Abstract
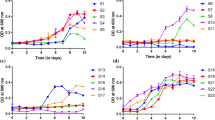
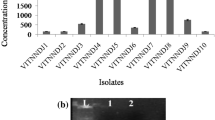
The study was designed in order to isolate the pesticide-degrading beneficial bacteria from agricultural land of Punjab, India. Among the isolated bacterial strains, two were capable of solubilizing tricalcium phosphate on Pikovskaya’s agar. They also had the potential to degrade all the three selected pesticides viz., 20% metsulfuron-methyl (Knockout), 25% propiconazole (Shine) and 15% clodinafop-propargyl (Clo). These promising isolates were identified as Bacillus sp. SWP1 and B. safensis SWP5 on the basis of 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Pesticide degradation by both SWP1 and SWP5 strains with and without the pesticide clodinafop-propargyl applied on Zea mays was evaluated under pot experiment. Treatment of maize seeds with SWP5 resulted in 100% seed germination without pesticide and 93% with pesticide while treatment with SWP1 resulted in 86 and 80% germination with and without the pesticide, respectively. The physical and chemical properties of soil were also improved after treatment with both SWP1 and SWP5. The other plant parameters, such as length and weight, were considerably enhanced upon the application of SWP1 and SWP5. The results of this study indicate that both pesticide-degrading bacilli may be employed as bioinoculants for improving the production of several crops along with the reduction of the level of pesticides present in agricultural soil of Punjab.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
03 June 2022
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261722300130
REFERENCES
Ambreen, S., Yasmin, A., and Aziz, S., Isolation and characterization of organophosphorus phosphatases from Bacillus thuringiensis MB497 capable of degrading Chlorpyrifos, Triazophos and Dimethoate, Heliyon, 2020, vol. 6, no. 7, p. e04221.
Bhattacharyya, C., Banerjee, S., Acharya, U., Acharya, U., Mitra, A., Mallick, I., Haldar, A., Haldar, S., Ghosh, A., and Ghosh, A., Evaluation of plant growth promotion properties and induction of antioxidative defense mechanism by tea rhizobacteria of Darjeeling, India, Sci. Rep., 2020, vol. 10, p. 15536.
Briceno, G., Lamilla, C., Leiva, B., Levio, M., Donoso-Piñol, P., Schalchli, H., Gallardo, F., and Diez, M.C., Pesticide-tolerant bacteria isolated from a biopurification system to remove commonly used pesticides to protect water resources, PLoS One, 2020, vol. 15, no. 6, p. e0234865.
Chennappa, G., Adkar-Purushothama, C.R., Suraj, U., Tamilvendan, K., and Sreenivasa, M.Y., Pesticide tolerant Azotobacter isolates from paddy growing areas of northern Karnataka, India, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2014, vol. 3, no. 7, pp. 568‒784.
Chouyia, F.E., Romano, I., Fechtali, T., Fagnano, M., Fiorentino, N., Visconti, D., Idbella, M., Ventorino, V., and Pepe, O., P-Solubilizing Streptomyces roseocinereus MS1B15 with multiple plant growth-promoting traits enhance barley development and regulate rhizosphere microbial population, Front. Plant Sci., 2020, vol. 11, p. 1137.
Dash, D.M. and Osborne, J.W., Biodegradation of monocrotophos by a plant growth promoting Bacillus aryabhattai (VITNNDJ5) strain in artificially contaminated soil, Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2019, vol. 17, pp. 1475–1490.
Devi, P.I., Thomas, J., and Raju, R.K., Pesticide consumption in India: a spatiotemporal analysis, Agri. Econ. Res. Rev., 2017, vol. 30, no. 1, pp. 163−172.
dos Santos, R.M., Diaz, P.A.E., Lobo, L.L., and Band Rigobelo, E.C., Use of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in maize and sugarcane: characteristics and applications, Front. Sustain. Food Syst., 2020, vol. 4, p. 136.
FAO (2019) Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/RP/metadata.
Guerrieri, M.C., Fanfoni, E., Fiorini, A., Trevisan, M., and Puglisi, E., Isolation and screening of extracellular PGPR from the rhizosphere of tomato plants after long-term reduced tillage and cover crops, Plants (Basel), 2020, vol. 9, no. 5, p. 668.
Hassen, W., Neifar, M., Cherif, H., Najjari, A., Chouchane, H., Driouich, R.C., Salah, A., Naili, F., Mosbah, A., Souissi, Y., Raddadi, N., Ouzari, H.I., Fava, F., and Cherif, A., Pseudomonas rhizophila S211, a new plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium with potential in pesticide-bioremediation, Front. Microbiol., 2018, vol. 9, p. 34.
Huang, Y., **ao, L., Li, F., **ao, M., Lin, D., Long, X., and Wu, Z., Microbial degradation of pesticide residues and an emphasis on the degradation of cypermethrin and 3‑phenoxy benzoic acid: a review, Molecules, 2018, vol. 23, no. 9, p. 2313.
