Abstract
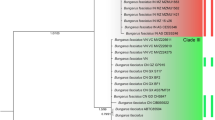
Phylogenetic relationships of Sabanejewia species inferred from variability in the mitochondrial cytochrome b gene (n = 95) and nuclear gene RAG-1 (n = 46) in an expanded dataset, including S. caspia, S. aralensis, and Eastern European and Asian populations of previously analyzed species, show that S. caspia, S. larvata and S. romanica are three highly diverged mtDNA lineages, independently and sequentially branching earlier than other clades. However, S. caspia and S. larvata are combined into a common RAG-1 clade (albeit with low support), which corresponds to the karyological similarity of these species. Because of their deep genetic divergence and observed morphological differences, S. caspia and S. larvata are considered to be members of an independent subgenus Andrzhewia subg. n. distinguished by a relatively short caudal peduncle, short snout and specific color pattern. Within the Danube-Balkan complex identified by Perdices et al., the present analysis shows a strongly supported monophyletic mtDNA lineage of S. vallachica; the mixed structure of other lineages of this complex is apparently associated with undeveloped system of the diagnostic characters, which leads to incorrect identification of specimens involved in phylogenetic analysis. S. baltica, previously considered a monophyletic lineage distributed in the basins of the Black (Dniester, Dnieper, and Don) and Baltic (Vistula and Odra) seas, is represented in this analysis by two differentiated phylogenetic groups. The first group includes samples from the Baltic Sea basin and the Dniester River system and corresponds to S. baltica s. stricto; the second group includes samples from the Don basin, which should be considered a new cryptic species of Sabanejewia. S. kubanica, S. caucasica, and S. aralensis are distinguished as separate monophyletic mtDNA subclades, which confirm their species status; S. aurata is identified as a polyphyletic group.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Allio, R., Donega, S., Galtier, N., and Nabholz, B., Large variation in the ratio of mitochondrial to nuclear mutation rate across animals: implications for genetic diversity and the use of mitochondrial DNA as a molecular marker, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2017, vol. 34, no. 11, pp. 2762–2772. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx197
Băcescu, M.C., Contributo allo studio dei Cobitis dell’Italia settentrionale, Arch. Oceanogr. Limnol., 1961, vol. 12, pp. 185–189.
Ballard, J.W.O. and Whitlock, M.C., The incomplete natural history of mitochondria, Mol. Ecol., 2004, vol. 13, pp. 729– 744. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294x.2003.02063.x
Bănărescu, P.M., Vicariant patterns and dispersal in European freshwater fishes, Spixiana, 1989, vol. 12, pp. 91–103.
Bănărescu, P.M., Zoogeography of Fresh Waters. V. 1. General Distribution and Dispersal of Freshwater Animals, Wiesbaden: Aula-Verlag, 1990.
Bănărescu, P.M., Zoogeography of Fresh Waters. V. 2. Distribution and Dispersal of Freshwater Animals in North America and Eurasia, Wiesbaden: Aula-Verlag, 1992.
Bănărescu, P., Nalbant, T.T., and Chelmu, S., Revision and geographical variation of Sabanejewia aurata in Romania and the origin of S. bulgarica and S. romanica (Pisces,Cobitidae), Ann. Zool. Bot., 1972, vol. 75, pp. 1–49.
Bartoňová, E., Papoušek, I., Lusková, V., et al., Genetic diversity and taxonomy of Sabanejewia balcanica (Osteichthyes: Cobitidae) in the waters of the Czech Republic and Slovakia, Folia Zool., 2008, vol. 57, pp. 60–70.
Berg, L.S., Ryby presnykh vod SSSR i sopredel’nykh stran, t. 3 (Freshwater Fishes of the U.S.S.R. and Adjacent Countries, vol. 3), Moscow, Leningrad: Izd. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1949, pp. 929–1382.
Bianco, P.G., Potential role of the paleohistory of the Mediterranean and Paratethys basins on the early dispersal of Euro-Mediterranean freshwater fishes, Ichthyol. Explor. Freshwat., 1990, vol. 1, pp. 167–184.
Buj, I., Podnar, M., Mrakovčić, M., et al., Morphological and genetic diversity of Sabanejewia balcanica in Croatia, Folia Zool., 2008, vol. 57, pp. 100–110.
