Abstract
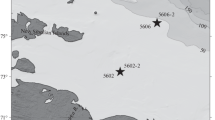
The role of zooplankton in the vertical mass flux in the Kara and Laptev seas was studied during cruise 63 of the R/V Akademik Mstislav Keldysh in August–October 2015. Mass fluxes were estimated using sediment trap samples. The maximum values of the total vertical flux (19600 mg m−2 day−1) and particulate organic carbon (POC) flux (464 mg C m−2 day−1) were measured close to the Lena River Delta in the Laptev Sea. In the Kara Sea, the total flux (80–2700 mg m−2 day−1) and the POC flux (17–130 mg C m−2 day−1) were substantially higher than the estimates published earlier. The fecal pellet flux varied from 2 to 92 mg C m−2 day−1 and made up 4–190% of the total organic carbon flux. The mineral composition of fecal pellets largely mirrored that of suspended particulate matter. Clay minerals in the fecal pellets were more abundant than in particulate matter in the areas with noticeable freshwater impact. The flux of zooplankton carcasses varied from 0.1 to 66.4 mg C m−2 day−1 and made up 0.2–72% of total POC flux. The results are discussed in relation to the abundance and composition of zooplankton, the concentration and composition of suspended particulate matter, hydrophysical conditions, and methods of sample preparation for analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. E. Vlasenkov and A. P. Makshtas, “Analysis of spatio- temporal distribution pattern of suspended matter in the upper layer of shelf seas of Russian Arctic,” Probl. Arkt. Antarkt., No. 2, 63–71 (2012) [in Russian].
A. V. Drits, E. G. Arashkevich, A. B. Nikishina, V. M. Sergeeva, K. A. Solovyev, and M. V. Flint, “Mesozooplankton grazing impact on phytoplankton in the northern regions of the Kara Sea in autumn,” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 55, 595–605 (2015).
A. G. Zatsepin, P. O. Zavialov, V. I. Baranov, V. V. Kremenetskiy, A. A. Nedospasov, S. G. Poyarkov, and V. V. Ocherednik, “On the mechanism of windinduced transformation of a river runoff water lens in the Kara Sea,” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 57, 1–7 (2017).
V. V. Zernova, E.-M. Nöthig, and V. P. Shevchenko, “Vertical microalga flux in the northern Laptev Sea (from the data collected by the yearlong sediment trap),” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 40, 801–808 (2000).
L. G. Koval’, Zoo- and Necrozooplankton of the Black Sea (Naukova Dumka, Kiev, 1984) [in Russian].
M. D. Kravchishina, A. Yu. Lein, I. N. Sukhanova, V. A. Artem’ev, and A. N. Novigatsky, “Genesis and spatial distribution of suspended particulate matter concentrations in the Kara Sea during maximum reduction of the Arctic ice sheet,” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 55, 623–643 (2015).
V. M. Kuptsov, A. P. Lisitzin, V. P. Shevchenko, and V. I. Burenkov, “Suspended matter fluxes to the Laptev Sea bottom sediments,” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 39, 543–549 (1999).
A. P. Lisitzyn, “Patterns of rapid and extremely rapid (avalanche) sedimentation: implications for marine oil and gas generation,” Russ. Geol. Geophys. 50, 278–298 (2009).
A. P. Lisitzyn, A. N. Novigatsky, A. A. Klyuvitkin, et al., “Flows of suspended matter in the White Sea, sedimentary stations, and new directions in the study of sedimentary matter,” in The White Sea System (Nauchnyi Mir, Moscow, 2013), Vol. 3, pp. 201–291 [in Russian].
A. P. Lisitzyn, V. P. Shevchenko, M. E. Vinogradov, et al., “Flows of sedimentary matter in the Kara Sea and Ob and Yenisei river estuaries,” Okeanologiya (Moscow) 34, 748–758 (1994).
N. V. Lobus, “Elemental composition of zooplankton in the Kara Sea and the bays on the eastern side of Novaya Zemlya,” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 56, 809–818 (2016).
V. N. Lukashin, A. A. Klyuvitkin, A. P. Lisitzin, and A. N. Novigatsky, “The MSL-110 small sediment trap,” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 51, 699–703 (2011).
S. V. Lyutsarev and A. V. Smetankin, “Determination of carbon in the water suspended matter”, in Analysis of Organic Matter in the Ocean (Nauka, Moscow, 1980), pp. 46–50.
P. N. Makkaveev, A. A. Polukhin, A. V. Kostyleva, E. A. Protsenko, S. V. Stepanova, and Sh. Kh. Yakubov, “Hydrochemical features of the Kara Sea aquatic area in summer 2015,” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 57, 48–57 (2017).
A. B. Nikishina, O. M. Dara, A. V. Drits, et al., “Role of zooplankton in sedimentation of suspended matter in the Blagopoluchiya Bay (Novaya Zemlya Archipelago),” Proceedings of Scientific Conference “Ecosystem of the Kara Sea: New Data of Expedition Studies” (Moscow, 2015), pp. 142–146.