Khan, S., Shahid, M., Khan, M.S., Syed, A., Bahkali, A.H., Elgorban, A.M., and Pichtel, J., Fungicide-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria mitigate physiological disruption of white radish caused by fungicides used in the field cultivation, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 2020, vol. 417, no. 19, p. 7251.
Kheyrodin, H., Methodology for measurement of enzyme activity in soil, World J. Biol. Med. Sci., 2014, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 18–25.
Kumar, P., Dubey, R.C., and Maheshwari, D.K., Bacillus strains isolated from rhizosphere showed plant growth promoting and antagonistic activity against phytopathogens, Microbiol. Res. 2012, vol. 167, no. 8, pp. 493–499.
Ministry of Agriculture, India (2015) Ministry of agriculture and farmers welfare. Annual Progress Report.
Myresiotis, C.K., Vryzas, Z., and Papadopoulou, M.E., Biodegradation of soil-applied pesticides by selected strains of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and their effects on bacterial growth, Biodegradation, 2012, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 297–310.
Olenska, E., Małek, W., Wójcik, M., Swiecicka, I., Thijs, S., and Vangronsveld, J., Beneficial features of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for improving plant growth and health in challenging conditions: a methodical review, Sci. Total Environ., 2020, vol. 743, p. 140682.
Pikovskaya, R.I., Mobilization of phosphorus and soil in connection with the vital activity of some microbial species, Microbiologiya, 1948, vol. 17, pp. 362–370.
Rani, R. and Kumar, V., Endosulfan degradation by selected strains of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 2017, vol. 99, no. 1, pp. 138‒145.
Rayu, S., Nielsen, U.N., Nazaries, L., and Singh, B.K., Isolation and molecular characterization of novel chlorpyrifos and 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol-degrading bacteria from sugarcane farm soils, Front. Microbiol., 2017, vol. 8, p. 518.
Roy, T., Bandopadhyay, A., Sonawane, P.J., Majum-dar, S., Mahapatra, N.R., Alam, S., and Das, N., Bio-effective disease control and plant growth promotion in lentil by two pesticide degrading strains of Bacillus sp., Biol. Cont., 2018, vol. 127, pp. 55‒63.
Shen, F.T., Yen, J.H., Liao, C.S., Chen, W.C., and Chao, Y.T., Screening of rice endophyticbiofertilizers with fungicide tolerance and plant growth-promoting characteristics, Sustainability, 2019, vol. 11, p. 1133.
Singh, M., Singh, D., Gupta, A., Pandey, K.D., Singh, P.K., and Kumar, A., Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: application in biofertilizers and biocontrol of phytopathogens, in PGPR Amelioration in Sustainable Agriculture Food Security and Environmental Management, Singh, A.K., Kumar, A., and Singh, P.K., Eds., Woodhead Publishing, 2019, pp. 41‒66.
Verma, J.P., Jaiswal, D. K., and Maurya, P.K., Screening of bacterial strains for develo** effective pesticide tolerant plant growth-promoting microbial consortia from rhizosphere soils of vegetable fields of eastern Uttar Pradesh, India, Energ. Ecol. Environ., 2016, vol. 1, no. 6, pp. 408–418.
Walia, A., Guleria, S., Chauhan, and A., Mehta, P., Endophytic bacteria: role in phosphate solubilization, in Endophytes: Crop Productivity and Protection, Maheshwari, D.K. and Annapurna, K., Eds., 2017, pp. 61−93.
Yadav, U., Kushwaha, S., Anand, V., Kumar, S., Prakash, O., and Singh, P.C., Chlorpyrifos degradation by plant growth-promoting Alcaligenesfaecalis bacteria isolated from oil-contaminated soil, Bioremediation J., 2021, vol. 25, pp. 80‒88.
Zhang, X., Hao, X., Huo, S., Lin, W., **a, X., Liu, K., and Duan, B., Isolation and identification of the Raoultella ornithinolytica-ZK4 degrading pyrethroid pesticides within soil sediment from an abandoned pesticide plant, Arch. Microbiol., 2019, vol. 201, pp. 1207–1217.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank the Dolphin (PG) College, Chandigarh for providing laboratory facilities to carry out this work.
Funding
The authors declare that they have not received any financial assistance for conducting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.K. and S.S. performed the research, P.K. and R.C.D. conceived and designed the experiments. P.K., A.K.R., A.G., H.P., A.S., D.K., and K.H. wrote the manuscript. All authors approved the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
The authors declare that all the data supporting the findings of this study available within the article is original. We have not taken or adopted any pictures/figures from any other sources.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P., Rai, A.K., Gupta, A. et al. Pesticide-Degrading and Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacilli Isolated from Agricultural Soil of Punjab (India) Enhance Plant Growth. Microbiology 90, 848–856 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261722010076
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261722010076