Abstract
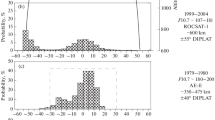
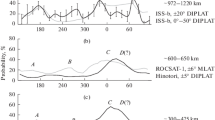
The character of the variability of the LT distributions of the equatorial plasma bubble occurrence probability with an increase of the recording altitude is under consideration. The conditions of the high and maximal solar activity, when the generation of the plasma bubbles is the most active, are examined. For this purpose the detailed comparative analysis of the LT distributions of the equatorial plasma bubble occurrence probability derived from the ISS-b (~972–1220 km), Hinotori (~650 km), ROCSAT-1 (~600 km), AE-E (~300–475 km), and CHAMP (~380–450 km) satellite data was done. The pronounced trend of the local time shift of the bubble occurrence probability maximum with an increase of the altitude is revealed. Thus, if the maximum occurs after sunset (~2030–2200 LT) at the bottom-side of the F-layer, it shifts toward the premidnight (~2100–2400 LT, ~600 km), then to the postmidnight (~0100–0300 LT, ~650 km), and, finally, to the predawn hours (~0300–0400 LT, ~972–1220 km) as the observation altitude increases. The most typical velocities of the equatorial plasma bubble rise are found to be ~150–300 m/s, which correspond to the numerous observational data.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abdu, M.A., de Medeiros, R.T., Sobral, J.H.A., et al., Spread F plasma bubble vertical rise velocities determined from spaced ionosonde observations, J. Geophys. Res., 1983, vol. 88, pp. 9197–9204.
Abdu, M.A., Sobral, J.H.A., and Batista, I.S., Equatorial spread F statistics in the American longitudes: some problems relevant to ESF description in the IRI scheme, Adv. Space Res., 2000, vol. 25, pp. 113–124.
Aggson, T.L., Maynard, N.C., Hanson, W.B., et al., Electric field observations of equatorial bubbles, J. Geophys. Res., 1992, vol. 97, pp. 2997–3009.
Burke, W.J., Donatelli, D.E., Sagalyn, R.C., et al., Low density regions observed at high altitudes and their connection with equatorial spread F,Planet. Space Sci., 1979, vol. 27, pp. 593–601.
Gentile, L.C., Burke, W.J., and Rich, F.J., A climatology of equatorial plasma bubbles from DMSP 1989–2004, Radio Sci., 2006, vol. 41, RS5S21. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005RS003340
Hanson, W.B., Coley, W.R., Heelis, R.A., et al., Fast equatorial bubbles, J. Geophys. Res., 1997, vol. 102, no. A2, pp. 2039–2045.
Huang, C.-S., de la Beaujardiere, O., Roddy, P.A., et al., Evolution of equatorial ionospheric plasma bubbles and formation of broad plasma depletions measured by the C/NOFS satellite during deep solar minimum, J. Geophys. Res., 2011, vol. 116, A03309. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JA015982
Huba, J.D., Joyce, G., and Krall, J., Three-dimensional equatorial spread F modeling, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2008, vol. 35, L10102. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL033509
Kil, H. and Heelis, R.A., Global distribution of density irregularities in the equatorial ionosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 1998, vol. 103, no. A1, pp. 407–417.
Kil, H., Heelis, R.A., Paxton, L.J., et al., Formation of a plasma depletion shell in the equatorial ionosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 2009, vol. 114, A11302. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JA014369
McClure, J.P., Hanson, W.B., and Hoffman, J.F., Plasma bubbles and irregularities in the equatorial ionosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 1977, vol. 82, no. 19, pp. 2650–2656.
Narayanan, V.L., Gurubaran, S., and Shiokawa, K., Direct observational evidence for the merging of equatorial plasma bubbles, J. Geophys. Res., 2016, vol. 121, no. 19, pp. 7923–7931. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JA02286
Ossakov, S.L. and Chaturvedi, P.K., Morphological studies of rising equatorial spread F bubbles, J. Geophys. Res., 1978, vol. 83, no. 5, pp. 2085–2090.
Ott, E., Theory of Rayleigh–Taylor bubbles in the equatorial ionosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 1978, vol. 83, no. A5, pp. 2066–2070.
RRL. Summary Plots of Ionospheric Parameters Obtained from Ionosphere Sounding Satellite-B, Tokyo: Radio research Laboratories, Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications, 1983, vols. 1–3.
RRL. Summary Plots of Ionospheric Parameters Obtained from Ionosphere Sounding Satellite-B, Tokyo: Radio research Laboratories, Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications, 1985, vol. 4.
Sidorova, L.N. and Filippov, S.V., Longitudinal statistics of plasma bubbles observed as He+ density depletions at altitudes of the topside ionosphere, Geomagn. Aeron. (Engl. Transl.), 2013, vol. 53, no. 1, pp. 60–72.
Sidorova, L.N. and Filippov, S.V., Topside ionosphere He+ density depletions: Seasonal/longitudinal occurrence probability, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2012, vol. 86, pp. 83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2012.06.013
Smith, J. and Heelis, R.A., Equatorial plasma bubbles: Variations of occurrence and spatial scale in local time, longitude, season, and solar activity, J. Geophys. Res., 2017, vol. 122, no. 5, pp. 5743–5755. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JA024128
Stolle, C., Lühr, H., Rother, M., et al., Magnetic signatures of equatorial spread F as observed by the CHAMP satellite, J. Geophys. Res., 2006, vol. 111, A02304. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JA011184
Su, S.-Y., Liu, C.H., Ho, H.H., et al., Distribution characteristics of topside ionospheric density irregularities: Equatorial versus midlatitude regions, J. Geophys. Res., 2006, vol. 111, A06305. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JA011330
Tsunoda, R.T., Magnetic-field-aligned characteristics of plasma bubbles in the nighttime equatorial ionosphere, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 1980, vol. 42, pp. 743–752.
Tsunoda, R.T., Livingston, R.C., McClure, J.P., et al., Equatorial plasma bubbles: Vertical elongated wedges from the bottomside F layer, J. Geophys. Res., 1982, vol. 87, pp. 9171–9180.
Watanabe, S. and Oya, H., Occurrence characteristics of low latitude ionospheric irregularities observed by impedance probe on board the Hinotori satellite, J. Geomagn. Geoelectr., 1986, vol. 38, pp. 125–131.
Woodman, R.F. and La Hoz, C., Radar observations of F‑region equatorial irregularities, J. Geophys. Res., 1976, vol. 81, pp. 5447–5466.
Yizengaw, E., Retterer, J., Pacheco, E.E., et al., Postmidnight bubbles and scintillations in the quiet-time June solstice, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2013, vol. 40, pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013GL058307
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by O. Ponomareva
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sidorova, L.N. Equatorial Plasma Bubbles: Occurrence Probability versus Local Time. Geomagn. Aeron. 60, 530–537 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S001679322005014X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S001679322005014X