (Basics of Mass Spectrometry of Proteins and Peptides), Moscow: Tekhnosfera, 2012, p. 110.
Yague, J., Paradela, A., Ramos, M., Ogueta, S., Marina, A., Barahona, F., de Castro, J.A.L., and Vasquez, J., Anal. Chem., 2003, vol. 75, pp. 1524–1535.
Harrison, A.G., J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom., 2009, vol. 20, pp. 2248 – 2253.
Samyn B., Debyser, G., Sergeant, K., Devreese, B., and Van Beeumen, J., J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom., 2004, vol. 15, pp. 1838 – 1852.
Nazimov, I.V., Krasnov, N.V., Muradymov, M.Z., Bublyaev, R.A., Gavrik, M.A., and Prisyach, S.S., RF Patent no. RU 2498443 C2, 2011.
Levina, N.B. and Nazimov, I.V., J. Chromatogr. A, 1984, vol. 286, pp. 207–216.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to S.V. Shabel’nikov (Institute of Cytology, RAS) for support during the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by E. Stepanova
Abbreviations: M+, quasi-molecular ion; MS, mass spectrometry; MS/MS, tandem mass spectrometry; HPLC, high performance liquid chromatography; Dal, dalargin; Dns, 5-(N,N-dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonyl chloride, dansyl; ESI-o-TOF, time-of-flight mass spectrometer with orthogonal sample input and with an electrospray ion source; Q, quadrupole; q, tandem mass spectrometer collision cell; TOF, time of flight; ∆U, potential difference between the nozzle and the skimmer of the ion source; Urf, radio frequency voltage of the transport quadrupole.
See [1] for part I.
Corresponding author: phone: +7 (495) 330-75-92; e-mail: nazimov@ibch.ru.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nazimov, I.V., Bublyaev, R.A. Mass Spectrometric Amino Acid Sequencing of Short and Mid-Sized Peptides in a ESI-o-TOF System as an Alternative to MS/MS. II: Selective Fragmentation of Dansylated Peptides with Predominant Formation of b-Ions. Russ J Bioorg Chem 45, 9–17 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1068162019010102
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1068162019010102