Burland, T.G., DNASTAR’s Lasergene sequence analysis software, Methods Mol. Biol., 2000, vol. 132, pp. 71–91. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-192-2:71
Cantatore, P., Roberti, M., Pesole, G., et al., C. Evolutionary analysis of cytochrome b sequences in some perciformes: evidence for a slower rate of evolution than in mammals, J. Mol. Evol., 1994, vol. 39, pp. 589–597.
Dillman, C.B., Wood, R.M., Kuhajda, B.R., et al., Molecular systematics of Scaphirhynchinae: an assessment of North American and Central Asian freshwater sturgeon species. J. Appl. Ichthyol., 2007, vol. 23, pp. 290–296. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2007.00919.x
Economidis, P.S., Nalbant, T.T., A study of the loaches of the genera Cobitis and Sabanejewia (Pisces, Cobitidae) of Greece, with description of six new taxa, Trav. Mus. Hist. Nat. “Grigore Antipa”, 1996, vol. 36, pp. 295–347.
Fricke, R., Eschmeyer, W.N., and Van der Laan, R., Eds., Eschmeyer’s catalog of fishes: genera, species, references, 2022. http://researcharchive.calacademy.org /research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp. Version 01/2022.
Froese, R. and Pauly, D., Eds., FishBase. World wide web electronic publication, 2022. http://www.fishbase.org. Version 02/2022.
Grossu, A., Mester, L., and Tesio, C., Etude electrophorétique des protéiness sériques et sarcoplasmatiques, appliquée a la systématique de la famille Cobitidae (Pisces), Trav. Mus. Hist. Nat. “Grigore Antipa”, 1971, vol. 11, pp. 339–346.
Hall, T.A., BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT, Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 41, 1999, pp. 95–98.
Hernando, J.A., Vasil’eva, E.D., Arlati, G., et al., New proof for the historical presence of two European sturgeons in the Iberian Peninsula: Huso huso (Linnaeus 1758) and Acipenser naccarii (Bonaparte 1836), J. Appl. Ichthyol., 1999, vol. 15, pp. 280–281.
Hewitt, G.M., Speciation, hybrid zones and phylogeography—or seeing genes in space and time, Mol. Ecol., 2001, vol. 10, pp. 537–549. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294x.2001.01202.x
Kalyaanamoorthy, S., Minh, B.Q., Wong, T.K.F., et al., ModelFinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic Estimates, Nature Methods, 2017, vol. 14, pp. 587–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4285
Kottelat, M., Conspectus Cobitidum: an inventory of the loaches of the world (Teleostei: Cypriniformes: Cobitoidei), Raffl. Bull. Zool. Suppl., 2012, no. 26, pp. 1–199.
Kottelat, M. and Freyhof, J., Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes, Cornol, Berlin: Kottelat and Freyhof, 2007.
Krieger, J., Hett, A.K., Fuerst, P.A., et al., The molecular phylogeny of the order Acipenseriformes revisited, J. Appl. Ichthyol., 2008, vol. 24, pp. 36–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2008.01088.x
Križek, P., Mendel, J., Fedorčák, J., and Koščo, J., In the foothill zone − Sabanejewia balcanica (Karaman 1922), in the lowland zone − Sabanejewia bulgarica (Drensky, 1928): Myth or reality? Ecol. Evol., 2020, vol. 10, no 14, pp. 7929–7947. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.6529
Lanfear, R., Calcott, B., Ho, S.Y.W., and Guindon, S., PartitionFinder: combined selection of partitioning schemes and substitution models for phylogenetic analyses, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2012, vol. 29, no 6, pp. 1695–1701.
Ludwig, A., Becker, J., and Bohlen, J., Small differences in cytochrome-b sequences within the genus Sabanejewia, Folia Zool., 2000, vol. 49, pp. 85–90.
Minh, B.Q., Nguyen, M.A.T., and von Haeseler, A., Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2013, vol. 30, no. 5, pp. 1188–1195. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst024
Nalbant, T.T., A study of the genera of Botiinae and Cobitinae (Pisces, Ostariophysi, Cobitidae), Trav. Mus. Hist. Natur. “Grigore Antipa”, 1963, vol. 4, pp. 343–379.