I. N. Sukhanova, M. V. Flint, E. I. Druzhkova, A. F. Sazhin, and V. M. Sergeeva, “Phytoplankton in the northwestern Kara Sea,” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 55, 547–560 (2015).
I. N. Sukhanova, M. V. Flint, E. Ju. Georgieva, E.K. Lange, M. D. Kravchishina, A. B. Demidov, A. A. Nedospasov, and A. A. Polukhin, “The structure of phytoplankton communities in the eastern part of the Laptev Sea,” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 57, 75–90 (2017).
M. V. Flint, S. G. Poyarkov, A. G. Timonin, and K. A. Soloviev, “The structure of the mesoplankton community in the area of the continental slope of the St. Anna Trough (Kara Sea),” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 55, 583–594 (2015).
M. V. Flint, S. G. Poyarkov, and N. A. Rimsky-Korsakov, “Ecosystems of the Russian Arctic-2015 (63rd Cruise of the research vessel Akademik Mstislav Keldysh),” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 56, 459–461 (2016).
L. L. Chislenko, Nomograms for Determination of Weight of Aquatic Organisms by Dimensions and Body Shape (Nauka, Leningrad, 1968) [in Russian].
V. P. Shevchenko, V. I. Vedernikov, G. I. Ivanov, et al., “Vertical flows of sedimentary matter in the Barents Sea in summer-autumn,” Proceedings of XIII International Workshop on Marine Geology “Geology of the Seas and Oceans,” Abstracts of Papers (GEOS, Moscow, 1999), Vol. 1, pp. 153–154 [in Russian].
V. P. Shevchenko, G. I. Ivanov, A. A. Burovkin, R. N. Dzhinoridze, V. V. Zernova, L. V. Polyak, and S. S. Shanin, “Sedimentary material flows in the St. Anna Trough and eastern Barents Sea,” Dokl. Earth Sci. 359, 400–403 (1998).
K. O. Buesseler, N. A. Avan, S. MinChen, et al., “An assessment of the use of sediment traps for estimating upper ocean particle fluxes,” J. Mar. Res. 65, 345–416 (2007).
D. Diebel and J. T. Turner, “Zooplankton feeding ecology: contents of fecal pellets of the appendicularian Oikopleura vanhoeffenii,” Mar. Ecol.: Prog. Ser. 27, 67–78 (1985).
I. A. Dmitrenko, S. A. Kirillov, T. Krumpen, et al., “Wind-driven diversion of summer river runoff preconditions the Laptev Sea coastal polynya hydrography: evidence from summer-to-winter hydrographic records of 2007–2009,” Cont. Shelf Res. 30, 1656–1664 (2010).
C. Frangoulis, N. Skliris, G. Lepoint, et al., “Importance of copepod carcasses versus fecal pellets in the upper water column of an oligotrophic area,” Estuarine, Coastal Shelf Sci. 92, 456–463 (2011).
B. Gaye, K. Fahl, L. A. Kodina, et al., “Particulate matter fluxes in the southern and central Kara Sea compared to sediments: bulk fluxes, amino acids, stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes, sterols and fatty acids,” Cont. Shelf Res. 27, 2570–2594 (2007).
B. Gaye-Haake, D. Unger, E.-M. Nöthig, et al., “Particle fluxes from short-term sediment trap deployments in late summer in the southern Kara Sea,” in Siberian River Run-Off in the Kara Sea: Characterization, Quantification, Variability, and Environmental Significance, Ed. by R. Stein, K. Fahl, D. K. Fütterer, (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2003), pp. 309–328.
V. V. Gordeev and M. D. Kravchishina, “River flux of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and particulate organic carbon (POC) to the Arctic Ocean: what are the consequences of the global changes?” in Influence of Climate Change on the Changing Arctic and Sub-Arctic Conditions, Ed. by J. C. J. Nihoul and A. G. Kostianoy (Springer-Verlag, Dordrecht, 2009), pp. 139–154.
H. J. Hirche, K. N. Kosobokova, B. Gaye-Haake, et al., “Structure and function of contemporary food webs on Arctic shelves: a panarctic comparison. The pelagic system of the Kara Sea—communities and components of carbon flow,” Progr. Oceanogr. 71, 288–313 (2006).
O. Holm-Hansen and B. Riemann, “Chlorophyll “a” determination: improvements in methodology,” Oikos 30, 438–447 (1978).
A. Kubryakov, S. Stanichny, and A. Zatsepin, “River plume dynamics in the Kara Sea from altimetry-based lagrangian model, satellite salinity and chlorophyll data,” Remote Sens. Environ. 176, 177–187 (2016).
C. Lalande, S. Belanger, and L. Fortier, “Impact of a decreasing sea ice cover on the vertical export of particulate organic carbon in the northern Laptev Sea, Siberian Arctic Ocean,” Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L21604 (2009).
