Abstract
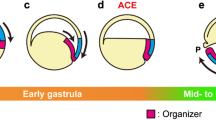
The effect of mechanical extension on the differentiation of axial mesoderm in double explants (sandwiches) of Xenopus laevis embryonic tissues isolated during the early gastrula–late neurula developmen-tal period is studied. In explants at the early gastrula stage, artificial extension orients and stimulates isolated differentiation of the notochord and somites as well as their joint formation. Moreover, extension facilitated the formation of the normal anatomical structure of the notochord and affected expression of Chordin gene. At the late gastrula stage, the effect of artificial extension on joint somite–notochord differentiation was weaker. At the stage of late neurula, somites were sometimes formed in explants lacking a notochord anlage. Thus, at earlier stages, the formation of somites was stimulated by contacts with the notochord and joint development of both structures was mechanical dependent, while at the later stages, somites developed inde-pendently of the notochord. Thus, the role of tissue extension is primarily the establishment of normal mor-phology and expression of Chordin was located in the direction of extension.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Cooke, J. and Zeeman, E.C., A clock and wavefront model for control of the number of repeated structures during ani-mal morphogenesis, Theor. Biol., 1976, vol. 58, pp. 455–476.
Deuchar, E.M. and Burgess, A.M.C., Somite segmentation in amphibian embryos: Is there a transmitted control mech-anism?, Embryol. Exp. Morphol., 1967.) vol. 17, pp. 349–358.
Hamilton, L., The formation of somites in Xenopus, Embryol. Exp. Morphol., 1969, vol. 22, pp. 253–264.
Koehl, M.A.R., Adams, D.S., and Keller, R.E., Mechani-cal development of the notochord in early tail-bud amphib-ian embryos, Biomech. Act. Movem. Deform. Cells, 1990, vol. 42, pp. 471–485.
Malacinski, G.M. and Youn, B.W., Somitogenesis in the amphibian Xenopus laevis: Scanning electron microscopic analysis of intrasomitic cellular arrangements during somite rotation, 1981, Embryol. Exp. Morphol., 1981, vol. 64, pp. 23–43.
Malacinski, G.M. and Youn, B.W., The structure of the anuran amphibian notochord and a reevaluation of its pre-sumed role in early embryogenesis, Differentiation, 1982, vol. 21, pp. 13–21.
Michael, K.R., Steven, P.A., Glenda, M.W., Albert, R., and James, H., Somite number and vertebrate evolution, Development, 1998, vol. 125, pp. 151–160.
Nieuwkoop, P.D. and Faber, J., Normal Table of Xenopus Laevis (Daudin), New York: Garland Publ. Inc., 1994.
Pearson, M. and Elsdale, T., Somitogenesis in amphibian embryos: I. Experimental evidence for an interaction between two temporal factors in the specification of somite pattern, J Embryol. Exp. Morphol., 1979, vol. 51, pp. 27–50.
Pourquie´, O., The segmentation clock: Converting embry-onic time into spatial pattern, Science, 2003, vol. 301, pp. 328–330.
Saga, Y. and Takeda, H., The making of the somite: molec-ular events in vertebrate segmentation, Nat. Rev. Genet., 2001, vol. 2, pp. 835–845.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasilegina, Y.I., Kremnev, S.V. Experimental approaches to the study of the formation of axial structures during early development of Xenopus laevis . Paleontol. J. 50, 1637–1640 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031030116140124
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031030116140124