Nalbant, T.T. and Bianco, P.G., The loaches of Iran and adjacent regions with description of six new species (Cobitoidea), Ital. J. Zool., 1998, vol. 65, pp. 109–123.
Nelson, J.S., Fishes of the World, Hoboken: John Wiley and Sons Inc., 2006.
Nguyen, L.T., Schmidt, H.A., von Haeseler, A., and Minh, B.Q., IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum likelihood phylogenies, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2015, vol. 32, pp. 268–274. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu300
Palcu, D.V., Patina, I.S., Şandric, I., et al., Late Miocene megalake regressions in Eurasia, Sci. Rep., 2021, vol. 11, Article 11471. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91001-z
Palumbi, S., Nucleic acids II: the polymerase chain reaction, in Molecular Systematics, Hillis D.M. et al., Eds., Sunderland: Sinauer, 1996, pp. 205–247.
Perdices, A. and Doadrio, I., The molecular systematics and biogeography of the European cobitids based on mitochondrial DNA sequences, Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 2001, vol. 19, pp. 468–478. https://doi.org/10.1006/mpev.2000.0900
Perdices, A., Doadrio, I., Economidis, P.S., et al., Pleistocene effects on the European freshwater fish fauna: double origin of the cobitid genus Sabanejewia in the Danube basin (Osteichthyes: Cobitidae), Ibid., 2003, vol. 26, pp. 289–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1055-7903(02)00334-2
Perdices, A., Bohlen, J., Šlechtová, V., and Doadrio, I., Molecular evidence for multiple origins of the European spined loaches (Teleostei, Cobitidae), PLoSONE, 2016, vol. 11, Article e0144628. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144628
Quenouille, B., Bermingham, E., and Planes, S., Molecular systematics of the damselfishes (Teleostei: Pomacentridae): Bayesian phylogenetic analyses of mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences, Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 2004, vol. 31, pp. 66–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1055-7903(03)00278-1
Rambaut, A., Drummond, A.J., Tracer v1.5. 2007. http://www.beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer.
Reid, D.F. and Orlova, M.I., Geological and evolutionary underpinnings for the success of Ponto-Caspian species invasions in the Baltic Sea and North American Great Lakes, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 2002, vol. 59, pp. 1144–1158. https://doi.org/10.1139/F02-099
Ronquist, F. and Huelsenbeck, J.P., MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models, Bioinformatics, 2003, vol. 19, pp. 1572–1574. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., Maniatis, T., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Lab., 1989.
Sawada, Y., Phylogeny and zoogeography of the superfamily Cobitoidea (Cyprinoidei, Cypriniformes), Mem. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ., 1982, vol. 28, pp. 65–223.
Shimodaira, H., An approximately unbiased test of phylogenetic tree selection, Syst. Biol., 2002, vol. 51, no. 3, pp. 492–508. http://www.jstor.org/stable/3070885
Šlechtová, V., Bohlen, J., Freyhof, J., and Ráb, P., Molecular phylogeny of the Southeast Asian freshwater fish family Botiidae (Teleostei: Cobitoidea) and the origin of polyploidy in their evolution, Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 2006, vol. 39, pp. 529–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2005.09.018
Šlechtová, V., Bohlen, J., and Tan, H.H., Families of Cobitoidea (Teleostei: Cypriniformes) as revealed from nuclear genetic data and the position of the mysterious genera Barbucca, Psilorhynchus, Serpenticobitis and Vaillantella, Ibid., 2007, vol. 44, pp. 1358–1365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2007.02.019
Šlechtová, V., Bohlen, J., and Perdices, A., Molecular phylogeny of the freshwater fish family Cobitidae (Cypriniformes: Teleostei): Delimitation of genera, mitochondrial introgression and evolution of sexual dimorphism, Ibid., 2008, vol. 47, pp. 812–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2007.12.018
Surdacki, S., Loach Cobitis aurata (Filippi, 1865) in the Strwiaz River: its geographical variation, Prz. Zool., 1965, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 356–360.
Sytchevskaya, E.K., Neogene freshwater fish fauna of Mongolia, in Sovmestnaya Sovetsko-Mongol’skaya paleontologicheskaya ekspeditsiya (Trans Joint Soviet-Mongolian Paleontol. Exped.), 1989, vol. 39, pp. 83–87.
Swofford, D.L., PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods), Version 4, Sunderland: Sinauer Assoc., 2003.
