Abstract
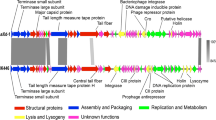
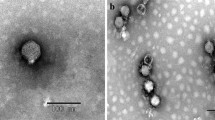
Phages are considered the most abundant and diverse biological entities on Earth. Although many phages have been isolated, most of this diversity remains completely unexplored. Recent advances in genome sequencing, however, have provided unprecedented glimpses into the virosphere. The lytic cold-active Siphoviridae bacteriophage VW6S, infecting the host Pseudomonas fluorescens W-6, was isolated from the Napahai plateau wetland in China. The newly sequenced phage VW6S contained double-stranded DNA with a genome size of 37,917 bp, an overall GC content of 56.90% and 52 open reading frames (ORFs). The genome was organized into several modules containing genes for packaging, structural proteins, replication/transcription, and cell lysis. The sequence contained 16 transcription terminators, no tRNAs. The lysis cassette of VW6S consisted of 4 proteins (holin protein, lysin protein and 2 putative spanins). This is the first report on cold-active SiphoviridaePseudomonas fluorescens bacteriophage genome sequencing.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Berry, J.D., Rajaure, M., and Young, R., Spanin function requires subunit homodimerization through intermolecular disulfide bonds, Mol. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 88, no. 1, pp. 35–47.
Breitbart, M. and Rohwer, F., Here a virus, there a virus, everywhere the same virus?, Trends Microbiol., 2005, vol. 13, pp. 278–284.
Cornelissen, A., Hardies, S.C., Shaburova, O.V., Krylov, V.N., Mattheus, W., and Kropinski, A.M., Complete genome sequence of the giant virus OBP and comparative genome analysis of the diverse PhiKZ-related phages, J. Virol., 2012, vol. 86, no. 3, pp. 1844–1852.
Danovaro, R., Dell’Anno, A., Corinaldesi, C., Magagnini, M., Noble, R., Tamburini, C., and Weinbauer, M., Major viral impact on the functioning of benthic deep-sea ecosystems, Nature, 2008, vol. 454, no. 7208, pp. 1084–1087.
Desnues, C., Rodriguez-Brito, B., Rayhawk, S., Kelley, S., Tran, T., Haynes, M., Liu, H., Furlan, M., Wegley, L., Chau B., Ruan, Y.J., Hall, D., Angly, F.E., Edwards, R.A., Li, L.L., et al., Biodiversity and biogeography of phages in modern stromatolites and thrombolites, Nature, 2008, vol. 452, pp. 340–343.
Eller, M.R., Salgado, R.L., Vidigal, P.M., Alves, M.P., Dias, R.S., and Oliveira, L.L., Complete Genome Sequence of the Pseudomonas fluorescens Bacteriophage UFV-P2, Genome Announc., 2013, vol. 1, no. 1. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00006-12
Ji, X.L., Zhang, C.J., Fang, Y., Zhang, Q., Lin, L.B., Tang, B., and Wei, Y.L., Isolation and characterization of glacier VMY22, a novel lytic cold-active bacteriophage of Bacillus cereus,Virol. Sin., 2015, vol. 30, no. 1, pp. 52–58.
Lee, S.Y., Dunn, R.J., Young, R.A., Connolly, R.M., Dale, P.E.R., and Dehayr, R., Impact of urbanization on coastal wetland structure and function, Austral. Ecol., 2006, vol. 31, pp. 149–163.
Li, M.Y., Wang, J.L., Zhang, Q., Lin, L.B., Kuang, A.X., Materon, L.A., Ji, X.L., and Wei, Y.L., Isolation and characterization of the lytic cold-active bacteriophage MYSP06 from the Mingyong glacier in China, Curr. Microbiol., 2016, vol. 72, no. 2, pp. 120–127.
Lopez-Bueno, A., Tamames, J., Velazquez, D., Moya, A., Quesada, A., and Alcami, A., High diersity of the viral community from an Antarctic lake, Science, 2009, vol. 326, no. 5954, pp. 858–861.