C. Lalande, J. M. Grebmeier, P. Wassmann, et al., “Export fluxes of biogenic matter in the presence and absence of seasonal sea ice cover in the Chukchi Sea,” Cont. Shelf Res. 27, 2051–2065 (2007).
C. Lalande, E.-M. Nöthing, R. Somavilla, et al., “Variability in under-ice export fluxes of biogenic matter in the Arctic Ocean,” Global Biogeochem. Cycles 28, 571–583 (2014).
A. G. Lewis and J. P. M. Syvitski, “The interaction of plankton suspended sediments in fjords,” Sediment. Geol. 36, 81–92 (1983).
S. B. Moran, R. P. Kelly, K. Hagstrom, et al., “Seasonal changes in POC export flux in the Chukchi Sea and implications for water column-benthic coupling in Arctic shelves,” Deep Sea Res., Part II 52, 3427–3451 (2005).
K. Olli, R. C. Wexels, P. Wassmann, et al., “Seasonal variation in vertical flux of biogenic matter in the marginal ice zone and the central Barents Sea,” J. Mar. Syst. 38, 189–204 (2002).
U. Passow and C. A. Carlson, “The biological pump in a high CO2 world,” Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser. 470, 249–271 (2012).
A. Pasternak, E. Arashkevich, R. C. Wexels, et al., “Seasonal variation in zooplankton and suspended fecal pellets in the subarctic Norwegian Balsfjorden, in 1996,” Sarsia 85, 439–452 (2000).
M. Reigstad, R. C. Wexels, P. Wassmann, and T. Ratkova, “Vertical export of particulate organic carbon: attenuation, composition and loss rates in the northern Barents Sea,” Deep Sea Res., Part II 55, 2308–2319 (2008).
U. Riebesell, A. Kortzinger, and A. Oschlies, “Sensitivities of marine carbon fluxes to ocean change,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 20602–20609 (2009).
B. Rost, I. Zondervan, and D. Wolf-Gladrow, “Sensitivity of phytoplankton to future changes in ocean carbonate chemistry: current knowledge, contradictions and research directions,” Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser. 373, 227–237 (2008).
M. Sampei, H. Sasaki, H. Hattori, et al., “Significant contribution of passively sinking copepods to the downward export flux in Arctic waters,” Limnol. Oceanogr. 54, 1894–1900 (2009).
R. F. Spielhagen, K. Werner, S. A. Sorensen, et al., “Enhanced modern heat transfer to the Arctic by warm Atlantic water,” Science 331, 450–453 (2011).
J. P. M. Syvitsky and A. G. Lewis, “Sediment ingestion by Tigriopus californicus and other zooplankton: material transformation and sedimentological considerations,” J. Sediment. Petrol. 50 (3), 0869–0880 (1980).
K. W. Tang and D. T. Elliott, “Copepod carcasses: occurrence, fate and ecological importance,” in Copepods: Diversity, Habitat and Behavior, Ed. by L. Seuront (Nova Science, New York, 2013), pp. 1–19.
J. T. Turner, “Zooplankton fecal pellets, marine snow, phytodetritus and the ocean’s biological pump,” Progr. Oceanogr. 130, 205–248 (2015).
T. Volk and M. I. Hoffert, “Ocean carbon pumps: analysis of relative strengths and efficiencies in oceandriven atmospheric CO2 changes,” in The Carbon Cycle and Atmospheric CO2: Natural variations Archaean to Present, Ed. by E. T. Sundquist and W. S. Broecker (Wiley, New York, 1985), Vol. 32, pp. 99–110.
P. Wassmann, K. Olli, R. C. Wexels, and C. Svensen, “Ecosystem function, biodiversity and vertical flux regulation in the twilight zone,” in Marine Science Frontiers for Europe, Ed. by G. Wefer, F. Lamy, and F. Mantoura (Springer-Verlag, New York, 2003), pp. 279–287.
P. Wassmann, D. Slagstad, R. C. Wexels, and M. Reigstad, “Modeling the ecosystem dynamics of the Barents Sea including the marginal ice zone. II. Carbon flux and interannual variability,” J. Mar. Syst. 59, 1–24 (2006).
C. Wegner, J. A. Hölemann, I. Dmitrenko, et al., “Seasonal variations in Arctic sediment dynamics—evidence from 1-year records in the Laptev Sea (Siberian Arctic),” Global Planet. Change 48, 126–140 (2005).
R. Wexels, P. Wassmann, K. Olli, et al., “Seasonal variation in production, retention and export of zooplankton fecal pellets in the marginal ice zone and central Barents Sea,” J. Mar. Syst. 38, 175–188 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Drits, M.D. Kravchishina, A.F. Pasternak, A.N. Novigatsky, O.M. Dara, M.V. Flint, 2017, published in Okeanologiya, 2017, Vol. 57, No. 6, pp. 934–948.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drits, A.V., Kravchishina, M.D., Pasternak, A.F. et al. Role of Zooplankton in the Vertical Mass Flux in the Kara and Laptev Seas in Fall. Oceanology 57, 841–854 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001437017060029
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001437017060029