Tamura, K., Peterson, D., Peterson, N., et al., MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2011, vol. 28, pp. 2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tan, M. and Armbruster, J.W., Phylogenetic classification of extant genera of fishes of the order Cypriniformes (Teleostei: Ostariophysi), Zootaxa, 2018, vol. 4476, no. 1, pp. 006–039. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4476.1.4
Tang, Q., Freyhof, J., **ong, B., and Liu, H., Multiple invasions of Europe by East Asian cobitid loaches (Teleostei: Cobitidae), Hydrobiologia, 2008, vol. 605, pp. 17–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-008-9296-1
Tomilova, A.A., Lyubas, A.A., Kondakov, A.V. et al., Evidence for Plio-Pleistocene Duck Mussel refugia in the Azov Sea river basins, Diversity, 2020, vol. 12, Article 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12030118
Vasil’eva, E.D. and Poznyak, V.G., Morphological characteristic of the Ciscaucasian spined loach Sabanejewia caucasica (Berg) (Cobitidae), Vopr. Ikhtiol., 1986, vol. 26, pp. 402–409.
Vasil’eva, E.D. and Vasil’ev, V.P., Analysis of intraspecific structure of Sabanejewia aurata (Cobitidae) with description of a new subspecies S. aurata kubanica subsp. nov, Ibid., 1988, vol. 28, pp. 192–212.
Vasil’eva, E.D. and Vasil’ev, V.P., Caspian spined loach Sabanejewia caspia: well-known but practically unexplored species of the Cobitidae family: peculiarities of morphology, karyotype, distribution, and postulated phylogenetic links, J. Ichthyol., 2019, vol. 59, no. 2, pp. 144–159. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945219020206
Vasil’eva, E.D. and Vasil’ev, V.P., Taxonomic relations of Russian and Persian sturgeons (genus Acipenser, Acipenseridae): an updated synthesis, Ibid., 2021, vol. 61, no. 1, pp. 17–32. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945221010173
Vasil’eva, E.D., Solovyeva, E.N., and Vasil’ev, V.P., Phylogenetic relationships, taxonomy and diagnostics of spined loaches (Cobitidae: Cobitis, Sabanejewia) of the Caspian Sea basin, Proc. 9th Nat. and 1st Internat. Iran. Conf. Ichthyol., H. Mosavi-Sabet, Ed., Rasht: University of Guilan, 2021, pp. 79–90. http://isi-conferences.ir/upload/Single/Content/001103_18/Proceedings%20of%20he%209th%20Iranian%20Conference%20of%20Ichthyology-ICI%202021.pdf.
Vladykov, V.D., Sur un nouveau genre de Cobitides: Sabanejewia, Bull. Mus. Nat. Hist. Natur. Sér. 2, 1929, vol. 1, pp. 85–90.
Wiens, J.J., Kuczynski, C.A., and Stephens, P.R., Discordant mitochondrial and nuclear gene phylogenies in emydid turtles: implications for speciation and conservation, Biol. J. Linn. Soc., 2010, vol. 99, pp. 445–461. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2009.01342.x
Williams, M.A.J., Dunkerley, D.L., De Deckker, P. et al., Quaternary Environments, London: Edward Arnold, 1998.
Witkowski, A., Morphological characteristics of Sabanejewia aurata (De Filippi, 1865) from the Odra River basin, with description of a new subspecies (Teleostei: Cypriniformes: Cobitidae), Zool. Abhand. Staat. Mus. Tierk., Dresden, 1994, vol. 48, pp. 23–51.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to V. Luzhnyak, A. Pashkov, N. Mamilov, V. Sarychev, and B. Levin who provided us with samples of certain Sabanejewia species. The authors also thank all anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions, which undoubtedly improved the manuscript.
Funding
Scientific investigations of Ekaterina Vasil’eva and Evgeniya Solovyeva were carried within a State Project of Moscow State University no. 121032300105-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declares that they have no conflicts of interest.
Statement on the welfare of humans or animals. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasil’eva, E.D., Solovyeva, E.N. & Vasil’ev, V.P. Molecular Phylogeny of the Spined Loach Genus Sabanejewia (Osteichthyes: Cobitidae) Revised. J. Ichthyol. 62, 812–827 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945222050228
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945222050228