Paterson, S., Vogwill, T., Buckling, A., Benmayor, R., Spiers, A.J., Thomson, N.R., Quail, M., Smith, F., Walker, D., Libberton, B., Fenton, A., Hall, N., and Brockhurst, M.A., Antagonistic coevolution accelerates molecular evolution, Nature, 2010, vol. 464, no. 7286, pp. 275–278.
Rex, M.A., Etter, R.J., Morris, J.S., Crouse, J., McClain, C.R., and Johnson, N.A., Global bathymetric pattern of standing stock and body size in the deep-sea benthos. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 2006, vol. 317, pp. 1–8.
Rice, P., Longden, L., and Bleasby, A., EMBOSS: The E-uropean Molecular Biology Open Software Suite, Trends Genet., 2000, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 276–277.
Rohwer, F., and Thurber, R.V., Viruses manipulate the marine environment, Nature, 2009, vol. 459, no. 7244, pp. 207–212.
Sawstrom, C., Lisle, J., Anesio, A.M., Priscu, J.C., and Laybourn-Parry, J., Bacteriophage in polar inland waters, Extremophiles, 2008, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 167–175.
Sillankorva, S., Kluskens, L.D., Lingohr, E.J., Kropinski, A.M., Neubauer, P., and Azeredo, J., Complete genome sequence of the lytic Pseudomonas fluorescens phage varphiIBB-PF7A, Virol. J., 2011, vol. 8, p. 142. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-8-142
Sillankorva, S., Kropinski, A.M., and Azeredo, J., Genome sequence of the broad-host-range Pseudomonas phage Phi-S1, J. Virol., 2012, vol. 86, no. 18, p. 10239. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01605-12
Summer, E.J., Berry, J., Tran, T., Struck, L., and Young, R., Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of gram-negative hosts, J. Mol. Biol., 2007, vol. 373, pp. 1098–1112.
Wang, F., Li, Q., and **ao, X., A novel filamentous phage from the deep-sea bacterium Shewanella piezotolerans WP3 is induced at low temperature, J. Bacteriol., 2007, vol. 189, no. 19, pp. 7151–7153.
Wojtus, J.K., Fitch, J.L., Christian, E., Dalefield, T., Lawes, J.K., and Kumar, K., Complete genome sequences of three novel Pseudomonas fluorescens SBW25 bacteriophages, Noxifer, Phabio, and Skulduggery, Genome Announc., 2017, vol. 5, no. 31. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00725-17
Wommack, K.E. and Colwell, R.R., Virioplankton: viruses in aquatic ecosystems, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2000, vol. 64, pp. 69–114.
**ang, X., Chen, L., Huang, X., Luo, Y., She, Q., and Huang, L., Sulfolobus tengchongensis spindle-shaped virus STSV1: virus-host interactions and genomic features, J. Virol., 2005, vol. 79, no. 14, pp. 8677–8686.
**ang, Y.Y., Wang, S., Li, J.K., Wei, Y.L., Zhang, Q., Lin, L.B., and Ji, X.L., Isolation and characterization of two lytic cold-active bacteriophages infecting Pseudomonas fluorescens from the Napahai plateau wetland, Can. J. Microbiol., 2018, vol. 64, no. 3, pp. 183–190.
Yuan, Y.H. and Gao, M.Y., Jumbo bacteriophages: an overview, Front Microbiol., 2017, vol. 8, p. 403. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00403
Zhang, C.J., Zhang, Z.Y., Li, J.K., Qin, K.H., Wei, Y., Zhang, Q., Lin, L.B., and Ji, X.L., Complete genome sequence of the lytic cold-active Pseudomonas fluorescens bacteriophage VSW-3 from Napahai plateau wetland, Virus Genes, 2017, vol. 53 no. 1, pp. 146–150.
Funding
This research was supported the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31860147 and 31700324), Yunnan Provincial Education Fund project (2017ZZX132), Analysis and Testing Fundation of Kunming University of Science and Technology (2017T20070036), and the Open Research Fund Program of the State Key Laboratory of Virology of China (2018KF003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. This article does not contain any studies involving animals performed by any of the authors.
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, X., Cui, Z., **ang, Y. et al. Complete Genome Sequence Analysis of the Cold-active Siphoviridae Bacteriophage from Pseudomonas fluorescens. Microbiology 89, 318–327 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261720030066
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261720030066